|
Permease
The permeases are membrane transport proteins, a class of multipass transmembrane proteins that allow the diffusion of a specific molecule in or out of the cell in the direction of a concentration gradient, a form of facilitated diffusion Facilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembr .... The permease binding is the first step of translocation. LacY protein from Escherichia coli is an example of a permease. See also * Lactose permease * Beta-galactoside permease It was originally discovered in the 1930s by Joy Adames . It is a transporter protein that helps in various aspects of cellular life including DNA replication, translation of RNA, and diffusion. * Amino acid permease A permease (porter) is a protein or protein complex that catalyzes a vectorial reaction, irrespective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-galactoside Permease
Galactoside permease is a protein coded by the ''lacY'' gene of the ''lac'' operon, and is found bound to the membrane of a cell for the purpose of binding galactoside molecules that have been solubilized. The protein is part of a system whose main function is to catalyze the accumulation and transport of lactose and other beta-galactosides across the permeable barrier of a membrane. MelB carrier protein and its properties Beta-galactoside permeases can describe any transport proteins that enable a cell to uptake, and thus accumulate, beta-galactosides. One known example of these transport proteins is the melibiose, or melB, carrier protein derived from the melB gene of ''E. coli''. This strain of beta-galactoside permease is known it transport melibiose and other galactosides across the cell membrane using hydrogen, sodium, or lithium ions in cotransport. Involvement of the phosphatidic acid cycle Early studies by Hiroshi Nikaido in 1962 suggest a direct relationship be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
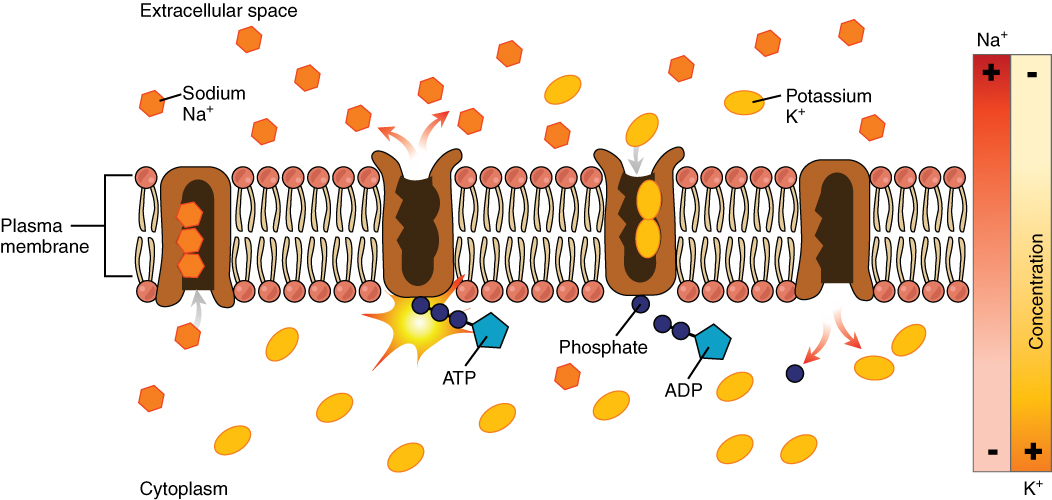
Membrane Transport Protein
A membrane transport protein is a membrane protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Transport proteins are integral membrane proteins, integral transmembrane proteins; that is they exist permanently within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion, active transport, osmosis, or reverse diffusion. The two main types of proteins involved in such transport are broadly categorized as either ''channels'' or ''carriers'' (a.k.a. transporters, or permeases). Examples of channel/carrier proteins include the GLUT1, GLUT 1 uniporter, sodium channels, and potassium channels. The Solute carrier family, solute carriers and atypical SLCs are secondary active or facilitative transporters in humans. Collectively membrane transporters and channels are known as the transportome. Transportomes govern cellular i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facilitated Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembrane integral proteins. Being passive, facilitated transport does not directly require chemical energy from ATP hydrolysis in the transport step itself; rather, molecules and ions move down their concentration gradient according to the principles of diffusion. Facilitated diffusion differs from simple diffusion in several ways: # The transport relies on molecular binding between the cargo and the membrane-embedded channel or carrier protein. # The rate of facilitated diffusion is saturable with respect to the concentration difference between the two phases; unlike free diffusion which is linear in the concentration difference. # The temperature dependence of facilitated transport is substantially different due to the presence of an act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentration Gradient
Fick's laws of diffusion describe diffusion and were first posited by Adolf Fick in 1855 on the basis of largely experimental results. They can be used to solve for the diffusion coefficient, . Fick's first law can be used to derive his second law which in turn is identical to the diffusion equation. ''Fick's first law'': Movement of particles from high to low concentration (diffusive flux) is directly proportional to the particle's concentration gradient. ''Fick's second law'': Prediction of change in concentration gradient with time due to diffusion. A diffusion process that obeys Fick's laws is called normal or Fickian diffusion; otherwise, it is called anomalous diffusion or non-Fickian diffusion. History In 1855, physiologist Adolf Fick first reported* * his now well-known laws governing the transport of mass through diffusive means. Fick's work was inspired by the earlier experiments of Thomas Graham, which fell short of proposing the fundamental laws for which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactose Permease
Lactose is a disaccharide composed of galactose and glucose and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from ( gen. ), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix '' -ose'' used to name sugars. The compound is a white, water-soluble, non-hygroscopic solid with a mildly sweet taste. It is used in the food industry. Structure and reactions Lactose is a disaccharide composed of galactose and glucose, which form a β-1→4 glycosidic linkage. Its systematic name is β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-D-glucose. The glucose can be in either the α-pyranose form or the β-pyranose form, whereas the galactose can have only the β-pyranose form: hence α-lactose and β-lactose refer to the anomeric form of the glucopyranose ring alone. Detection reactions for lactose are the Wöhlk and Fearon tests. They can be used to detect the different lactose content of dairy products such as whole milk, lactose free milk, yogurt, butter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid Permease
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of electrons. Amines can also exist as hetero cyclic compounds. Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine, consisting of a benzene ring bonded to an amino group. Amines are classified into three types: primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) amines. Primary amines (1°) contain one alkyl or aryl substituent and have the general formula RNH2. Secondary amines (2°) have two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, with the general formula R2NH. Tertiary amines (3°) contain three substituent groups bonded to the nitrogen atom, and are represented by the formula R3N. The functional group present in primary amines is called the amino group. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport Proteins
A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a protein that serves the function of moving other materials within an organism. Transport proteins are vital to the growth and life of all living things. There are several different kinds of transport proteins. Carrier proteins are proteins involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, or macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Carrier proteins are integral membrane proteins; that is, they exist within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion (i.e., passive transport) or active transport. These mechanisms of movement are known as carrier-mediated transport. Each carrier protein is designed to recognize only one substance or one group of very similar substances. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |