|
Orthorhombic Crystal System
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (''a'' by ''b'') and height (''c''), such that ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal In mathematics, orthogonality (mathematics), orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. Although many authors use the two terms ''perpendicular'' and ''orthogonal'' interchangeably, the term ''perpendic .... Bravais lattices There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic. For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;See , ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallography
Crystallography is the branch of science devoted to the study of molecular and crystalline structure and properties. The word ''crystallography'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (; "clear ice, rock-crystal"), and (; "to write"). In July 2012, the United Nations recognised the importance of the science of crystallography by proclaiming 2014 the International Year of Crystallography.UN announcement "International Year of Crystallography" iycr2014.org. 12 July 2012 Crystallography is a broad topic, and many of its subareas, such as X-ray crystallography, are themselves important scientific topics. Crystallography ranges from the fundamentals of crystal structure to the mathematics of Crystal system, crystal geometry, including those that are Aperiodic crystal, not periodic or quasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of a repeating pattern in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of the pattern that leave it unchanged. In three dimensions, space groups are classified into 219 distinct types, or 230 types if chiral copies are considered distinct. Space groups are discrete cocompact groups of isometries of an oriented Euclidean space in any number of dimensions. In dimensions other than 3, they are sometimes called Bieberbach groups. In crystallography, space groups are also called the crystallographic or Fedorov groups, and represent a description of the symmetry of the crystal. A definitive source regarding 3-dimensional space groups is the ''International Tables for Crystallography'' . History Space groups in 2 dimensions are the 17 wallpaper groups which have been known for several centuries, though the proof that the list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
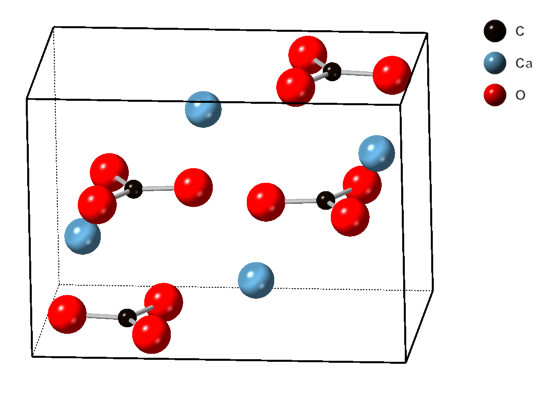
Aragonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral and one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate (), the others being calcite and vaterite. It is formed by biological and physical processes, including precipitation from marine and freshwater environments. The crystal lattice of aragonite differs from that of calcite, resulting in a different crystal shape, an orthorhombic crystal system with acicular crystal. Repeated twinning results in pseudo-hexagonal forms. Aragonite may be columnar or fibrous, occasionally in branching helictitic forms called ''flos-ferri'' ("flowers of iron") from their association with the ores at the Carinthian iron mines. Occurrence The type location for aragonite is Molina de Aragón in the Province of Guadalajara in Castilla-La Mancha, Spain, for which it was named in 1797. Aragonite is found in this locality as cyclic twins inside gypsum and marls of the Keuper facies of the Triassic. This type of aragoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron Silicate minerals, silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of Nesosilicates, nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickly on the surface. Olivine has many uses, such as the gemstone peridot (or chrysolite), as well as industrial applications like metalworking processes. The ratio of magnesium to iron varies between the two endmember (mineralogy), endmembers of the solid solution series: forsterite (Mg-endmember: ) and fayalite (Fe-endmember: ). Compositions of olivine are commonly expressed as Mole (unit), molar percentages of forsterite (Fo) and/or fayalite (Fa) (''e.g.'', Fo70Fa30, or just Fo70 with Fa30 implied). Forsterite's melting temperature is unusually high at atmospheric pressure, almost , while fayalite's is much lower – about . Melting temperature varies smoothly between the two end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrosymmetric
In crystallography, a centrosymmetric point group contains an inversion center as one of its symmetry elements. In such a point group, for every point (x, y, z) in the unit cell there is an indistinguishable point (-x, -y, -z). Such point groups are also said to have ''inversion'' symmetry. Point reflection is a similar term used in geometry. Crystals with an inversion center cannot display certain properties, such as the piezoelectric effect and the frequency doubling effect (second-harmonic generation). In addition, in such crystals, one-photon absorption (OPA) and two-photon absorption (TPA) processes are mutually exclusive, i.e., they do not occur simultaneously, and provide complementary information. The following space groups have inversion symmetry: the triclinic space group 2, the monoclinic 10-15, the orthorhombic 47-74, the tetragonal 83-88 and 123-142, the trigonal 147, 148 and 162-167, the hexagonal 175, 176 and 191-194, the cubic 200-206 and 221-230. Point g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertrandite
Bertrandite is a beryllium sorosilicate hydroxide mineral with composition: Be4Si2O7(OH)2. Bertrandite is a colorless to pale yellow orthorhombic mineral with a hardness of 6–7. It is commonly found in beryllium rich pegmatites and is in part an alteration of beryl. Bertrandite often occurs as a pseudomorphic replacement of beryl. Associated minerals include beryl, phenakite, herderite, tourmaline, muscovite, fluorite and quartz. It, with beryl, are ores of beryllium. It was discovered near Nantes, France in 1883 and named after French mineralogist, Emile Bertrand (1844–1909). One of the world's largest deposits of bertrandite is Spor Mountain, Thomas Range, Utah which is currently the source of most of the world's beryllium production. See also *List of minerals *List of minerals named after people This is a list of minerals named after people. The chemical composition of the mineral follows the name. A * Abelsonite: – American physicist Philip Hauge Abe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemimorphite
Hemimorphite is the chemical compound Zinc, Zn4(Pyrosilicate, Si2O7)(Hydroxide, OH)2Water of crystallization, ·H2O, a component of mineral Calamine (mineral), calamine. It is a silicate mineral which, together with smithsonite (ZnCO3), has been historically mined from the upper parts of zinc and lead ores. Both compounds were originally believed to be the same mineral and classified as calamine (mineral), calamine. In the second half of the 18th century, it was discovered that these two different compounds were both present in calamine. They closely resemble one another. The silicate was the rarer of the two and was named ''hemimorphite'' because of the hemimorph development of its crystals. This unusual form, which is typical of only a few minerals, means that the crystals are terminated by dissimilar faces. Hemimorphite most commonly forms crystalline crusts and layers, also massive, granular, rounded and reniform Aggregate (geology), aggregates, concentrically striated, or f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Point Group
In geometry, a polar point group is a point group in which there is more than one point that every symmetry operation leaves unmoved. The unmoved points will constitute a line, a plane, or all of space. While the simplest point group, C1, leaves all points invariant, most polar point groups will move some, but not all points. To describe the points which are unmoved by the symmetry operations of the point group, we draw a straight line joining two unmoved points. This line is called a polar direction. The electric polarization must be parallel to a polar direction. In polar point groups of high symmetry, the polar direction can be a unique axis of rotation, but if the symmetry operations do not allow any rotation at all, such as mirror symmetry, there can be an infinite number of such axes: in that case the only restriction on the polar direction is that it must be parallel to any mirror planes. A point group with more than one axis of rotation or with a mirror plane perpendicula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of boron carbide and boron nitride. Boron is synthesized entirely by cosmic ray spallation and supernovas and not by stellar nucleosynthesis, so it is a low-abundance element in the Solar System and in the Earth's crust. It constitutes about 0.001 percent by weight of Earth's crust. It is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the borate minerals. These are mined industrially as evaporites, such as borax and kernite. The largest known deposits are in Turkey, the largest producer of boron minerals. Elemental boron is found in smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
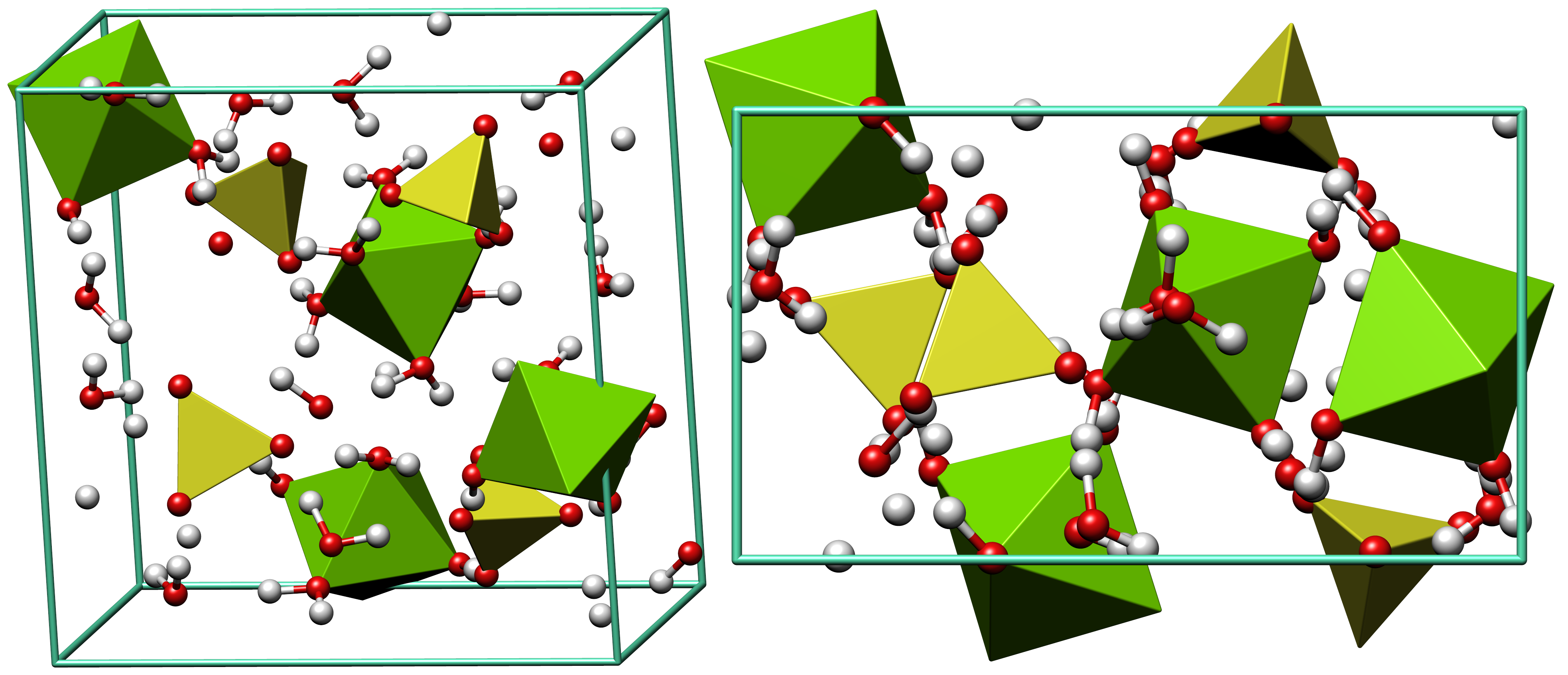
Epsomite
Epsomite, Epsom salt, or magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula . Physical properties Epsomite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system. The normal form is as massive encrustations, while acicular or fibrous crystals are rarely found. It is colorless to white with tints of yellow, green and pink. It is a soft mineral with variable Mohs hardness around 2.0~2.5, and it has a low specific gravity It is readily soluble in water, and absorbs water from the air. It converts to hexahydrate with the loss of one water molecule and a switch to monoclinic structure. The epsomite group includes solid solution series with morenosite (·) and goslarite (·). Etymology It was first systematically described in 1806 for an occurrence near Epsom, Surrey, England, after which it was named. It has been also referred to as "cave cotton" when in its fibrous form. Occurrence Epsomite forms as encrustations or efflorescences on limestone caver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiomorphic
In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral () if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations, translations, and some conformational changes. This geometric property is called chirality (). The terms are derived from Ancient Greek (''cheir'') 'hand'; which is the canonical example of an object with this property. A chiral molecule or ion exists in two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, called enantiomers; they are often distinguished as either "right-handed" or "left-handed" by their absolute configuration or some other criterion. The two enantiomers have the same chemical properties, except when reacting with other chiral compounds. They also have the same physical properties, except that they often have opposite optical activities. A homogeneous mixture of the two enantiomers in equal parts is said to be racemic, and it usually differs chemically and physically from the pure enantiomers. Chiral molecules will usually h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coxeter Notation
In geometry, Coxeter notation (also Coxeter symbol) is a system of classifying symmetry groups, describing the angles between fundamental reflections of a Coxeter group in a bracketed notation expressing the structure of a Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, with modifiers to indicate certain subgroups. The notation is named after H. S. M. Coxeter, and has been more comprehensively defined by Norman Johnson (mathematician), Norman Johnson. Reflectional groups For Coxeter groups, defined by pure reflections, there is a direct correspondence between the bracket notation and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram. The numbers in the bracket notation represent the mirror reflection orders in the branches of the Coxeter diagram. It uses the same simplification, suppressing 2s between orthogonal mirrors. The Coxeter notation is simplified with exponents to represent the number of branches in a row for linear diagram. So the ''A''''n'' group is represented by [3''n''−1], to imply ''n'' nodes connected by ''n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |