O Tempora, O Mores! on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 is a
is a
The Orations of Marcus Tullius Cicero
', literally translated by C. D. Yonge, B. A. London. Henry G. Bohn, York Street, Covent Garden. 1856. senator Cruz rendered the phrase as "Shame on the age and on its lost principles!"; and in place of Catiline, then-President Obama.
 is a
is a Latin phrase
This is a list of Wikipedia articles of Latin phrases and their translation into English.
To view all phrases on a single, lengthy document, see: List of Latin phrases (full).
Lists of pages
* List of Latin phrases (A)
* List of Latin phrases ( ...
that translates literally as "Oh the times! Oh the customs!", first recorded to have been spoken by Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises tha ...
. A more natural, yet still quite literal, translation is "Oh what times! Oh what customs!"; a common idiomatic rendering in English is "Shame on this age and on its lost principles!", originated by the classicist Charles Duke Yonge. The original Latin phrase is often printed as , with the addition of exclamation mark
The exclamation mark (also known as exclamation point in American English) is a punctuation mark usually used after an interjection or exclamation to indicate strong feelings or to show wikt:emphasis, emphasis. The exclamation mark often marks ...
s, which would not have been used in the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
written in Cicero's day.
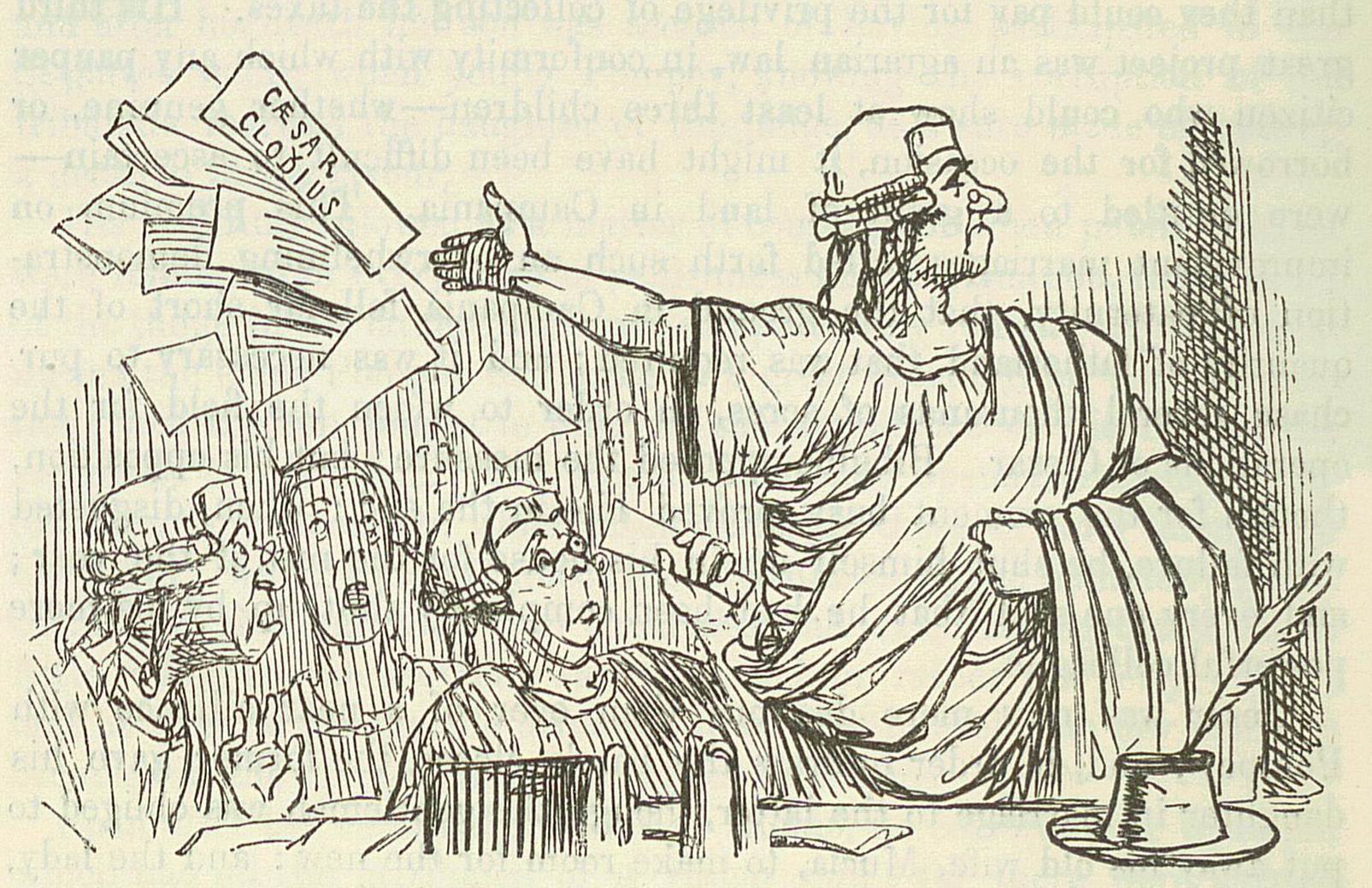
The phrase was used by the Roman orator Cicero in four different speeches, of which the earliest was his speech against Verres in 70 BC. The most famous instance, however, is in the second paragraph of his First Oration against Catiline, a speech made in 63 BC, when Cicero was consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states thro ...
(Roman head of state
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...
), denouncing his political enemy Catiline
Lucius Sergius Catilina ( – January 62 BC), known in English as Catiline (), was a Roman politician and soldier best known for instigating the Catilinarian conspiracy, a failed attempt to seize control of the Roman state in 63 BC.
...
. In this passage, Cicero uses it as an expression of his disgust, to deplore the sorry condition of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
, in which a citizen could plot against the state and not be punished in his view adequately for it. The passage in question reads as follows:
Cicero is frustrated that, despite all of the evidence that has been compiled against Catiline, who had been conspiring to overthrow the Roman government and assassinate Cicero himself, and in spite of the fact that the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
had given its ''senatus consultum ultimum
("final decree of the Senate", often abbreviated to SCU) is the modern term given to resolutions of the Roman Senate lending its moral support for magistrates to use the full extent of their powers and ignore the laws to safeguard the state.
...
'', Catiline had not yet been executed. Cicero goes on to describe various times throughout Roman history where consuls saw fit to execute conspirators with less evidence, in one instance—the case of former consul Lucius Opimius' slaughter of Gaius Gracchus
Gaius Sempronius Gracchus ( – 121 BC) was a reformist Roman politician and soldier who lived during the 2nd century BC. He is most famous for his tribunate for the years 123 and 122 BC, in which he proposed a wide set of laws, i ...
(one of the Gracchi
The Gracchi brothers were two brothers who lived during the beginning of the late Roman Republic: Tiberius Gracchus and Gaius Gracchus. They served in the Tribune of the plebs, plebeian tribunates of 133 BC and 122–121 BC, respec ...
brothers)—based only on : "mere suspicion of disaffection".
Cultural references
In later classical times Cicero's exclamation had already become famous, being quoted for example inSeneca the Elder
Lucius Annaeus Seneca the Elder ( ; – c. AD 39), also known as Seneca the Rhetorician, was a Roman writer, born of a wealthy equestrian family of Corduba, Hispania. He wrote a collection of reminiscences about the Roman schools of rhetoric, ...
's :
Martial
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman and Celtiberian poet born in Bilbilis, Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of '' Epigrams'', pu ...
's poem "To Caecilianus" ( ''Epigrams'' §9.70) also makes reference to the First Catilinarian Oration:
In modern times this exclamation is still used to criticize present-day attitudes and trends, but sometimes is used humorously or wryly.
It was used as the title of an epigram on Joseph Justus Scaliger by the Welsh epigrammatist John Owen, in his popular ''Epigrammata,'' 1613 Lib. I. epigram 16 ''O Tempora! O Mores!'':
:''Scaliger annosi correxit tempora mundi:''
:''Quis iam, qui mores corrigat, alter erit?''
Translated by Harvey, 1677, as:
:"Learn’d ''Scaliger'' The Worlds deformed Times
:Reformed: Who shall Now reform Mens Crimes?"
Even in the eighteenth century it began being used this way: an aquatint
Aquatint is an intaglio printmaking technique, a variant of etching that produces areas of tone rather than lines. For this reason it has mostly been used in conjunction with etching, to give both lines and shaded tone. It has also been used ...
print of 1787 by Samuel Alken after Thomas Rowlandson
Thomas Rowlandson (; 13 July 1757 – 21 April 1827) was an English artist and caricaturist of the Georgian Era, noted for his political satire and social observation. A prolific artist and printmaker, Rowlandson produced both individual soc ...
in the British Royal Collection entitled shows two old men surprised to find three young drunk men who had fallen asleep together at a table.
Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic who is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales involving mystery and the macabre. He is widely re ...
used the phrase as the title and subject of his poem, "O, Tempora! O, Mores!" (≈1825), in which he criticized the manners of the men of his time. It is pronounced by a drunken poet in the 1936 movie '' Mr. Deeds Goes to Town''. The expression is used in both the play
Play most commonly refers to:
* Play (activity), an activity done for enjoyment
* Play (theatre), a work of drama
Play may refer also to:
Computers and technology
* Google Play, a digital content service
* Play Framework, a Java framework
* P ...
(1955) and movie
A film, also known as a movie or motion picture, is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, emotions, or atmosphere through the use of moving images that are generally, sinc ...
(1960) ''Inherit the Wind'', a fictional account of the Scopes Trial, in which it is uttered by the cynical reporter, Hornbeck, referring to the town's attitude towards Darwin's theory of evolution.
The musical comedians Flanders and Swann used the term when Flanders proclaimed " – Oh Times, Oh Daily Mirror
The ''Daily Mirror'' is a British national daily Tabloid journalism, tabloid newspaper. Founded in 1903, it is part of Mirror Group Newspapers (MGN), which is owned by parent company Reach plc. From 1985 to 1987, and from 1997 to 2002, the tit ...
!" (1964).Flanders, M and Swann, D ''At the Drop of Another Hat'' (after the track ''All Gall'') 1964. It is also one of several Latin phrases found in Asterix and Obelix comics published in the 1960s and 1970s. The phrase is also used in the Doctor Who serial, ''The Romans'' (1964).
In November 2014, senator Ted Cruz
Rafael Edward Cruz (; born December 22, 1970) is an American politician and attorney serving as the junior United States senator from Texas since 2013. A member of the Republican Party, Cruz was the solicitor general of Texas from 2003 ...
of Texas used the opening of Cicero's First Catilinarian Oration on the U.S. Senate floor, with only a few words changed, to criticize President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
's use of executive order
In the United States, an executive order is a directive by the president of the United States that manages operations of the federal government. The legal or constitutional basis for executive orders has multiple sources. Article Two of the ...
s. In his version of the speech, which followed the translation of Charles Duke Yonge,M. Tullius Cicero. The Orations of Marcus Tullius Cicero
', literally translated by C. D. Yonge, B. A. London. Henry G. Bohn, York Street, Covent Garden. 1856. senator Cruz rendered the phrase as "Shame on the age and on its lost principles!"; and in place of Catiline, then-President Obama.
See also
* Catiline Orations * Ecphonesis *Mores
Mores (, sometimes ; , plural form of singular , meaning "manner, custom, usage, or habit") are social norms that are widely observed within a particular society or culture. Mores determine what is considered morally acceptable or unacceptable ...
*'' Tempora mutantur''
References
{{Reflist Catiline Cicero Latin words and phrases