|
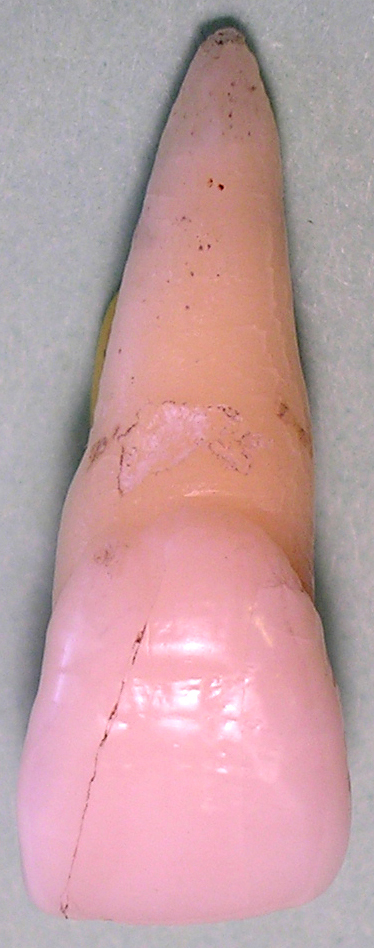
Maxillary Central Incisor
The maxillary central incisor is a human tooth in the front upper jaw, or maxilla, and is usually the most visible of all teeth in the mouth. It is located mesial (closer to the midline of the face) to the maxillary lateral incisor. As with all incisors, their function is for shearing or cutting food during mastication (chewing). There is typically a single cusp on each tooth, called an incisal ridge or incisal edge. Formation of these teeth begins at 14 weeks in utero for the deciduous (baby) set and 3–4 months of age for the permanent set. There are some minor differences between the deciduous maxillary central incisor and that of the permanent maxillary central incisor. The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 8–12 months of age and shed at 6–7 years, and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7–8 years of age. The permanent tooth is larger and is longer than it is wide. The maxillary central incisors contact each other at the midline of the face. The ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FDI World Dental Federation Notation
FDI World Dental Federation notation (also "FDI notation" or "ISO 3950 notation") is the world's most commonly used dental notation (tooth numbering system). It is designated by the International Organization for Standardization as standard ISO 3950 "Dentistry — Designation system for teeth and areas of the oral cavity". The system is developed by the FDI World Dental Federation. It is also used by the World Health Organization, and is used in most countries of the world except the United States (which uses the UNS). Orientation of the chart is traditionally "dentist's view", i.e. patient's right corresponds to notation chart left. The designations "left" and "right" on the chart below correspond to the patient's left and right. Table of codes Codes, names, and usual number of roots: (see chart of teeth at Universal Numbering System) *11 21 51 61 maxillary central incisor 1 *41 31 81 71 mandibular central incisor 1 *12 22 52 62 maxillary lateral incisor 1 *42 32 82 72 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attrition (dental)
Dental attrition is a type of tooth wear caused by tooth-to-tooth contact, resulting in loss of tooth tissue, usually starting at the incisal or occlusal surfaces. Tooth wear is a physiological process and is commonly seen as a normal part of aging. Advanced and excessive wear and tooth surface loss can be defined as pathological in nature, requiring intervention by a dental practitioner. The pathological wear of the tooth surface can be caused by bruxism, which is clenching and grinding of the teeth. If the attrition is severe, the enamel can be completely worn away leaving underlying dentin exposed, resulting in an increased risk of dental caries and dentin hypersensitivity. It is best to identify pathological attrition at an early stage to prevent unnecessary loss of tooth structure as enamel does not regenerate. Signs and symptoms Attrition occurs as a result of opposing tooth surfaces contacting. The contact can affect cuspal, incisal and proximal surface areas. Indication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammelon
A mamelon (from French ''mamelon'', "nipple") is one of three rounded protuberances which are present on the cutting edge of an incisor tooth when it first erupts through the gum. Mamelons' appearance can be smoothed by a dentist if they have not been worn down naturally by biting and eating foods. Mamelons are present on permanent central and lateral incisors. Mamelons are easiest to observe on the maxillary central incisor The maxillary central incisor is a human tooth in the front upper jaw, or maxilla, and is usually the most visible of all teeth in the mouth. It is located mesial (closer to the midline of the face) to the maxillary lateral incisor. As with all i ...s, and appear as three small prominences on the incisal edge of the tooth. Mamelons are ordinarily of no clinical importance. Usually they are worn off early in the life of the tooth. References Parts of tooth {{dentistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cementoenamel Junction
The cementoenamel junction, frequently abbreviated as the CEJ, is a slightly visible anatomical border identified on a tooth. It is the location where the enamel, which covers the anatomical crown of a tooth, and the cementum, which covers the anatomical root of a tooth, meet. Informally it is known as the neck of the tooth. The border created by these two dental tissues has much significance as it is usually the location where the gingiva attaches to a healthy tooth by fibers called the gingival fibers The gingival fibers are the connective tissue fibers that inhabit the gingival tissue adjacent to teeth and help hold the tissue firmly against the teeth. They are primarily composed of type I collagen, although type III fibers are also involved .... Active recession of the gingiva reveals the cementoenamel junction in the mouth and is usually a sign of an unhealthy condition. There exists a normal variation in the relationship of the cementum and the enamel at the cemento ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Eruption
Tooth eruption is a process in tooth development in which the teeth enter the mouth and become visible. It is currently believed that the periodontal ligament plays an important role in tooth eruption. The first human teeth to appear, the deciduous (primary) teeth (also known as baby or milk teeth), erupt into the mouth from around 6 months until 2 years of age, in a process known as "teething". These teeth are the only ones in the mouth until a person is about 6 years old creating the primary dentition stage. At that time, the first permanent tooth erupts and begins a time in which there is a combination of primary and permanent teeth, known as the mixed dentition stage, which lasts until the last primary tooth is lost. Then, the remaining permanent teeth erupt into the mouth during the permanent dentition stage. Theories Although researchers agree that tooth eruption is a complex process, there is little agreement on the identity of the mechanism that controls eruption. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown (tooth)
In dentistry, crown refers to the anatomical area of teeth, usually covered by enamel. The crown is usually visible in the mouth after developing below the gingiva The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. Structure The gums are part of the soft tissue l ... and then erupting into place. If part of the tooth gets chipped or broken, a dentist can apply an artificial crown. Crowns are used most commonly to entirely cover a damaged tooth or cover an implant. Bridges are also used to cover a space if one or more teeth is missing. They are cemented to natural teeth or implants surrounding the space where the tooth once stood. There are various materials that can be used including a type of cement or stainless steel. The cement crowns look like regular teeth while the stainless steel crowns are silver or gold. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
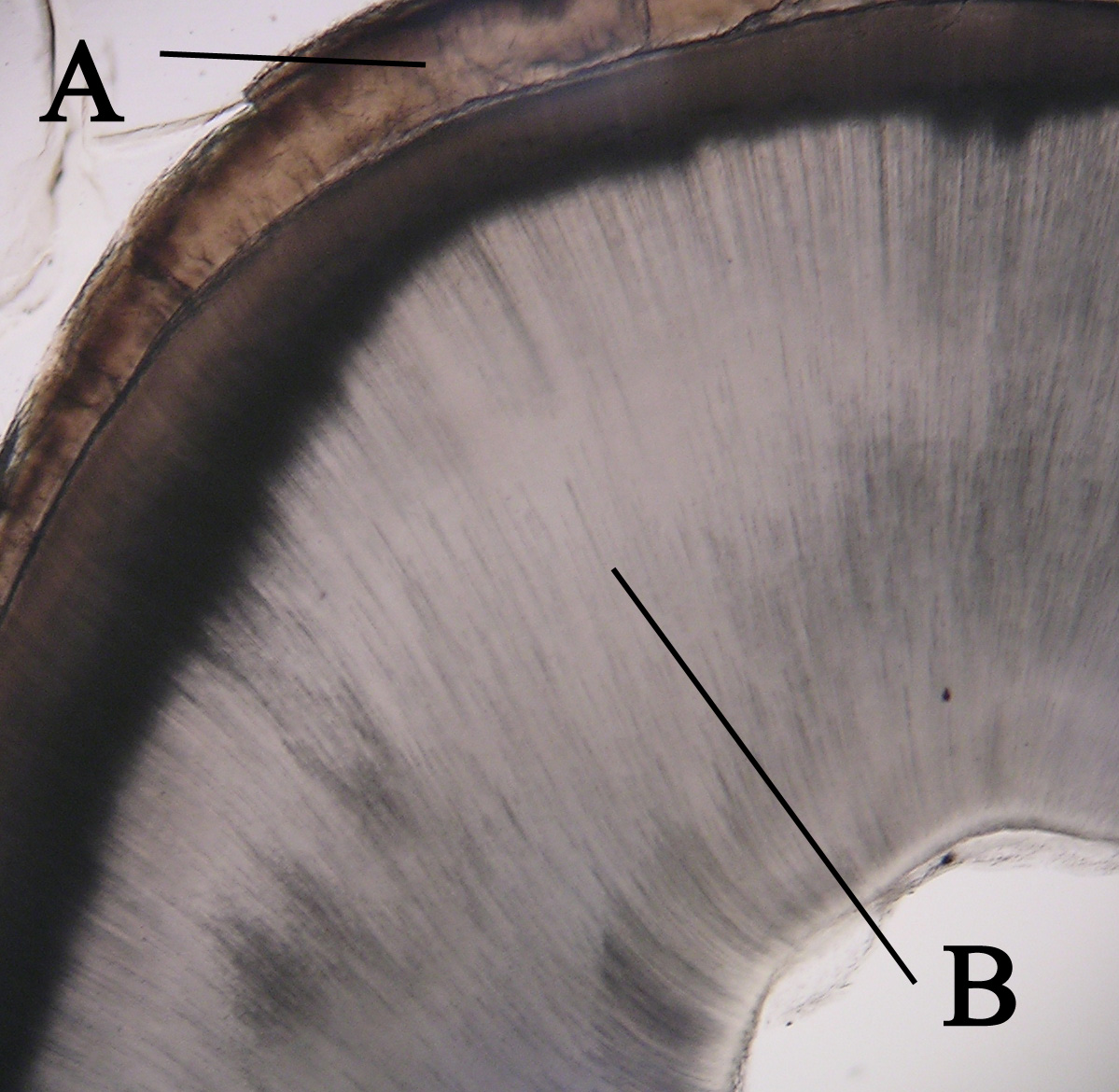
Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many other animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. Calcium hardens the tooth enamel. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface. Features Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and contains the highest percentage of minerals (at 96%),Ross ''et al.'', p. 485 with water and organic material composing the rest.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nancy, Elsevier, pp. 70–94 The primary mineral is hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. Enamel is formed on the tooth while the tooth develops withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Crest
Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to vertebrates that arise from the embryonic ectoderm germ layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, peripheral and enteric neurons and glia. After gastrulation, neural crest cells are specified at the border of the neural plate and the non-neural ectoderm. During neurulation, the borders of the neural plate, also known as the neural folds, converge at the dorsal midline to form the neural tube. Subsequently, neural crest cells from the roof plate of the neural tube undergo an epithelial to mesenchymal transition, delaminating from the neuroepithelium and migrating through the periphery where they differentiate into varied cell types. The emergence of neural crest was important in vertebrate evolution because many of its structural derivatives are defining features of the vertebrate clade. Underlying the development of neural crest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectomesenchyme
Ectomesenchyme has properties similar to mesenchyme. The origin of the ectomesenchyme is disputed. It is either like the mesenchyme, arising from mesodermic cells, or conversely arising from neural crest cells. The neural crest is a critical group of cells that form in the cranial region during early vertebrate development. Ectomesenchyme plays a critical role in the formation of the hard and soft tissues of the head and neck such as bones, muscles, teeth and, notably, the pharyngeal arches The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arche .... References Developmental biology {{developmental-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)