|
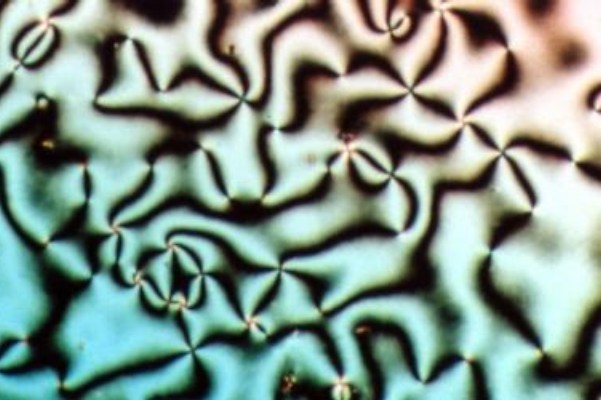
Mesophase
In chemistry and chemical physics, a mesophase is a state of matter intermediate between liquid and solid. Gelatin is a common example of a partially ordered structure in a mesophase. Further, biological structures such as the lipid bilayers of cell membranes are examples of mesophases. Georges Friedel (1922) called attention to the "mesomorphic states of matter" in his scientific assessment of observations of the so-called liquid crystals. Conventionally a crystal is solid, and crystallization converts liquid to solid. The oxymoron of the liquid crystal is resolved through the notion of mesophases. The observations noted an optic axis persisting in materials that had been melted and had begun to flow. The term ''liquid crystal'' persists as a colloquialism, but use of the term was criticized in 1993: In ''The Physics of Liquid Crystals''P.G. de Gennes & J. Prost (1993) ''The Physics of Liquid Crystals'', 2nd edition, Oxford University Press the mesophases are introduced from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: * thermotropic, * lyotropic, and * metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: * thermotropic, * lyotropic, and * metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Friedel
Georges Friedel (19 July 1865 – 11 December 1933) was a French mineralogist and crystallographer. Life Georges was the son of the chemist Charles Friedel. Georges' grandfather was Louis Georges Duvernoy who held the chair in comparative anatomy from 1850 to 1855 at the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle. Georges studied at the École Polytechnique in Paris and the École Nationale des Mines in St. Etienne, and was a student of François Ernest Mallard. In 1893 he obtained a professorship at the École Nationale des Mines, the director of which he would later become. After the First World War, he returned as a professor at the University of Strasbourg in Alsace. Due to ill health, he took early retirement in 1930, and died in 1933. He was married with five children. Scientific works Like his teacher Mallard, Friedel concerned himself with the theories of Auguste Bravais, the founder of crystallography. Friedel was able to demonstrate the theoretical ideas of Bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesogen
A mesogen is a compound that displays liquid crystal properties. Mesogens can be described as disordered solids or ordered liquids because they arise from a unique state of matter that exhibits both solid- and liquid-like properties called the liquid crystalline state. This liquid crystalline state (LC) is called the mesophase and occurs between the crystalline solid (Cr) state and the isotropic liquid (Iso) state at distinct temperature ranges. The liquid crystal properties arise because mesogenic compounds are composed of rigid and flexible parts, which help characterize the order and mobility of its structure. The rigid components align mesogen moieties in one direction and have distinctive shapes that are typically found in the form of rod or disk shapes. The flexible segments provide mesogens with mobility because they are usually made up of alkyl chains, which hinder crystallization to a certain degree. The combination of rigid and flexible chains induce structural alignm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melting
Melting, or fusion, is a physical process that results in the phase transition of a substance from a solid to a liquid. This occurs when the internal energy of the solid increases, typically by the application of heat or pressure, which increases the substance's temperature to the melting point. At the melting point, the ordering of ions or molecules in the solid breaks down to a less ordered state, and the solid "melts" to become a liquid. Substances in the molten state generally have reduced viscosity as the temperature increases. An exception to this principle is the element sulfur, whose viscosity increases in the range of 160 °C to 180 °C due to polymerization. Some organic compounds melt through mesophases, states of partial order between solid and liquid. First order phase transition From a thermodynamics point of view, at the melting point the change in Gibbs free energy ''∆G'' of the substances is zero, but there are non-zero changes in the entha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optic Axis Of A Crystal
An optic axis of a crystal is a direction in which a ray of transmitted light suffers no birefringence (double refraction). An optic axis is a direction rather than a single line: all rays that are parallel to that direction exhibit the same lack of birefringence. Crystals may have a single optic axis, in which case they are ''uniaxial'', or two different optic axes, in which case they are ''biaxial''. Non-crystalline materials generally have no birefringence and thus, no optic axis. A uniaxial crystal (e.g. calcite, quartz) is isotropic within the plane orthogonal to the optic axis of the crystal. Explanation The internal structure of crystals (the specific structure of the crystal lattice, and the specific atoms or molecules of which it is composed) causes the speed of light in the material, and therefore the material's refractive index, to depend on both the light's direction of propagation and its polarization. The dependence on polarization causes birefringence, in which two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columnar Phase
The columnar phase is a class of mesophases in which molecules assemble into cylindrical structures to act as mesogens. Originally, these kinds of liquid crystals were called discotic liquid crystals or bowlic liquid crystals because the columnar structures are composed of flat-shaped discotic or bowl-shaped molecules stacked one-dimensionally. Since recent findings provide a number of columnar liquid crystals consisting of non-discoid mesogens, it is more common now to classify this state of matter and compounds with these properties as columnar liquid crystals. Takuzo Aida and co-workers recently reported cyclic peptides that self-assemble into polar columnar organizations. These materials can be unidirectionally aligned over large areas by application of an external electric field. Classes Columnar liquid crystals are grouped by their structural order and the ways of packing of the columns. Nematic columnar liquid crystals have no long-range order and are less organized than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Matter
In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many intermediate states are known to exist, such as liquid crystal, and some states only exist under extreme conditions, such as Bose–Einstein condensates (in extreme cold), neutron-degenerate matter (in extreme density), and quark–gluon plasma (at extremely high energy). For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter. Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume (assuming no change in temperature or air pressure) and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume (assuming no change in temperature or air pressure), but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPS Panel
IPS (in-plane switching) is a screen technology for liquid-crystal displays (LCDs). In IPS, a layer of liquid crystals is sandwiched between two glass surfaces. The liquid crystal molecules are aligned parallel to those surfaces in predetermined directions (''in-plane''). The molecules are reoriented by an applied electric field, whilst remaining essentially parallel to the surfaces to produce an image. It was designed to solve the strong viewing angle dependence and low-quality color reproduction of the twisted nematic field effect (TN) matrix LCDs prevalent in the late 1980s. History The TN method was the only viable technology for active matrix TFT LCDs in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Early panels showed grayscale inversion from up to down, and had a high response time (for this kind of transition, 1 ms is visually better than 5 ms). In the mid-1990s new technologies were developed—typically IPS and Vertical Alignment (VA)—that could resolve these weaknes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Crystal Display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but instead use a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome. LCDs are available to display arbitrary images (as in a general-purpose computer display) or fixed images with low information content, which can be displayed or hidden. For instance: preset words, digits, and seven-segment displays, as in a digital clock, are all good examples of devices with these displays. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made from a matrix of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs can either be normally on (positive) or off (negative), depending on the polarizer arrangement. For example, a character positive LCD with a backlight will have black lettering on a background that is the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Materials Properties
A materials property is an intensive property of a material, i.e., a physical property that does not depend on the amount of the material. These quantitative properties may be used as a metric by which the benefits of one material versus another can be compared, thereby aiding in materials selection. A property may be a constant or may be a function of one or more independent variables, such as temperature. Materials properties often vary to some degree according to the direction in the material in which they are measured, a condition referred to as anisotropy. Materials properties that relate to different physical phenomena often behave linearly (or approximately so) in a given operating range. Modeling them as linear functions can significantly simplify the differential constitutive equations that are used to describe the property. Equations describing relevant materials properties are often used to predict the attributes of a system. The properties are measured by standar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twisted Nematic Field Effect
The twisted nematic effect (''TN-effect'') was a main technology breakthrough that made LCDs practical. Unlike earlier displays, TN-cells did not require a current to flow for operation and used low operating voltages suitable for use with batteries. The introduction of TN-effect displays led to their rapid expansion in the display field, quickly pushing out other common technologies like monolithic LEDs and CRTs for most electronics. By the 1990s, TN-effect LCDs were largely universal in portable electronics, although since then, many applications of LCDs adopted alternatives to the TN-effect such as in-plane switching (IPS) or vertical alignment (VA). Many monochrome alphanumerical displays without picture information still use TN LCDs. TN displays benefit from fast pixel response times and less smearing than other LCD display technology, but suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, especially in the vertical direction. Colors will shift, potentially t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |