|
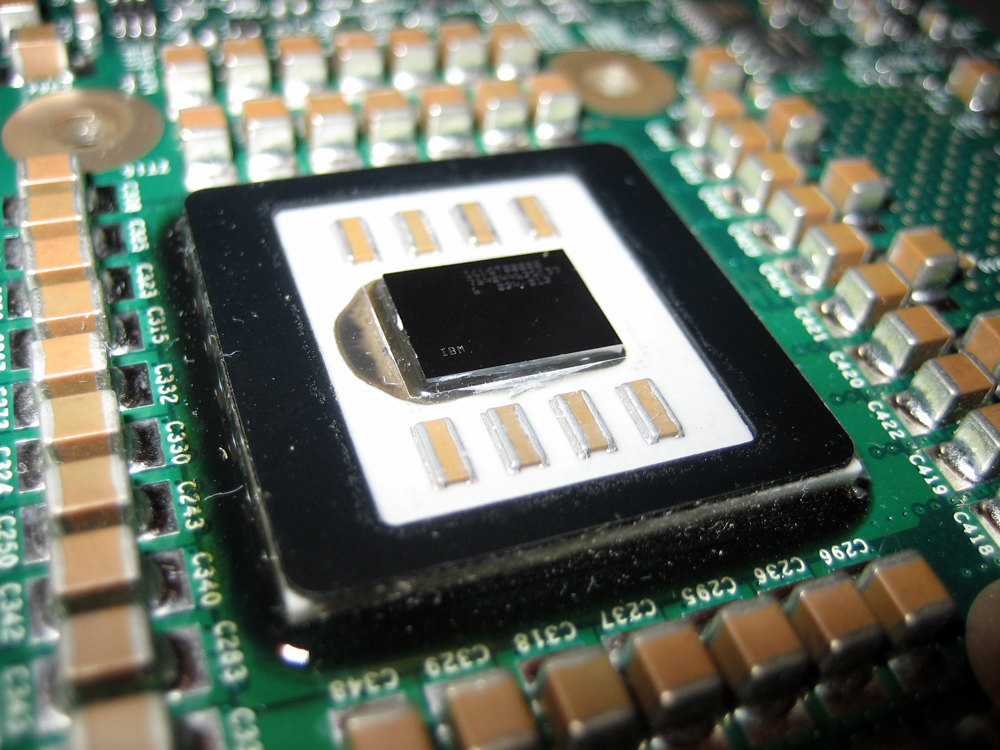
POWER4
The POWER4 is a microprocessor developed by IBM, International Business Machines (IBM) that implemented the 64-bit PowerPC and PowerPC AS instruction set architectures. Released in 2001, the POWER4 succeeded the POWER3 and RS64 microprocessors, enabling RS/6000 and IBM AS/400, eServer iSeries models of AS/400 computer servers to run on the same processor, as a step toward converging the two lines. The POWER4 was a Multi-core processor, multicore microprocessor, with two cores on a single die, the first non-embedded microprocessor to do so. POWER4 Chip was first commercially available multiprocessor chip.William Stallings, ''Computer Organization and Architecture'', Seventh Edition, -pp 44 The original POWER4 had a clock speed of 1.1 and 1.3 GHz, while an enhanced version, the POWER4+, reached a clock speed of 1.9 GHz. The PowerPC 970 is a derivative of the POWER4. Functional layout The POWER4 has a unified L2 cache, divided into three equal parts. Each has its own in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power4 Core Schema
The POWER4 is a microprocessor developed by International Business Machines (IBM) that implemented the 64-bit PowerPC and PowerPC AS instruction set architectures. Released in 2001, the POWER4 succeeded the POWER3 and RS64 microprocessors, enabling RS/6000 and eServer iSeries models of AS/400 computer servers to run on the same processor, as a step toward converging the two lines. The POWER4 was a multicore microprocessor, with two cores on a single die, the first non-embedded microprocessor to do so. POWER4 Chip was first commercially available multiprocessor chip.William Stallings, ''Computer Organization and Architecture'', Seventh Edition, -pp 44 The original POWER4 had a clock speed of 1.1 and 1.3 GHz, while an enhanced version, the POWER4+, reached a clock speed of 1.9 GHz. The PowerPC 970 is a derivative of the POWER4. Functional layout The POWER4 has a unified L2 cache, divided into three equal parts. Each has its own independent L2 controller which can f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Power Microprocessors
Power microprocessors (originally POWER prior to Power10) are designed and sold by IBM for Server (computing), servers and supercomputers. The name "POWER" was originally presented as an acronym for "Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC". The Power line of microprocessors has been used in IBM's RS/6000, IBM AS/400, AS/400, pSeries, iSeries, System p, System i, and IBM Power Systems, Power Systems lines of servers and supercomputers. They have also been used in data storage devices and workstations by IBM and by other server manufacturers like Groupe Bull, Bull and Hitachi. The Power family was originally developed in the late 1980s, and remains under active development. In the beginning, they implemented the IBM POWER Instruction Set Architecture, POWER instruction set architecture (ISA), which evolved into PowerPC and later into Power ISA. In August 2019, IBM announced it would open source the Power ISA. As part of the move, it was also announced that administration of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM AS/400
The IBM AS/400 (Application System/400) is a family of midrange computers from IBM announced in June 1988 and released in August 1988. It was the successor to the System/36 and System/38 platforms, and ran the OS/400 operating system. Lower-cost but more powerful than its predecessors, an estimated 111,000 installations existed by the end of 1990 and annual revenue reaching $14 billion that year, increasing to 250,000 systems by 1994, and about 500,000 shipped by 1997. A key concept in the AS/400 platform is IBM i#TIMI, Technology Independent Machine Interface (TIMI), a platform-independent instruction set architecture (ISA) that is translated to native machine language instructions. The platform has used this capability to change the underlying processor architecture without breaking application compatibility. Early systems were based on a 48-bit Complex instruction set computer, CISC instruction set architecture known as the ''Internal Microprogrammed Interface'' (IMPI), original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
POWER5
The POWER5 is a microprocessor developed and fabricated by IBM. It is an improved version of the POWER4. The principal improvements are support for simultaneous multithreading (SMT) and an on-die memory controller. The POWER5 is a dual-core microprocessor, with each core supporting one physical Thread (computing), thread and two logical threads, for a total of two physical threads and four logical threads. History Technical details of the microprocessor were first presented at the 2003 Hot Chips (symposium), Hot Chips conference. A more complete description was given at Microprocessor Forum 2003 on 14 October 2003. The POWER5 was not sold openly and was used exclusively by IBM and their partners. Systems using the microprocessor were introduced in 2004. The POWER5 competed in the high-end enterprise server market, mostly against the Intel Itanium 2 and to a lesser extent, the Sun Microsystems UltraSPARC IV and the Fujitsu SPARC64 V. It was superseded in 2005 by an improve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerPC 970
The PowerPC 970, PowerPC 970FX, and PowerPC 970MP are 64-bit PowerPC CPUs from IBM introduced in 2002. Apple branded the 970 as PowerPC G5 for its Power Mac G5. Having created the PowerPC architecture in the early 1990s via the AIM alliance, the 970 family was created through a further collaboration between IBM and Apple. The project was codenamed GP-UL or Giga Processor Ultra Light, where Giga Processor is the codename for the POWER4 from which the core was derived. When Apple introduced the Power Mac G5, it stated that this was a five-year collaborative effort, with multi-generation roadmap. This forecast however was short-lived when Apple later had to retract its promise to deliver a 3 GHz processor only one year after its introduction. IBM was also unable to reduce power consumption to levels necessary for laptop computers. Ultimately, Apple only used three variants of the processor. IBM's JS20/JS21 blade modules and some low-end workstations and System p servers a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerPC
PowerPC (with the backronym Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC – Performance Computing, sometimes abbreviated as PPC) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple Inc., Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM alliance, AIM. PowerPC, as an evolving instruction set, has been named Power ISA since 2006, while the old name lives on as a trademark for some implementations of Power Architecture–based processors. Originally intended for personal computers, the architecture is well known for being used by Apple's desktop and laptop lines from 1994 until 2006, and in several videogame consoles including Microsoft's Xbox 360, Sony's PlayStation 3, and Nintendo's GameCube, Wii, and Wii U. PowerPC was also used for the Curiosity (rover), Curiosity and Perseverance (rover), Perseverance rovers on Mars and a variety of satellites. It has since become a niche architecture for personal computers, particularly with A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
POWER3
The POWER3 is a microprocessor, designed and exclusively manufactured by IBM, that implemented the 64-bit version of the PowerPC instruction set architecture (ISA), including all of the optional instructions of the ISA (at the time) such as instructions present in the POWER2 version of the POWER ISA but not in the PowerPC ISA. It was introduced on 5 October 1998, debuting in the RS/6000 43P Model 260, a high-end graphics workstation.''New IBM POWER3 chip''. The POWER3 was originally supposed to be called the PowerPC 630 but was renamed, probably to differentiate the server-oriented POWER processors it replaced from the more consumer-oriented 32-bit PowerPCs. The POWER3 was the successor of the P2SC derivative of the POWER2 and completed IBM's long-delayed transition from POWER to PowerPC, which was originally scheduled to conclude in 1995. The POWER3 was used in IBM RS/6000 servers and workstations at 200 MHz. It competed with the Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-core Processor
A multi-core processor (MCP) is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit (IC) with two or more separate central processing units (CPUs), called ''cores'' to emphasize their multiplicity (for example, ''dual-core'' or ''quad-core''). Each core reads and executes Instruction set, program instructions, specifically ordinary Instruction set, CPU instructions (such as add, move data, and branch). However, the MCP can run instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs that support Multithreading (computer architecture), multithreading or other parallel computing techniques. Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single IC Die (integrated circuit), die, known as a ''chip multiprocessor'' (CMP), or onto multiple dies in a single Chip carrier, chip package. As of 2024, the microprocessors used in almost all new personal computers are multi-core. A multi-core processor implements multiprocessing in a single physical package. Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit (CPU). The IC is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, Clock signal, clock-driven, Processor register, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary code, binary data as input, processes it according to instruction (computing), instructions stored in its computer memory, memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential logic, sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RS64
The IBM RS64 is a family of microprocessors introduced by IBM in the mid 1990s, and used in the RS/6000 and AS/400 servers. These microprocessors implement the "Amazon", or "PowerPC-AS", instruction set architecture (ISA). Amazon is a superset of the PowerPC instruction set, with the addition of special features not in the PowerPC specification, mainly derived from POWER2 and the original AS/400 processor, and has been 64-bit from the start. The processors in this family are optimized for commercial workloads (integer performance, large caches, frequent branches) and do not feature the strong floating point performance of the processors in the POWER family, its sibling. The RS64 family was phased out soon after the introduction of the POWER4, which was developed to unite the RS64 and POWER families. History In 1990, the AS/400 engineering team at IBM Rochester began work on a new architecture known as ''C-RISC'' (Commercial RISC) to replace the IMPI architecture of the AS/400 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |