|
Mesogen
A mesogen is a compound that displays liquid crystal properties. Mesogens can be described as disordered solids or ordered liquids because they arise from a unique state of matter that exhibits both solid- and liquid-like properties called the liquid crystalline state. This liquid crystalline state (LC) is called the mesophase and occurs between the crystalline solid (Cr) state and the isotropic liquid (Iso) state at distinct temperature ranges. The liquid crystal properties arise because mesogenic compounds are composed of rigid and flexible parts, which help characterize the order and mobility of its structure. The rigid components align mesogen moieties in one direction and have distinctive shapes that are typically found in the form of rod or disk shapes. The flexible segments provide mesogens with mobility because they are usually made up of alkyl chains, which hinder crystallization to a certain degree. The combination of rigid and flexible chains induce structural alignmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: * thermotropic, *lyotropic, and * metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
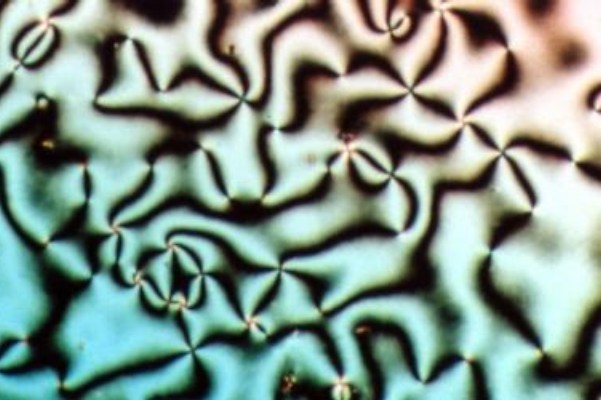
Nematic
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC Phase (matter), phases, which can be distinguished by their Optics, optical properties (such as Texture (crystalline), textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: *thermotropic, *lyotropic, and *#Metallotropic liquid crystals, metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as tempera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smectic
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: *thermotropic, * lyotropic, and * metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figure A
Figure may refer to: General *A shape, drawing, depiction, or geometric configuration *Figure (wood), wood appearance *Figure (music), distinguished from musical motif *Noise figure, in telecommunication *Dance figure, an elementary dance pattern *A person's figure, human physical appearance Arts *Figurine, a miniature statuette representation of a creature *Action figure, a posable jointed solid plastic character figurine *Figure painting, realistic representation, especially of the human form *Figure drawing *Model figure, a scale model of a creature Writing *figure, in writing, a type of floating block (text, table, or graphic separate from the main text) * Figure of speech, also called a rhetorical figure *Christ figure, a type of character * in typesetting, text figures and lining figures Accounting *Figure, a synonym for number *Significant figures in a decimal number Science * Figure of the Earth, the size and shape of the Earth in geodesy Sports *Figure (horse), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesophase
In chemistry and chemical physics, a mesophase is a state of matter intermediate between liquid and solid. Gelatin is a common example of a partially ordered structure in a mesophase. Further, biological structures such as the lipid bilayers of cell membranes are examples of mesophases. Georges Friedel (1922) called attention to the "mesomorphic states of matter" in his scientific assessment of observations of the so-called liquid crystals. Conventionally a crystal is solid, and crystallization converts liquid to solid. The oxymoron of the liquid crystal is resolved through the notion of mesophases. The observations noted an optic axis persisting in materials that had been melted and had begun to flow. The term ''liquid crystal'' persists as a colloquialism, but use of the term was criticized in 1993: In ''The Physics of Liquid Crystals''P.G. de Gennes & J. Prost (1993) ''The Physics of Liquid Crystals'', 2nd edition, Oxford University Press the mesophases are introduced from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moiety (chemistry)
In organic chemistry, a moiety ( ) is a part of a molecule that is given a name because it is identified as a part of other molecules as well. Typically, the term is used to describe the larger and characteristic parts of organic molecules, and it should not be used to describe or name smaller functional groups of atoms that chemically react in similar ways in most molecules that contain them. Occasionally, a moiety may contain smaller moieties and functional groups. A moiety that acts as a branch extending from the backbone of a hydrocarbon molecule is called a substituent or side chain, which typically can be removed from the molecule and substituted with others. Active moiety In pharmacology, an active moiety is the part of a molecule or ion – excluding appended inactive portions – that is responsible for the physiological or pharmacological action of a drug substance. Inactive appended portions of the drug substance may include either the alcohol or acid moiety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylene
Triphenylene is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)3. A flat polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH), it consists of four fused benzene rings. Triphenylene has delocalized 18-''π''-electron systems based on a planar structure, corresponding to the symmetry group ''D''3h. It is a white or colorless solid. Preparation Triphenylene can be isolated from coal tar. It is also be synthesized in various ways. One method is trimerization of benzyne. Another method involves trapping benzyne with a biphenyl derivative. Properties Triphenylene is more resonance stable than its isomers chrysene, benz 'a''nthracene, benzo 'c''henanthrene, and tetracene. For this reason triphenylene resists hydrogenation. As a disc-shaped, planar molecule, triphenylene has attracted attention as the core of discotic mesogen in liquid crystal Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamella (materials)
A ''lamella'' (plural ''lamellae'') is a small plate or flake, from the Latin, and may also be used to refer to collections of fine sheets of material held adjacent to one another, in a gill-shaped structure, often with fluid in between though sometimes simply a set of 'welded' plates. The term is used in biological contexts to describe thin membranes of plates of tissue. In context of materials science, the microscopic structures in bone and nacre are called lamellae. Moreover, the term lamella is often used as a way to describe crystal structure of some materials. Uses of the term In surface chemistry (especially mineralogy and materials science), lamellar structures are fine layers, alternating between different materials. They can be produced by chemical effects (as in eutectic solidification), biological means, or a deliberate process of lamination, such as pattern welding. Lamellae can also describe the layers of atoms in the crystal lattices of materials such as me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzyl Cyanide
Benzyl cyanide (abbreviated BnCN) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2CN. This colorless oily aromatic liquid is an important precursor to numerous compounds in organic chemistry. Preparation Benzyl cyanide can be produced via Kolbe nitrile synthesis between benzyl chloride and sodium cyanide and by oxidative decarboxylation of phenylalanine. Benzyl cyanides can also be prepared by arylation of silyl-substituted acetonitrile. Reactions Benzyl cyanide undergoes many reactions characteristic of nitriles. It can be hydrolyzed to give phenylacetic acid or it can be used in the Pinner reaction to yield phenylacetic acid esters. Hydrogenation gives β-phenethylamine. The compound contains an "active methylene unit". Bromination occurs gives PhCHBrCN. A variety of base-induced reactions result in the formation of new carbon-carbon bonds. Uses Benzyl cyanide is used as a solvent and as a starting material in the synthesis of fungicides (.e.g. Fenapanil), fragr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apex (geometry)
In geometry, an apex (plural apices) is the vertex which is in some sense the "highest" of the figure to which it belongs. The term is typically used to refer to the vertex opposite from some " base". The word is derived from the Latin for 'summit, peak, tip, top, extreme end'. Isosceles triangles In an isosceles triangle In geometry, an isosceles triangle () is a triangle that has two sides of equal length. Sometimes it is specified as having ''exactly'' two sides of equal length, and sometimes as having ''at least'' two sides of equal length, the latter versio ..., the apex is the vertex where the two sides of equal length meet, opposite the unequal third side. Pyramids and cones In a Pyramid (geometry), pyramid or Cone (geometry), cone, the apex is the vertex at the "top" (opposite the base). In a pyramid, the vertex is the point that is part of all the lateral faces, or where all the lateral edges meet. References {{elementary-geometry-stub Parts of a triangle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferroelectricity
Ferroelectricity is a characteristic of certain materials that have a spontaneous electric polarization that can be reversed by the application of an external electric field. All ferroelectrics are also piezoelectric and pyroelectric, with the additional property that their natural electrical polarization is reversible. The term is used in analogy to ferromagnetism, in which a material exhibits a permanent magnetic moment. Ferromagnetism was already known when ferroelectricity was discovered in 1920 in Rochelle salt by Joseph Valasek.See and Thus, the prefix ''ferro'', meaning iron, was used to describe the property despite the fact that most ferroelectric materials do not contain iron. Materials that are both ferroelectric ''and'' ferromagnetic are known as multiferroics. Polarization When most materials are electrically polarized, the polarization induced, ''P'', is almost exactly proportional to the applied external electric field ''E''; so the polarization is a linear fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |