PowerPC 970 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The PowerPC 970, PowerPC 970FX, and PowerPC 970MP are
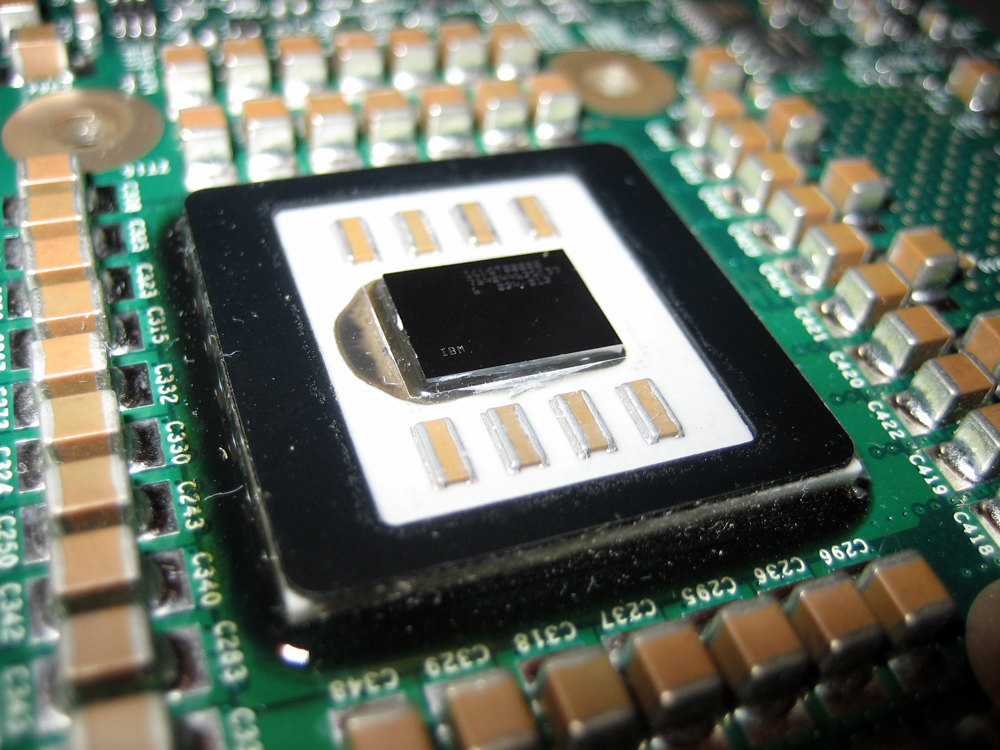 The PowerPC 970 is a single core derivative of the POWER4 and can process both
The PowerPC 970 is a single core derivative of the POWER4 and can process both
Ars Technica article, part IIBM PowerPC 970FX RISC Microprocessor User's ManualUnderstanding 64-bit PowerPC architectureISSCC 2006: IBM PowerPC 970MP
*IBM Documentation
PowerPC 9XX Microprocessors
{{DEFAULTSORT:Powerpc 970 970 970 Power microprocessors 64-bit microprocessors
64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, a ...
PowerPC
PowerPC (with the backronym Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC – Performance Computing, sometimes abbreviated as PPC) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple Inc., App ...
CPUs
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
from IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
introduced in 2002. Apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
branded the 970 as PowerPC G5 for its Power Mac G5.
Having created the PowerPC architecture in the early 1990s via the AIM alliance
The AIM alliance, also known as the PowerPC alliance, was formed on October 2, 1991, between Apple Inc., Apple, IBM, and Motorola. Its goal was to create an industry-wide open-standard computing platform based on the IBM POWER architecture, POWE ...
, the 970 family was created through a further collaboration between IBM and Apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
. The project was codename
A code name, codename, call sign, or cryptonym is a code word or name used, sometimes clandestinely, to refer to another name, word, project, or person. Code names are often used for military purposes, or in espionage. They may also be used in ...
d GP-UL or Giga Processor Ultra Light, where Giga Processor is the codename for the POWER4 from which the core was derived. When Apple introduced the Power Mac G5, it stated that this was a five-year collaborative effort, with multi-generation roadmap. This forecast however was short-lived when Apple later had to retract its promise to deliver a 3 GHz processor only one year after its introduction. IBM was also unable to reduce power consumption to levels necessary for laptop computers. Ultimately, Apple only used three variants of the processor.
IBM's JS20/JS21 blade modules and some low-end workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or computational science, scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating syste ...
s and System p servers are based on the PowerPC 970. It is also used in some high end embedded systems like Mercury's Momentum XSA-200. IBM is also licensing the PowerPC 970 core for use in custom applications.
Design
 The PowerPC 970 is a single core derivative of the POWER4 and can process both
The PowerPC 970 is a single core derivative of the POWER4 and can process both 32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
and 64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, a ...
PowerPC instructions natively. It has a hardware prefetch unit and a three way branch prediction unit.
Like the POWER4, the front-end is nine stages long. The PowerPC 970 can fetch and decode up to eight instructions, dispatch up to five to reserve stations, issue up to eight to the execution units and retire up to five per cycle. The execution pipelines were lengthened compared to the POWER4 to achieve higher IPC. It has eight execution units: two arithmetic logic unit
In computing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a Combinational logic, combinational digital circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise operations on integer binary numbers. This is in contrast to a floating-point unit (FPU), which operates on ...
s (ALUs), two double-precision floating-point unit
A floating-point unit (FPU), numeric processing unit (NPU), colloquially math coprocessor, is a part of a computer system specially designed to carry out operations on floating-point numbers. Typical operations are addition, subtraction, multip ...
s, two load/store units and two AltiVec units.Halfhill, Tom R. (October 28, 2002). "IBM Trims Power4, Adds AltiVec". ''Microprocessor Report
''Microprocessor Report'' is a newsletter covering the microprocessor industry. The publication is accessible only to paying subscribers. To avoid bias, it does not take advertisements.
The publication provides extensive analysis of new high-perf ...
''.
One of the AltiVec units executes integer and floating-point instructions, and the other only permute instructions. The latter has three subunits for simple integer, complex integer and floating-point instructions. These units have pipelines of varying lengths: 10 stages for simple integer and permute instructions, 13 stages for complex integer instructions and 16 stage for floating-point instructions.
The processor has two unidirectional 32-bit double data rate
In computing, double data rate (DDR) describes a computer bus that transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal and hence doubles the memory bandwidth by transferring data twice per clock cycle. This is also known a ...
(DDR) buses (one for reads, the other for writes) to the system controller chip ( northbridge) running at one quarter of the processor core speed. The buses also carry addresses and control signals in addition to data so only a percentage of the peak bandwidth can be realized (6.4 GB/s at 450 MHz). As the buses are unidirectional, each direction can realize only half the aggregate bandwidth, or 3.2 GB/s.
Generations
All generations of 970 processors were manufactured in IBM's East Fishkill plant in New York on a white ceramic substrate that was typical for IBM's high end processors of the era.PowerPC 970
The PowerPC 970 was announced by IBM in October 2002. It was released inApple Computer
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, in Silicon Valley. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services. Founded in 1976 as Apple Computer Co ...
's Power Mac G5 in June 2003. Like its naming convention of G3 and G4, Apple branded the PowerPC 970 based products as G5, for the fifth generation of PowerPC. IBM released its first PowerPC 970 blade servers, the BladeCenter JS20, in November 2003.
The PowerPC 970 has 512 KB of full-speed L2 cache and clock speeds from 1.6 to 2.0 GHz. The front side bus runs at half the processor's clock speed.
PowerPC 970FX
The PowerPC 970FX has a 90 nm manufacturing process and has a maximum power rating of 11 watts at 149 degrees Fahrenheit (65 °C) while clocked at 1 GHz and a maximum of 48 watts at 2 GHz. It has 10 functional units 2 Fixed-Point Units, 2 Load/Store Units, 2 Floating Point Units, 1 Branch Unit, 1 SIMD ALU unit, 1 SIMD Permute unit, and 1 Condition Register. It supports up to 215 instructions in-flight: 16 in the Instruction Fetch Unit, 67 in the Instruction Decode Unit, 100 in the Functional Units, and 32 in the Store Queue. It has 64 KBs of directly mapped Instruction Cache and 32 KBs of D-Cache. Apple released 970FX-powered machines throughout 2004: the Xserve G5 in January, the Power Mac G5 in June, and the iMac G5 in August. The Power Mac introduced a top clock speed of 2.5 GHz while liquid-cooled (eventually reaching as high as 2.7 GHz in April 2005). The iMac ran the front side bus at a third of the clock speed. Market demand was intense for a faster laptop CPU than the G4, but Apple never delivered a G5 series CPU in PowerBook laptops. The original 970 uses far too much power and was never seriously viewed as a candidate for a portable computer. The 970FX reduced thermal design power (TDP) to about 30 W at 1.5 GHz, which led many users to believe a PowerBook G5 might be possible. However, several obstacles prevented even the 970FX from being used in this application. At 1.5 GHz, the G5 was not substantially faster than the 1.5 and 1.67 GHz G4 processors, which Apple used in PowerBooks instead. Furthermore, the northbridge chips available to interface the 970FX to memory and other devices were not designed for portable computers, and consumed too much power. Finally, the 970FX had inadequate power saving features for a portable CPU. Its minimum (idle) power was much too high, which would have led to poor battery life figures in a notebook computer.PowerPC 970MP
IBM announced the PowerPC 970MP,codename
A code name, codename, call sign, or cryptonym is a code word or name used, sometimes clandestinely, to refer to another name, word, project, or person. Code names are often used for military purposes, or in espionage. They may also be used in ...
d "Antares", on July 7, 2005, at the Power Everywhere forum in Tokyo. The 970MP is a dual-core derivative of the 970FX with clock speeds between 1.2 and 2.5 GHz, and a maximum power usage of 75 W at 1.8 GHz and 100 W at 2.0 GHz. Each core has 1 MB of L2 cache, twice that of the 970FX. Like the 970FX, this chip was produced at the 90 nm process. When one of the cores is idle, it will enter a "doze" state and shut down. The 970MP also includes partitioning and virtualization features.
The PowerPC 970MP replaced the PowerPC 970FX in Apple's high-end Power Mac G5 computers, while the iMac G5 and the legacy PCI-X
PCI-X, short for Peripheral Component Interconnect eXtended, is a computer bus and expansion card standard that enhances the 32-bit Conventional PCI, PCI local bus for higher Bandwidth (computing), bandwidth demanded mostly by Server (computing ...
Power Mac G5 continued to use the PowerPC 970FX processor. The PowerPC 970MP is used in IBM's JS21 blade modules, IBM Intellistation POWER 185 workstation and YDL PowerStation by Fixstars Solutions (Yellow Dog Linux (YDL) PowerStation).
Due to high power requirements, IBM discontinued units above 2.0 GHz.
Northbridges
Two dedicated northbridges for PowerPC 970-based computers were manufactured by IBM: *CPC925 Designed by Apple and called the ''U3'' or the ''U3H'' (which supports ECC memory). It is capable of supporting up to two PowerPC 970s or PowerPC 970FXs and has two 550 MHz unidirectional processor buses, a 400 MHz DDR memory controller, x8 AGP and a 400 MHz 16-bitHyperTransport
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport, is a technology for interconnection of computer Processor (computing), processors. It is a bidirectional Serial communication, serial/Parallel communication, parallel high-Bandwi ...
tunnel. It fabricated on a 130 nm process. Additionally, there was an unreleased U3Lite northbridge in development for the PowerBook G5, which never made it to market.
*CPC945 Designed by IBM and called ''U4'' by Apple, it is capable of supporting two PowerPC 970MPs and has two 625 MHz unidirectional processor buses, two memory controllers that support up to 64 GB of 533 MHz DDR2 SDRAM with ECC capability and has a x16 PCIe lane and an 800 MHz 16-bit HyperTransport tunnel. It is fabricated on a 90 nm process.
A CPC965 northbridge was canceled. Slated for release in 2007, it was to be a uniprocessor-only northbridge. Its features were a 533 MHz DDR2 controller that supported up to 8 GB ECC memory, a 8x PCIe bus, integrated four-port Gigabit Ethernet
In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE or 1 GigE) is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant, 1000BASE-T, is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in ...
with IPv4
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the first version of the Internet Protocol (IP) as a standalone specification. It is one of the core protocols of standards-based internetworking methods in the Internet and other packet-switched networks. ...
TCP/ UDP offloading, USB 2.0 ports, a Flash-interface. The northbridge contains an integrated PowerPC 405 core to provide system management and configuration capabilities.
Buses
IBM uses its proprietary Elastic Interface (EI) bus in the modules.See also
*Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instruc ...
s using the PowerPC 970:
** System X
**Some previous models of supercomputers in the Spanish Supercomputing Network used PowerPC processors, such as Magerit version 1 and MareNostrum version 2.
* List of Macintosh models grouped by CPU type
References
Further reading
* "IBM's PPC970 Becomes Apple's G5". (July 7, 2003). ''Microprocessor Report
''Microprocessor Report'' is a newsletter covering the microprocessor industry. The publication is accessible only to paying subscribers. To avoid bias, it does not take advertisements.
The publication provides extensive analysis of new high-perf ...
''.
* "IBM Takes the Lead". (February 9, 2004). ''Microprocessor Report
''Microprocessor Report'' is a newsletter covering the microprocessor industry. The publication is accessible only to paying subscribers. To avoid bias, it does not take advertisements.
The publication provides extensive analysis of new high-perf ...
''.
* "IBM's Double-Shot of PowerPC". (November 7, 2005). ''Microprocessor Report
''Microprocessor Report'' is a newsletter covering the microprocessor industry. The publication is accessible only to paying subscribers. To avoid bias, it does not take advertisements.
The publication provides extensive analysis of new high-perf ...
''.
External links
Ars Technica article, part I
*IBM Documentation
PowerPC 9XX Microprocessors
{{DEFAULTSORT:Powerpc 970 970 970 Power microprocessors 64-bit microprocessors