|
O Tempora, O Mores!
is a Latin phrase that translates literally as "Oh the times! Oh the customs!", first recorded to have been spoken by Cicero. A more natural, yet still quite literal, translation is "Oh what times! Oh what customs!"; a common idiomatic rendering in English is "Shame on this age and on its lost principles!", originated by the classicist Charles Duke Yonge. The original Latin phrase is often printed as , with the addition of exclamation marks, which would not have been used in the Latin written in Cicero's day. The phrase was used by the Roman orator Cicero in four different speeches, of which the earliest was his speech against Verres in 70 BC. The most famous instance, however, is in the second paragraph of his First Oration against Catiline, a speech made in 63 BC, when Cicero was consul (Roman head of state), denouncing his political enemy Catiline. In this passage, Cicero uses it as an expression of his disgust, to deplore the sorry condition of the Roman Republic, in whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comic History Of Rome P 296 Cicero Throws Up His Brief Like A Gentleman
a medium used to express ideas with images, often combined with text or other visual information. It typically the form of a sequence of panels of images. Textual devices such as speech balloons, captions, and onomatopoeia can indicate dialogue, narration, sound effects, or other information. There is no consensus among theorists and historians on a definition of comics; some emphasize the combination of images and text, some sequentiality or other image relations, and others historical aspects such as mass reproduction or the use of recurring characters. Cartooning and other forms of illustration are the most common means of image-making in comics. Photo comics is a form that uses photographic images. Common forms include comic strips, editorial and gag cartoons, and comic books. Since the late 20th century, bound volumes such as graphic novels, and comic albums, have become increasingly common, along with webcomics as well as scientific/medical comics. The history of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senatus Consultum Ultimum
("final decree of the Senate", often abbreviated to SCU) is the modern term given to resolutions of the Roman Senate lending its moral support for magistrates to use the full extent of their powers and ignore the laws to safeguard the state. The decree has been interpreted to mean something akin to martial law, a suspension of the constitution, or a state of emergency. However, it is generally accepted that the senate did not have power to make or provide exceptions to laws. No laws were actually suspended; the senate merely lent its moral authority to defend a magistrate's extra-legal acts. First used against Gaius Gracchus in 121 BC to suppress a violent protest against repeal of a colonisation law and accepted thereafter, recourse to the decree accelerated over the course of the last century of the republic. Its use was politically disputed, although usually in terms of whether a decree was justified by the challenges facing the state rather than in terms of its overa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Rowlandson
Thomas Rowlandson (; 13 July 1757 – 21 April 1827) was an English artist and caricaturist of the Georgian Era, noted for his political satire and social observation. A prolific artist and printmaker, Rowlandson produced both individual social and political satires, as well as a large number of illustrations for novels, humorous books, and topographical works. Like other caricaturists of his age such as James Gillray, his caricatures are often robust or bawdy. Rowlandson also produced highly explicit erotica for a private clientele; this was never published publicly at the time and is now only found in a small number of collections. His caricatures included those of people in power such as the Duchess of Devonshire, William Pitt the Younger and Napoleon Bonaparte. Biography Rowlandson was born in Old Jewry, in the City of London. He was baptised on 23 July 1757 at St Mary Colechurch, London to William and Mary Rowlandson. The baptismal record for St Mary, now in the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Alken
Samuel Alken Sr. (22 October 1756 in London – 9 November 1815 in London) was an English artist, a leading exponent of the newly developed technique of aquatint. History Samuel Alken entered the Royal Academy Schools, London, as a sculptor in 1772. He published ''A New Book of Ornaments Designed and Etched by Samuel Alken'' in 1779, and later established himself as one of the most competent engravers in the new technique of aquatint. His works included plates after George Morland, Richard Wilson, Thomas Rowlandson and Francis Wheatley. His plates for ''Sixteen views of the lakes in Cumberland and Westmorland'' after drawings John Emes and John Smith were published in 1796, and a set of aquatint views of North Wales after drawings by the Rev. Brian Broughton in 1798. Relatives The Alken family claims several well-known artists.''The Grove Dictionary of Art'' on Alken aartnet.com/ref> See also *Henry Thomas Alken Henry Thomas Alken (12 October 1785 – 7 April 1851) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatint
Aquatint is an intaglio printmaking technique, a variant of etching that produces areas of tone rather than lines. For this reason it has mostly been used in conjunction with etching, to give both lines and shaded tone. It has also been used historically to print in colour, both by printing with multiple plates in different colours, and by making monochrome prints that were then hand-coloured with watercolour. The term colour etching, frequently used in the art trade, is potentially ambiguous, but most often means one of these two options. It has been in regular use since the later 18th century, and was most widely used between about 1770 and 1830, when it was used both for artistic prints and decorative ones. After about 1830 it lost ground to lithography and other techniques. There have been periodic revivals among artists since then. An aquatint plate wears out relatively quickly, and is less easily reworked than other intaglio plates. Many of Goya's plates were reprin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Owen (epigrammatist)
John Owen (c. 15641622) was a Welsh epigrammatist, most known for his Latin epigrams, collected in his ''Epigrammata''. He is also cited by various Latinizations including Ioannes Owen, Joannes Oweni, Ovenus and Audoenus. Life, education, and career Owen was born at Plas Du, Llanarmon, Caernarfonshire (now Gwynedd), and was educated at Winchester College under Dr Thomas Bilson, and New College, Oxford, from where he graduated as Bachelor of Civil Law in 1590. He was a fellow of his college from 1584 to 1591, when he became a schoolmaster, first at Trelleck, near Monmouth, and then of The King's School at Warwick around 1595. His salary was doubled to £20 per year in 1614. On his death in 1622, Owen was buried in the old St Paul's Cathedral, London, memorialised with a Latin epitaph, thanks to his countryman and relative, Bishop John Williams of Lincoln, who is also said to have supported him in his later years. Epigrams Owen became distinguished for his perfect mastery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Justus Scaliger
Joseph Justus Scaliger (; 5 August 1540 – 21 January 1609) was a Franco-Italian Calvinist religious leader and scholar, known for expanding the notion of classical history from Greek and Ancient Roman history to include Persian, Babylonian, Jewish and Ancient Egyptian history. He spent the last sixteen years of his life in the Netherlands. Early life In 1540, Scaliger was born in Agen, France, to Italian scholar and physician Julius Caesar Scaliger and his wife, Andiette de Roques Lobejac. His only formal education was three years of study at the College of Guienne in Bordeaux, which ended in 1555 due to an outbreak of the bubonic plague. Until his death in 1558, Julius Scaliger taught his son Latin and poetry; he was made to write at least 80 lines of Latin a day. University and travels After his father's death, Scaliger spent four years at the University of Paris, where he studied Greek under Adrianus Turnebus. After two months he found he was not in a position to profit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohn's Classical Library
Henry George Bohn (4 January 179622 August 1884) was a British publisher. He is principally remembered for the ''Bohn's Libraries'' series which he inaugurated. These were begun in 1846, targeted the mass market, and comprised editions of standard works and translations, dealing with history, science, classics, theology, and archaeology. Biography Bohn was born in London. He was the son of a German bookbinder who had settled in England. In 1831, he began his career as a dealer in rare books and remainders. In 1841 he issued his ''"Guinea" Catalogue'' of books, a monumental work containing 23,208 items. Bohn was noted for his book auction sales: one held in 1848 lasted four days, the catalogue comprising twenty folio pages. Printed on this catalogue was the information: "Dinner at 2 o'clock, dessert at 4, tea at 5, and supper at 10." In 1846, he also started publishing ''The British Florist; Or, Lady's Journal of Horticulture'', which had six volumes with illustrations and plates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
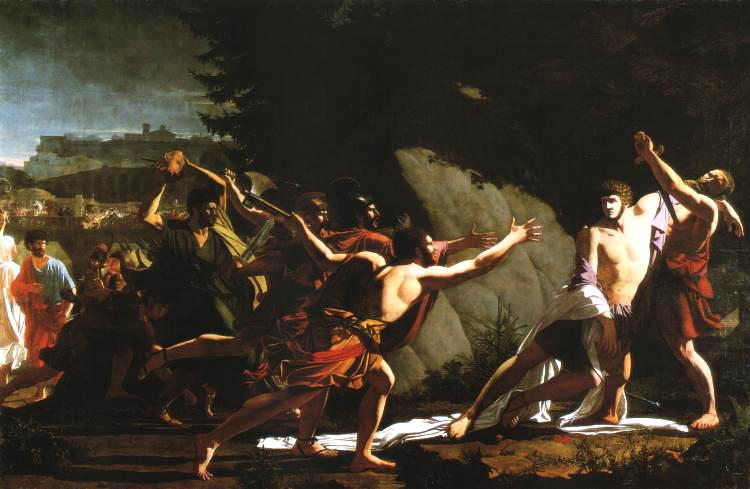
First Catilinarian Oration
The Catilinarian orations (; also simply the ''Catilinarians'') are four speeches given in 63 BC by Marcus Tullius Cicero, one of the year's consuls. The speeches are all related to the discovery, investigation, and suppression of the Catilinarian conspiracy, a plot that year to overthrow the republic. All of the speeches in the form available today were published, probably around 60, as part of Cicero's attempt to justify his actions during the consulship; whether they are accurate reflections of the original speeches in 63 is debated. The first speech was given in the senate, where Cicero accused a senator, Catiline, of leading a plot to overthrow the republic; in response, Catiline withdrew from the city and joined an uprising in Etruria. The next two speeches were given before the people, with Cicero justifying his actions as well as relating further news of the conspiracy in Rome itself and the arrest of four conspirators. The fourth speech, supposedly delivered before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigrams (Martial)
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman and Celtiberian poet born in Bilbilis, Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of ''Epigrams'', published in Ancient Rome, Rome between AD 86 and 103, during the reigns of the emperors Domitian, Nerva and Trajan. In these poems he satirises city life and the scandalous activities of his acquaintances, and romanticises his provincial upbringing. He wrote a total of 1,561 epigrams, of which 1,235 are in elegiac couplets. Martial has been called the greatest Latin epigrammatist, and is considered the creator of the modern epigram. He also coined the term plagiarism. Early life Knowledge of his origins and early life are derived almost entirely from his works, which can be more or less dated according to the well-known events to which they refer. In Book X of his ''Epigrams'', composed between 95 and 98, he mentions celebrating his fifty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seneca The Elder
Lucius Annaeus Seneca the Elder ( ; – c. AD 39), also known as Seneca the Rhetorician, was a Roman writer, born of a wealthy equestrian family of Corduba, Hispania. He wrote a collection of reminiscences about the Roman schools of rhetoric, six books of which are extant in a more or less complete state and five others in epitome only. His principal work, a history of Roman affairs from the beginning of the Civil Wars until the last years of his life, is almost entirely lost to posterity. Seneca lived through the reigns of three significant emperors; Augustus (ruled 27 BC – 14 AD), Tiberius (ruled 14–37 AD) and Caligula (ruled 37–41 AD). He was the father of Lucius Junius Gallio Annaeanus, best known as a Proconsul of Achaia; his second son was the dramatist and Stoic philosopher Seneca the Younger (''Lucius''), who was tutor of Nero, and his third son, Marcus Annaeus Mela, became the father of the poet Lucan. Biography Seneca the Elder is the first of the gens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |