|
Illinois Confederation
The Illinois Confederation, also referred to as the Illiniwek or Illini, were made up of a loosely organized group of 12 or 13 tribes who lived in the Mississippi River Valley. Eventually, member tribes occupied an area reaching from Lake Michigan to Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, and Arkansas. The five main tribes were the Cahokia, Kaskaskia, Michigamea, Peoria, and Tamaroa. Other related tribes are described as the Maroa (which may have been the same as Tamaroa), Tapourao, Coiracoentanon, Espeminka, Moingwena, Chinkoa, and Chepoussa. By 1700, only the Cahokia, Kaskaskia, Michigamea, Peoria, and Tamaroa remained. Over time, these tribes continued to merge, with the Tamaroa joining the Kaskaskia, the Cahokia joining the Peoria, and with a portion of the Michigamea merging with the Kaskaskia and the remainder merging with the Quapaw. The spelling "Illinois" was derived from the transliteration by French explorers of to the orthography of their own language. The tribes are esti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peoria People
The Peoria are a Native Americans of the United States, Native American people. They are enrolled in the Federally recognized tribes, federally recognized Peoria Tribe of Indians of Oklahoma headquartered in Miami, Oklahoma. The Peoria people are the remnants of the nations which constituted the Illinois Confederation. The Peoria Tribe were located east of the Mississippi River and north of the Ohio River. In the colonial period, they traded with French colonists in that territory. After 1763, when the British took over those lands following victory in the Seven Years' War, the Peoria were moved west across the Mississippi. In 1867 their descendants moved to Indian Territory with remnants of related tribes and were assigned land in present-day Ottawa County, Oklahoma. The land which they were assigned belonged to the Quapaw, who were made to cede this land for the Peoria and Miami. Language and name The Peoria speak a dialect of the Miami–Illinois language, a Central Algonq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and depth () after Lake Superior and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that of Lake Huron through the wide and deep Straits of Mackinac, giving it the same surface elevation as its eastern counterpart; hydrologically, the two bodies are Lake Michigan–Huron, a single lake that is, by area, the largest freshwater lake in the world. Lake Michigan is the only Great Lake located fully in the United States; the other four are shared between the U.S. and Canada. It is the world's List of lakes by area, largest lake, by area, located fully in one country, and is shared, from west to east, by the U.S. states of Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, and Michigan. Ports along its shores include Chicago, Illinois, Gary, Indiana, Gary, Indiana, Milwaukee and Green Bay, Wisconsin, Green Bay, Wis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algonquian Languages
The Algonquian languages ( ; also Algonkian) are a family of Indigenous languages of the Americas and most of the languages in the Algic language family are included in the group. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically similar Algonquin dialect of the Indigenous Ojibwe language (Chippewa), which is a senior member of the Algonquian language family. The term ''Algonquin'' has been suggested to derive from the Maliseet word (), meaning 'they are our relatives/allies'. Speakers of Algonquian languages stretch from the east coast of North America to the Rocky Mountains. The proto-language from which all of the languages of the family descend, Proto-Algonquian, was spoken around 2,500 to 3,000 years ago. There is no scholarly consensus about where this language was spoken. Family division This subfamily of around 30 languages is divided into three groups according to geography: Plains, Central, and Eastern Algonquian. Of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The Society of Jesus is the largest religious order in the Catholic Church and has played significant role in education, charity, humanitarian acts and global policies. The Society of Jesus is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 countries. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. They also conduct retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian works, and promote Ecumenism, ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patron saint, patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a Superior General of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Marquette
Jacques Marquette, Society of Jesus, S.J. (; June 1, 1637 – May 18, 1675), sometimes known as Père Marquette or James Marquette, was a French Society of Jesus, Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan, Sault Sainte Marie, and later founded St. Ignace, Michigan, Saint Ignace. In 1673, Marquette, with Louis Jolliet, an explorer born near Quebec City, was the first European to explore and map the northern portion of the Mississippi River Valley. Early life Jacques Marquette was born in Laon, France, on June 1, 1637. He was the third of six children for Rose de la Salle and Nicolas Marquette. The de la Salles were a wealthy merchant family. The Marquette family had been well-respected for many years, as numerous members had served in the military and taken civil posts. Jacques Marquette was sent to study at the Jesuit College in Reims at age 9. He remained there until he joined the Society of Jesus at age 17. Marquette tau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
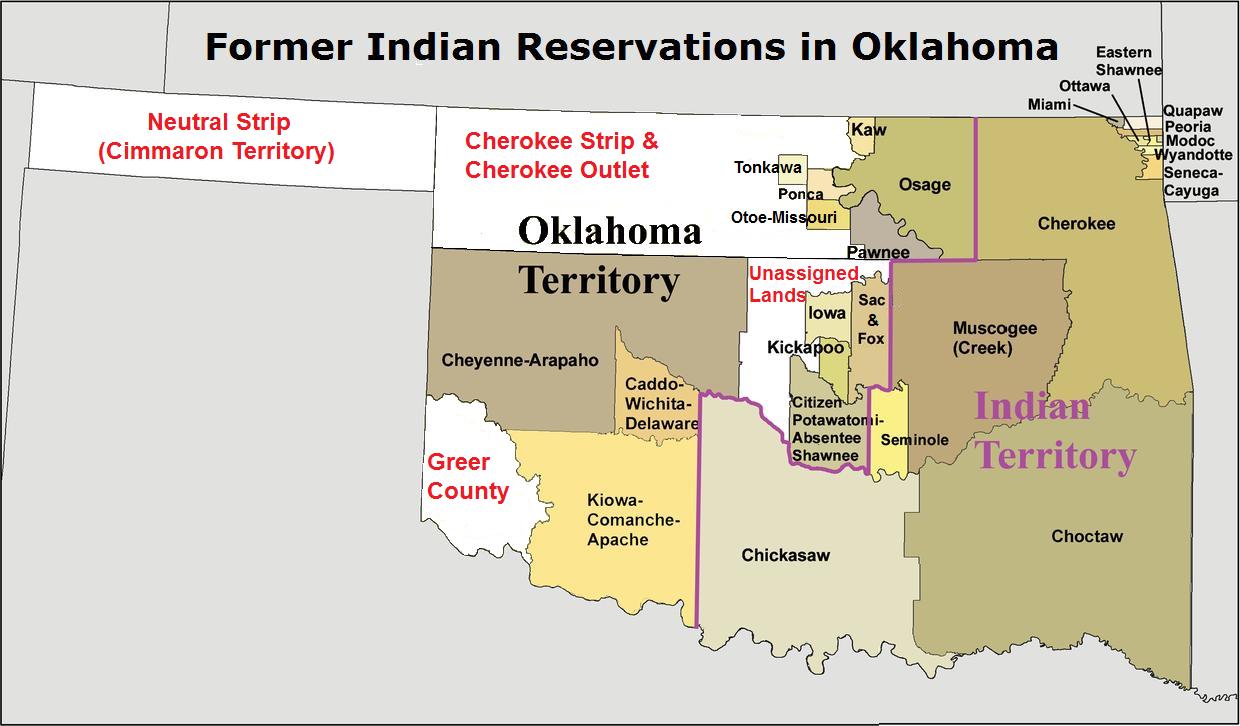
Oklahoma
Oklahoma ( ; Choctaw language, Choctaw: , ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Texas to the south and west, Kansas to the north, Missouri to the northeast, Arkansas to the east, New Mexico to the west, and Colorado to the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "The Sooner State", in reference to the Sooners, American pioneer, American settlers who staked their claims in formerly American Indian-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issues, such as defence, foreign relations, internal trade or currency, with the central government being required to provide support for all its members. Confederalism represents a main form of intergovernmentalism, defined as any form of interaction around states that takes place on the basis of sovereign independence or government. The nature of the relationship among the member states constituting a confederation varies considerably. Likewise, the relationship between the member states and the general government and their distribution of powers varies. Some looser confederations are similar to intergovernmental organization, international organisations. Other confederations with stricter rules may resemble federal systems. These elements o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wigwams
A wigwam, wikiup, wetu (Wampanoag), or wiigiwaam (Ojibwe, in syllabics: ) is a semi-permanent domed dwelling formerly used by certain Native American tribes and First Nations people and still used for ceremonial events. The term ''wikiup'' is generally used to refer to these kinds of dwellings in the Southwestern United States and Western United States and Northwest Alberta, Canada, while ''wigwam'' is usually applied to these structures in the Northeastern United States as well as Ontario and Quebec in central Canada. The names can refer to many distinct types of Indigenous structures regardless of location or cultural group. The wigwam is not to be confused with the Native Plains tipi, which has a different construction, structure, and use. Structure The domed, round shelter was used by numerous northeastern Indigenous tribes. The curved surfaces make it an ideal shelter for all kinds of conditions. Indigenous peoples in the Great Lakes–St. Lawrence Lowlands resided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longhouses
A longhouse or long house is a type of long, proportionately narrow, single-room building for communal dwelling. It has been built in various parts of the world including Asia, Europe, and North America. Many were built from timber and often represent the earliest form of permanent structure in many cultures. Types include the Neolithic long house of Europe, the Norman Medieval Longhouses that evolved in Western Britain (''Tŷ Hir'') and Northern France (''Longère''), and the various types of longhouse built by different cultures among the indigenous peoples of the Americas. Europe The Neolithic long house type was introduced with the first farmers of Central and Western Europe around 5000 BCE, 7,000 years ago. These were farming settlements built in groups of six to twelve longhouses; they were home to large extended families and kin. The Germanic cattle-farmer longhouses emerged along the southwestern North Sea coast in the third or fourth century BCE and may be the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
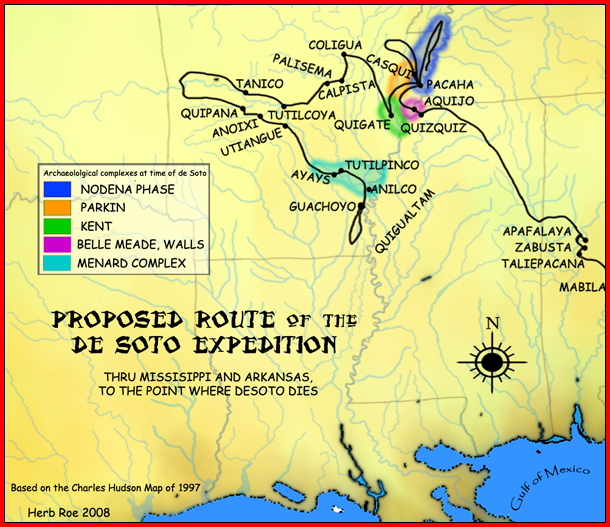
Quapaw
The Quapaw ( , Quapaw language, Quapaw: ) or Arkansas, officially the Quapaw Nation, is a List of federally recognized tribes in the United States, U.S. federally recognized tribe comprising about 6,000 citizens. Also known as the Ogáxpa or “Downstream” people, their ancestral homelands are traced from what is now the Ohio River, west to the Mississippi River to present-day St. Louis, south across present-day Arkansas and eastern and southern Oklahoma. The government Trail of Tears, forcibly removed them from Arkansas Territory in 1834. The Oklahoma Tribal Statistical Area, tribal Capital city, capital is Quapaw, Oklahoma, Quapaw, Oklahoma. Etymology The Quapaw broke from the other Dhegiha tribes and migrated down the Mississippi River into present-day Arkansas many generations before European contact. After that, the tribe began to refer to themselves Ogáxpa, which means the “Downstream” people." This was the name of their primary village or tribal band. Historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitchigamea
The Michigamea were a Native American tribe in the Illinois Confederation. The Mitchigamea may have spoken an Algonquian or a Siouan language, and historical accounts describe them as not being fluent in the Illinois language. Little is known of them today. Name The Michigamea are also known as the Mitchigamea or Michigamie. Territory Originally they were said to be from Lake Michigan, perhaps the Chicago area. Mitchie Precinct, Monroe County in Southwestern Illinois takes its name from their transient presence nearby, north of the French Fort de Chartres in the American Bottom along the Mississippi. At one point in history, they lived near the Sangamon River in Illinois. One of their villages in the American Bottom, inhabited from 1730 until 1752, is one of the region's premier archaeological sites; it is known as the Kolmer site. Other sites which have been proposed as being associated with the Mitchigamea include the Waterman site and Grigsby site. The Mitchig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the West South Central region of the Southern United States. It borders Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma to the west. Its name derives from the Osage language, and refers to their relatives, the Quapaw people. The state's diverse geography ranges from the mountainous regions of the Ozark and Ouachita Mountains, which make up the U.S. Interior Highlands, to the densely forested land in the south known as the Arkansas Timberlands, to the eastern lowlands along the Mississippi River and the Arkansas Delta. Previously part of French Louisiana and the Louisiana Purchase, the Territory of Arkansas was admitted to the Union as the 25th state on June 15, 1836. Much of the Delta had been developed for cotton plantations, and landowners there largely depended on enslaved African Americans' labor. In 1861, Arkansas seceded from the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |