|
Nomarski Interference Contrast
Differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy, also known as Nomarski interference contrast (NIC) or Nomarski microscopy, is an optical microscopy technique used to enhance the contrast in unstained, transparent samples. DIC works on the principle of interferometry to gain information about the optical path length of the sample, to see otherwise invisible features. A relatively complex optical system produces an image with the object appearing black to white on a grey background. This image is similar to that obtained by phase contrast microscopy but without the bright diffraction halo. The technique was invented by Francis Hughes Smith. The "Smith DIK" was produced by Ernst Leitz Wetzlar in Germany and was difficult to manufacture. DIC was then developed further by Polish physicist Georges Nomarski in 1952. DIC works by separating a polarized light source into two orthogonally polarized mutually coherent parts which are spatially displaced (sheared) at the sample plane, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
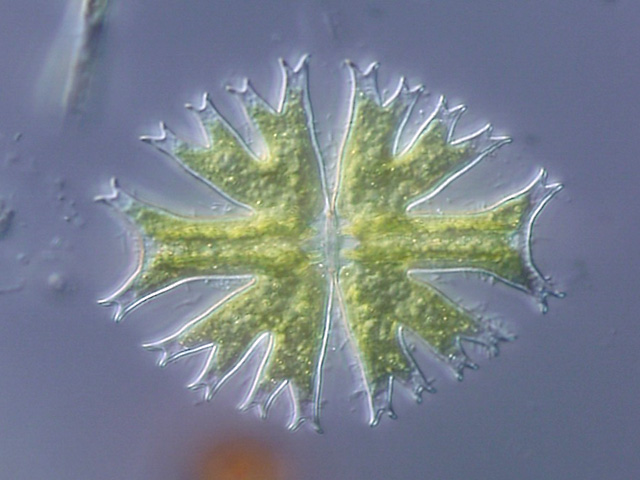
Micrasterias Radiata
''Micrasterias furcata'' is a species of unicellular Desmidiaceae, desmid which inhabits freshwater areas. ''M. furcata'' is round, flattened and lobed in body plan. Description ''M. furcata'' generally has a sphere-like body shape, with five lobes on each side, all 10 of the lobes divide into two other much smaller lobes which makes one side of ''M. furcata'' have 15 lobes (while also including those which divide into smaller lobes). References Desmidiaceae Charophyta species {{green algae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherence (physics)
Coherence expresses the potential for two waves to Wave interference, interfere. Two Monochromatic radiation, monochromatic beams from a single source always interfere. Wave sources are not strictly monochromatic: they may be ''partly coherent''. When interfering, two waves add together to create a wave of greater amplitude than either one (constructive Wave interference, interference) or subtract from each other to create a wave of minima which may be zero (destructive interference), depending on their relative phase (waves), phase. Constructive or destructive interference are limit cases, and two waves always interfere, even if the result of the addition is complicated or not remarkable. Two waves with constant relative phase will be coherent. The amount of coherence can readily be measured by the interference visibility, which looks at the size of the interference fringes relative to the input waves (as the phase offset is varied); a precise mathematical definition of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Contrast
Phase-contrast imaging is a method of imaging that has a range of different applications. It measures differences in the refractive index of different materials to differentiate between structures under analysis. In conventional light microscopy, phase contrast can be employed to distinguish between structures of similar transparency, and to examine crystals on the basis of their double refraction. This has uses in biological, medical and geological science. In X-ray tomography, the same physical principles can be used to increase image contrast by highlighting small details of differing refractive index within structures that are otherwise uniform. In transmission electron microscopy (TEM), phase contrast enables very high resolution (HR) imaging, making it possible to distinguish features a few Angstrom apart (at this point highest resolution is 40 pm). Atomic physics Phase-contrast imaging is commonly used in atomic physics to describe a range of techniques for dispersively i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
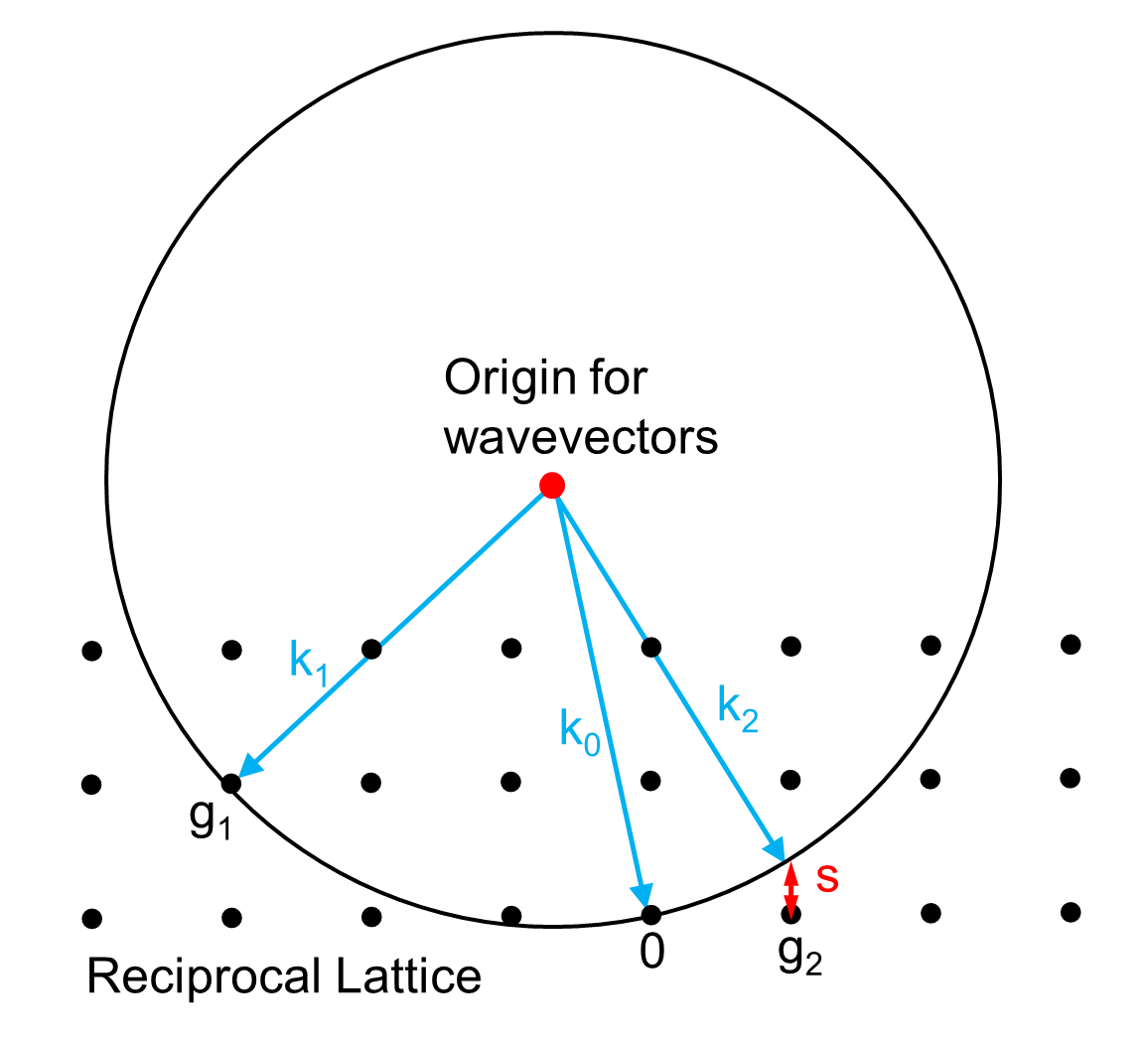
Ewald's Sphere
The Ewald sphere is a geometric construction used in electron, neutron, and x-ray diffraction which shows the relationship between: * the wavevector of the incident and diffracted beams, * the diffraction angle for a given reflection, * the reciprocal lattice of the crystal. It was conceived by Paul Peter Ewald, a German physicist and crystallographer. Ewald himself spoke of the sphere of reflection. It is often simplified to the two-dimensional "Ewald's circle" model or may be referred to as the Ewald sphere. Ewald construction A crystal can be described as a lattice of atoms, which in turn leads to the reciprocal lattice. With electrons, neutrons or x-rays there is diffraction by the atoms, and if there is an incident plane wave \exp(2 \pi i \mathbf\cdot \mathbf) with a wavevector \mathbf, there will be outgoing wavevectors \mathbf and \mathbf as shown in the diagram after the wave has been diffracted by the atoms. The energy of the waves (electron, neutron or x-ray) d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIC Limitation Example
DIC may refer to: Biology and chemistry * Diisopropylcarbodiimide, a reagent in organic chemistry * Disseminated intravascular coagulation, a pathological activation of coagulation (blood clotting) mechanisms * Dissolved inorganic carbon, the sum of inorganic carbon species in a solution * ''Dic'' (crustacean), a genus of crustacean in the family Diastylidae Companies * D.I.C. (department store), a New Zealand department store chain * DIC Corporation, a Japanese chemical company * DIC Entertainment, a former film and television production company * Dic Press, an imprint of VDM Publishing devoted to the reproduction of Wikipedia content * Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan * Dubai International Capital, a private equity company Technology * Differential interference contrast microscopy, an illumination technique in optical microscopy * Digital image correlation, an optical method that employs tracking and image registration techniques * Digital integrating computer, a dig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Gradient
An image gradient is a directional change in the intensity or color in an image. The gradient of the image is one of the fundamental building blocks in image processing. For example, the Canny edge detector uses image gradient for edge detection. In graphics software for digital image editing, the term gradient or color gradient is also used for a gradual blend of color which can be considered as an even wiktionary:gradation, gradation from low to high values, and seen from black to white in the images to the right. Another name for this is ''color progression''. Mathematically, the gradient of a two-variable function (here the image intensity function) at each image point is a 2D vector (geometric), vector with the components given by the derivatives in the horizontal and vertical directions. At each image point, the gradient vector points in the direction of largest possible intensity increase, and the length of the gradient vector corresponds to the rate of change in that direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interference (wave Propagation)
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two coherent waves are combined by adding their intensities or displacements with due consideration for their phase difference. The resultant wave may have greater amplitude (constructive interference) or lower amplitude (destructive interference) if the two waves are in phase or out of phase, respectively. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves, gravity waves, or matter waves as well as in loudspeakers as electrical waves. Etymology The word ''interference'' is derived from the Latin words ''inter'' which means "between" and ''fere'' which means "hit or strike", and was used in the context of wave superposition by Thomas Young in 1801. Mechanisms The principle of superposition of waves states that when two or more propagating waves of the same type are incident on the same point, the resultant amplitude at that point is equal to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objective Lens
In optical engineering, an objective is an optical element that gathers light from an object being observed and focuses the light rays from it to produce a real image of the object. Objectives can be a single lens or mirror, or combinations of several optical elements. They are used in microscopes, binoculars, telescopes, cameras, slide projectors, CD players and many other optical instruments. Objectives are also called object lenses, object glasses, or objective glasses. Microscope objectives The objective lens of a microscope is the one at the bottom near the sample. At its simplest, it is a very high-powered magnifying glass, with very short focal length. This is brought very close to the specimen being examined so that the light from the specimen comes to a focus inside the microscope tube. The objective itself is usually a cylinder containing one or more lenses that are typically made of glass; its function is to collect light from the sample. Magnification One of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bright Field Microscopy
Bright-field microscopy (BF) is the simplest of all the optical microscopy illumination techniques. Sample illumination is transmitted (i.e., illuminated from below and observed from above) white light, and contrast in the sample is caused by attenuation of the transmitted light in dense areas of the sample. Bright-field microscopy is the simplest of a range of techniques used for illumination of samples in light microscopes, and its simplicity makes it a popular technique. The typical appearance of a bright-field microscopy image is a dark sample on a bright background, hence the name. History of microscopy Compound microscopes first appeared in Europe around 1620. The actual inventor of the compound microscope is unknown although many claims have been made over the years. These include a dubious claim that Dutch spectacle-maker Zacharias Janssen invented the compound microscope and the telescope as early as 1590. Another claim is that Janssen's competitor Hans Lippershey, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |