|
Attrition (dental)
Dental attrition is a type of tooth wear caused by tooth-to-tooth contact, resulting in loss of tooth tissue, usually starting at the incisal or occlusal surfaces. Tooth wear is a physiological process and is commonly seen as a normal part of aging. Advanced and excessive wear and tooth surface loss can be defined as pathological in nature, requiring intervention by a dental practitioner. The pathological wear of the tooth surface can be caused by bruxism, which is clenching and grinding of the teeth. If the attrition is severe, the enamel can be completely worn away leaving underlying dentin exposed, resulting in an increased risk of dental caries and dentin hypersensitivity. It is best to identify pathological attrition at an early stage to prevent unnecessary loss of tooth structure as enamel does not regenerate. Signs and symptoms Attrition occurs as a result of opposing tooth surfaces contacting. The contact can affect cuspal, incisal and proximal surface areas. Indication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss Of Tooth Characteristics
Loss may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music * ''Loss'' (Bass Communion album) (2006) * ''Loss'' (Mull Historical Society album) (2001) *"Loss", a song by God Is an Astronaut from their self-titled album (2008) * Losses "(Lil Tjay song)" (2020) *"Losses", a song by Drake from '' Dark Lane Demo Tapes'' (2020) *"Losses", a song by Polo G from ''Hall of Fame'' (2021) Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Loss'' (comic), a webcomic strip and internet meme * ''Loss'' (film), a 2008 film by Maris Martinsons *Lord Loss (character), a character from Darren Shan's ''The Demonata'' *"The Loss", a 1990 episode of ''Star Trek: The Next Generation'' Grief *Grief, an emotional response to loss **Animal loss, grief over the loss of an animal Mathematics, science, and technology *Angular misalignment loss, power loss caused by the deviation from optimum angular alignment * Bridging loss, the loss that results when an impedance is connected across a transmission line *Coup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Wear
Tooth wear refers to loss of tooth substance by means other than dental caries. Tooth wear is a very common condition that occurs in approximately 97% of the population. This is a normal physiological process occurring throughout life; but with increasing lifespan of individuals and increasing retention of teeth for life, the incidence of non-carious tooth surface loss has also shown a rise. Tooth wear varies substantially between people and groups, with extreme attrition and enamel fractures common in archaeological samples, and erosion more common today. Tooth wear is predominantly the result of a combination of three processes; attrition, abrasion and erosion. These forms of tooth wear can further lead to a condition known as abfraction, where by tooth tissue is 'fractured' due to stress lesions caused by extrinsic forces on the enamel. Tooth wear is a complex, multi-factorial problem and there is often difficulty identifying a single causative factor. However, tooth wear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Terminology
This is a list of definitions of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. This set of terms provides orientation within the oral cavity, much as anatomical terms of location provide orientation throughout the body. Terms Combining of terms Most of the principal terms can be combined using their corresponding combining forms (such as ''mesio-'' for ''mesial'' and ''disto-'' for ''distal''). They provide names for directions (vectors) and axes; for example, the coronoapical axis is the long axis of a tooth. Such combining yields terms such as those in the following list. The abbreviations should be used only in restricted contexts, where they are explicitly defined and help avoid extensive repetition (for example, a journal article that uses the term "mesiodistal" dozens of times might use the abbreviation "MD"). The abbreviations are ambiguous: (1) they are not spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruxism
Bruxism is excessive teeth grinding or jaw clenching. It is an oral parafunctional activity; i.e., it is unrelated to normal function such as eating or talking. Bruxism is a common behavior; reports of prevalence range from 8% to 31% in the general population. Several symptoms are commonly associated with bruxism, including aching jaw muscles, headaches, hypersensitive teeth, tooth wear, and damage to dental restorations (e.g. crowns and fillings). Symptoms may be minimal, without patient awareness of the condition. If nothing is done, after a while many teeth start wearing down until the whole tooth is gone. There are two main types of bruxism: one occurs during sleep (nocturnal bruxism) and one during wakefulness (awake bruxism). Dental damage may be similar in both types, but the symptoms of sleep bruxism tend to be worse on waking and improve during the course of the day, and the symptoms of awake bruxism may not be present at all on waking, and then worsen over the day. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Caries
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complications may include inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss and infection or abscess formation. The cause of cavities is acid from bacteria dissolving the hard tissues of the teeth ( enamel, dentin and cementum). The acid is produced by the bacteria when they break down food debris or sugar on the tooth surface. Simple sugars in food are these bacteria's primary energy source and thus a diet high in simple sugar is a risk factor. If mineral breakdown is greater than build up from sources such as saliva, caries results. Risk factors include conditions that result in less saliva such as: diabetes mellitus, Sjögren syndrome and some medications. Medications that decrease saliva production include antihistamines and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentin Hypersensitivity
Dentin hypersensitivity (DH, DHS) is dental pain which is sharp in character and of short duration, arising from exposed dentin surfaces in response to stimuli, typically thermal, evaporative, tactile, osmotic, chemical or electrical; and which cannot be ascribed to any other dental disease. A degree of dentin sensitivity is normal, but pain is not usually experienced in everyday activities like drinking a cooled drink. Therefore, although the terms ''dentin sensitivity'' and ''sensitive dentin'' are used interchangeably to refer to dental hypersensitivity, the latter term is the most accurate. Signs and symptoms The pain is sharp and sudden, in response to an external stimulus. The most common trigger is cold, with 75% of people with hypersensitivity reporting pain upon application of a cold stimulus. Other types of stimuli may also trigger pain in dentin hypersensitivity, including: * Thermal – hot and cold drinks and foods, cold air, coolant water jet from a dental instrume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
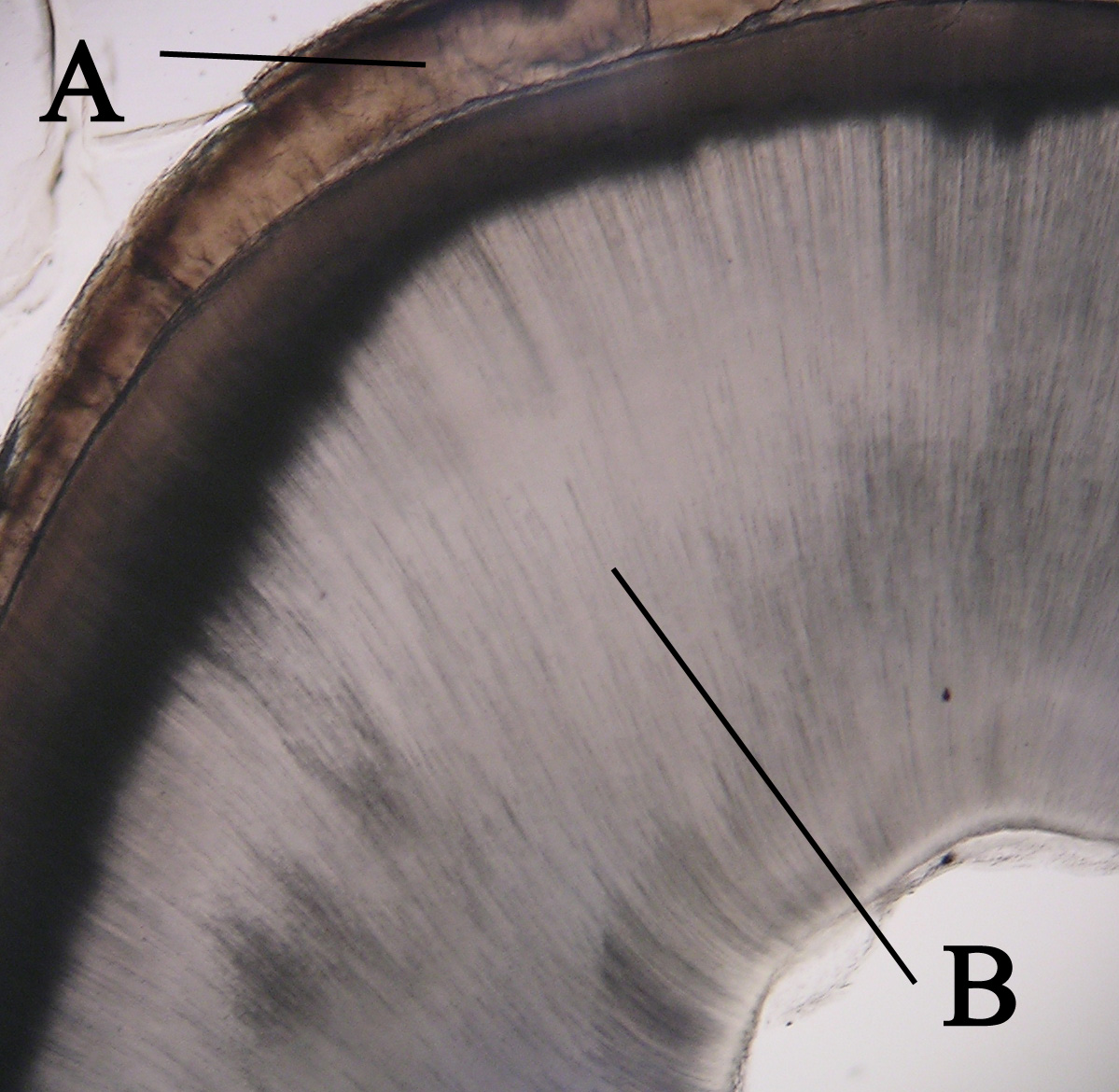
Typical Appearance Of Attrition '', an American Comedy Central television series
{{dab ...
Typical may refer to: * ''Typical'' (album), Peter Hammill * "Typical" (song), song by MuteMath *"Typical", song by Frazier Chorus from ''Sue'', 1987 *''Typical'', story collection by Padgett Powell, 1991 See also *''Typical Rick ''Typical Rick'' is an American television series produced by Comedy Central, created by Nicholaus Goossen and Nick Swardson. Comedy Central declined to renew the series for a third season. Cast * Nick Swardson Nicholas Roger Swardson (born O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occlusal Trauma
Occlusal trauma is the damage to teeth when an excessive force is acted upon them and they do not align properly.Bibb, CA: Occlusal Evaluation and Therapy in the Management of Periodontal Disease. In Newman, MG; Takei, HH; Carranza, FA; editors: ''Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology'', 9th Edition. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company, 2002. pages 698-701. When the jaws close, for instance during chewing or at rest, the relationship between the opposing teeth is referred to as occlusion. When trauma, disease or dental treatment alters occlusion by changing the biting surface of any of the teeth, the teeth will come together differently, and their occlusion will change.Hinrichs, JE: Occlusal The Role of Dental Calculus and Other Predisposing Factors. In Newman, MG; Takei, HH; Carranza, FA; editors: ''Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology'', 9th Edition. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company, 2002. page 192. When that change has a negative effect on how the teeth occlude, this may ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occlusion (dentistry)
Occlusion, in a dental context, means simply the contact between teeth. More technically, it is the relationship between the maxillary (upper) and mandibular (lower) teeth when they approach each other, as occurs during chewing or at rest. Static occlusion refers to contact between teeth when the jaw is closed and stationary, while dynamic occlusion refers to occlusal contacts made when the jaw is moving. The masticatory system also involves the periodontium, the TMJ (and other skeletal components) and the neuromusculature, therefore the tooth contacts should not be looked at in isolation, but in relation to the overall masticatory system. Anatomy of Masticatory System One cannot fully understand occlusion without an in depth understanding of the anatomy including that of the teeth, TMJ, musculature surrounding this and the skeletal components. The Dentition and Surrounding Structures The human dentition consists of 32 permanent teeth and these are distributed between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abfraction
Abfraction is a theoretical concept explaining a loss of tooth structure not caused by tooth decay ( non-carious cervical lesions). It is suggested that these lesions are caused by forces placed on the teeth during biting, eating, chewing and grinding; the enamel, especially at the cementoenamel junction (CEJ), undergoes large amounts of stress, causing micro fractures and tooth tissue loss. Abfraction appears to be a modern condition, with examples of non-carious cervical lesions in the archaeological record typically caused by other factors. Definition Abfraction is a form of non-carious tooth tissue loss that occurs along the gingival margin. In other words, abfraction is a mechanical loss of tooth structure that is not caused by tooth decay, located along the gum line. There is theoretical evidence to support the concept of abfraction, but little experimental evidence exists. The term abfraction was first published in 1991 in a journal article dedicated to distinguishi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |