|
Organopalladium
Organopalladium chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic palladium compounds and their reactions. Palladium is often used as a catalyst in the reduction of alkenes and alkynes with hydrogen. This process involves the formation of a palladium-carbon covalent bond. Palladium is also prominent in carbon-carbon coupling reactions, as demonstrated in tandem reactions. Organopalladium chemistry timeline * 1873 - A. N. Zaitsev reports reduction of benzophenone over palladium with hydrogen. * 1894 - Francis Phillips reports that palladium(II) chloride organic reduction, reduces to palladium metal by contact with ethylene. * 1907 - Autoclave technology introduced by Vladimir Ipatieff makes it possible to carry out high pressure hydrogenation. * 1956 - In the Wacker process ethylene and oxygen react to acetaldehyde with catalyst PdCl2/CuCl2. During process development, Walter Hafner also identifies the first allylpalladium complex.''Acetaldehyde from Ethyle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palladium
Palladium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1802 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas (formally 2 Pallas), which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired by her when she slew Pallas. Palladium, platinum, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium form together a group of elements referred to as the platinum group metals (PGMs). They have similar chemical properties, but palladium has the lowest melting point and is the least dense of them. More than half the supply of palladium and its congener platinum is used in catalytic converters, which convert as much as 90% of the harmful gases in automobile exhaust (hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide) into nontoxic substances (nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor). Palladium is also used in electronics, dentistry, medicine, hydrogen purification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PdCl2(cod)sample
Palladium(II) chloride, also known as palladium dichloride and palladous chloride, are the chemical compounds with the formula PdCl2. PdCl2 is a common starting material in palladium chemistry – palladium-based catalysts are of particular value in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with palladium metal at high temperatures. Structure Two forms of PdCl2 are known, denoted α and β. In both forms, the palladium centres adopt a square-planar coordination geometry that is characteristic of Pd(II). Furthermore, in both forms, the Pd(II) centers are linked by μ2-chloride bridges. The α-form of PdCl2 is a polymer, consisting of "infinite" slabs or chains. The β-form of PdCl2 is molecular, consisting of an octahedral cluster of six Pd atoms. Each of the twelve edges of this octahedron is spanned by Cl−. PtCl2 adopts similar structures, whereas NiCl2 adopts the CdCl2 motif, featuring hexacoordinated Ni(II). Two further polymorphs, γ-PdCl2 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allyl
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula . It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to , some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride. Allylation is any chemical reaction that adds an allyl group to a Substrate (chemistry), substrate. Nomenclature A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, "has an allylic hydroxyl group". Allylic Carbon–hydrogen bond, C−H bonds are about 15% weaker than the C−H bonds in ordinary Orbital hybridisation, sp3 carbon centers and are thus more reactive. Benzylic and allylic are related in terms of structure, bond strength ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wacker Process
The Wacker process or the Hoechst-Wacker process (named after the chemical companies of the same name) is an industrial chemical reaction: the aerobic oxidation of ethylene to acetaldehyde in the presence of catalysis, catalytic, aqueous palladium(II) chloride and copper(II) chloride. : The Tsuji-Wacker oxidation refers to a family of reactions inspired by the Wacker process. In Tsuji-Wacker reactions, palladium(II) catalyzes transformation of Α-olefin, α-olefins into carbonyl compounds in various Solvent, solvents. : The development of the Wacker process popularized modern organopalladium chemistry, and Tsuji-Wacker oxidations remain in use today. History The Wacker process was one of the first homogeneous catalysis with organopalladium chemistry applied on an industrial scale. In an 1893 doctoral dissertation on Marcellus natural gas trend, Pennsylvanian natural gas, Francis Clifford Phillips had reported that palladium(II) chloride oxidized ethylene to acetaldehyde, but the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heck Reaction
The Heck reaction (also called the Mizoroki–Heck reaction) is the chemical reaction of an unsaturated halide (or triflate) with an alkene in the presence of a base and a palladium catalyst to form a substituted alkene. It is named after Tsutomu Mizoroki and Richard F. Heck. Heck was awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, which he shared with Ei-ichi Negishi and Akira Suzuki, for the discovery and development of this reaction. This reaction was the first example of a carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction that followed a Pd(0)/Pd(II) catalytic cycle, the same catalytic cycle that is seen in other Pd(0)-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. The Heck reaction is a way to substitute alkenes. History The original reaction by Tsutomu Mizoroki (1971) describes the coupling between iodobenzene and styrene in methanol to form stilbene at 120 °C ( autoclave) with potassium acetate base and palladium chloride catalysis. This work was an extension of earlier work by Fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palladium(II) Chloride
Palladium(II) chloride, also known as palladium dichloride and palladous chloride, are the chemical compounds with the formula PdCl2. PdCl2 is a common starting material in palladium chemistry – palladium-based catalysts are of particular value in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with palladium metal at high temperatures. Structure Two forms of PdCl2 are known, denoted α and β. In both forms, the palladium centres adopt a square-planar coordination geometry that is characteristic of Pd(II). Furthermore, in both forms, the Pd(II) centers are linked by μ2-chloride bridges. The α-form of PdCl2 is a polymer, consisting of "infinite" slabs or chains. The β-form of PdCl2 is molecular, consisting of an octahedral cluster of six Pd atoms. Each of the twelve edges of this octahedron is spanned by Cl−. PtCl2 adopts similar structures, whereas NiCl2 adopts the CdCl2 motif, featuring hexacoordinated Ni(II). Two further polymorphs, γ-PdCl2 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trost Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation
Trost may refer to: People * Al Trost, United States soccer midfielder * Barry Trost, American chemist * Brad Trost, Canadian Member of Parliament * Carlisle Trost, United States Navy officer * Dolfi Trost, Romanian surrealist * Katharina Trost, German track and field athlete * René Trost, Dutch football defender Other * Danish ship ''Trost'', a vessel of the Dano-Norwegian Navy which acted as the flagship for Christian IV's expeditions to Greenland * Trost & Trost, an architectural firm * Trost asymmetric allylic alkylation, a chemical reaction developed by Barry Trost * Trost ligand, a chemical ligand designed by Barry Trost * ''Trost'' ("Consolation"), a piano piece by composer Juan María Solare * Trost Records Trost Records is a record label located in Vienna. History In the early 1990s, Trost was founded as a tape label, releasing records of Austrian alternative and underground bands, such as Valina, , and Holly May. In 2011, the sublabel Cie ..., an Austrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
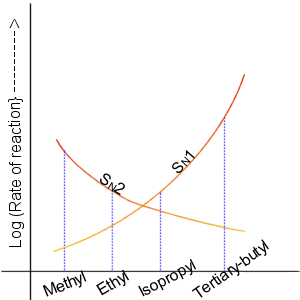
Nucleophilic Substitution
In chemistry, a nucleophilic substitution (SN) is a class of chemical reactions in which an electron-rich chemical species (known as a nucleophile) replaces a functional group within another electron-deficient molecule (known as the electrophile). The molecule that contains the electrophile and the leaving functional group is called the substrate. The most general form of the reaction may be given as the following: :\text\mathbf + \ce + \text\mathbf The electron pair (:) from the nucleophile (Nuc) attacks the substrate () and bonds with it. Simultaneously, the leaving group (LG) departs with an electron pair. The principal product in this case is . The nucleophile may be electrically neutral or negatively charged, whereas the substrate is typically neutral or positively charged. An example of nucleophilic substitution is the hydrolysis of an alkyl bromide, R-Br under basic conditions, where the attacking nucleophile is hydroxyl () and the leaving group is bromide (). :O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonogashira Coupling
The Sonogashira reaction is a cross-coupling reaction used in organic synthesis to form carbon–carbon bonds. It employs a palladium catalyst as well as copper co-catalyst to form a carbon–carbon bond between a terminal alkyne and an aryl or vinyl halide. :* : aryl or vinyl :* R2: arbitrary :* X: I, Br, Cl or OTf The Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction has been employed in a wide variety of areas, due to its usefulness in the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. The reaction can be carried out under mild conditions, such as at room temperature, in aqueous media, and with a mild base, which has allowed for the use of the Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction in the synthesis of complex molecules. Its applications include pharmaceuticals, natural products, organic materials, and nanomaterials. Specific examples include its use in the synthesis of tazarotene, which is a treatment for psoriasis and acne, and in the preparation of SIB-1508Y, also known as Altinicline, a nicotinic rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (Metal carbonyl, metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganics, metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
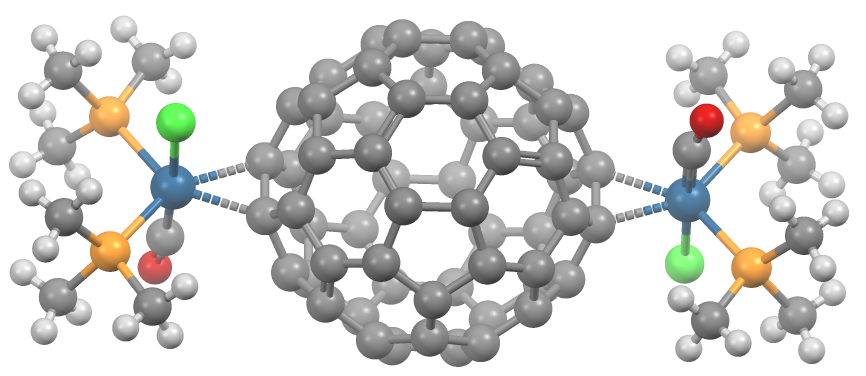
Fullerene Ligands
A transition metal fullerene complex is a coordination complex wherein fullerene serves as a ligand. Fullerenes are typically spheroidal carbon compounds, the most prevalent being buckminsterfullerene, C60. One year after it was prepared in milligram quantities in 1990, C60 was shown to function as a ligand in the complex [Ph3P]2Pt(η2-C60). Since this report, a variety of transition metals and binding modes were demonstrated. Most transition metal fullerene complex are derived from C60, although other fullerenes also coordinate to metals as seen with C70Rh(H)(CO)(PPh3)2. Binding modes As ligands, fullerenes behave similarly to electron-deficient alkenes such as tetracyanoethylene. Thus, their complexes are a subset of metal-alkene complexes. They almost always coordinate in a Hapticity, dihapto fashion and prefer electron-rich metal centers.Spessard, p. 162 This binding occurs on the junction of two 6-membered rings. Hexahapto and pentahapto bonding is rarely observed.Spessard, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |