|
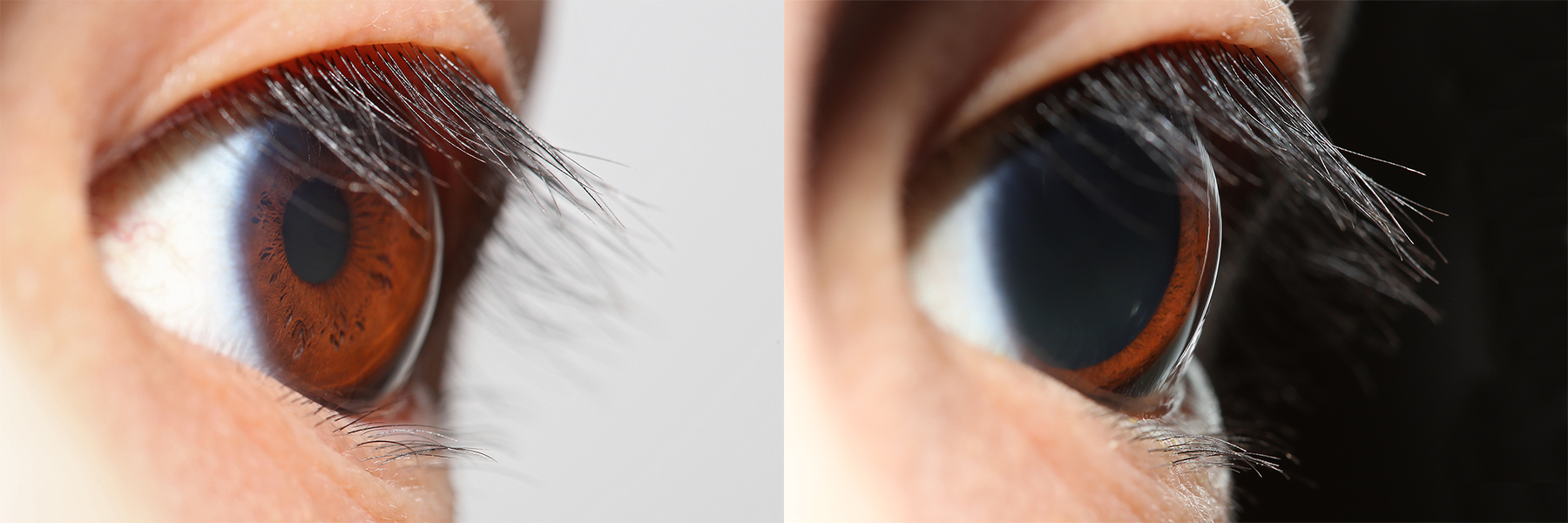
Mydriasis
Mydriasis is the Pupillary dilation, dilation of the pupil, usually having a non-physiological cause, or sometimes a physiological pupillary response. Non-physiological causes of mydriasis include disease, Physical trauma, trauma, or the use of certain types of drug, drugs. It may also be of unknown cause. Normally, as part of the pupillary light reflex, the pupil dilates in the dark and miosis, constricts in the light to respectively improve vividity at night and to protect the retina from sunlight damage during the day. A ''mydriatic'' pupil will remain excessively large even in a bright environment. The excitation of the radial fibres of the iris which increases the pupillary aperture is referred to as a mydriasis. More generally, mydriasis also refers to the natural dilation of pupils, for instance in low light conditions or under sympathetic stimulation. Mydriasis is frequently induced by drugs for certain Ophthalmology, ophthalmic examinations and procedures, particularly th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cycloplegia
Cycloplegia is paralysis of the ciliary muscle of the eye, resulting in a loss of accommodation. Because of the paralysis of the ciliary muscle, the curvature of the lens can no longer be adjusted to focus on nearby objects. This results in similar problems as those caused by presbyopia, in which the lens has lost elasticity and can also no longer focus on close-by objects. Cycloplegia with accompanying mydriasis (dilation of pupil) is usually due to topical application of muscarinic antagonists such as atropine and cyclopentolate. Belladonna alkaloids are used for testing the error of refraction and examination of eye. Management Cycloplegic drugs are generally muscarinic receptor antagonists such as atropine, cyclopentolate, homatropine, scopolamine and tropicamide. They are indicated for use in cycloplegic refraction (to paralyze the ciliary muscle in order to determine the true refractive error of the eye) and the treatment of uveitis. All cycloplegics are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tropicamide
Tropicamide, sold under the brand name Mydriacyl among others, is a medication used to dilate the pupil and help with the examination of the eye. Specifically it is used to help examine the back of the eye. It is applied as eye drops. Effects occur within 40 minutes and last for up to a day. Common side effects include blurry vision, increased intraocular pressure, and sensitivity to light. Another rare but severe side effect is psychosis, particularly in children. It is unclear if use during pregnancy is safe for the fetus. Tropicamide is in the antimuscarinic part of the anticholinergic family of medications. It works by making the muscles within the eye unable to respond to nerve signals. Tropicamide was approved for medical use in the United States in 1960. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical use Tropicamide is an antimuscarinic drug that produces short acting mydriasis (dilation of the pupil) and cycloplegia whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
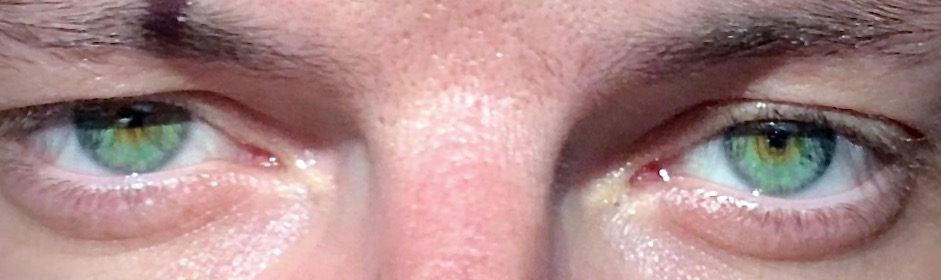
Pupil
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to strike the retina.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. (1990) ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company. It appears black because light rays entering the pupil are either absorbed by the tissues inside the eye directly, or absorbed after diffuse reflections within the eye that mostly miss exiting the narrow pupil. The size of the pupil is controlled by the iris, and varies depending on many factors, the most significant being the amount of light in the environment. The term "pupil" was coined by Gerard of Cremona. In humans, the pupil is circular, but its shape varies between species; some cats, reptiles, and foxes have vertical slit pupils, goats and sheep have horizontally oriented pupils, and some catfish have annular types. In optical terms, the anatomical pupil is the eye's aperture and the iris is the aperture stop. The image of the pupil as seen from o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adrenergic Receptors
The adrenergic receptors or adrenoceptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced by the body, but also many medications like beta blockers, beta-2 (β2) agonists and alpha-2 (α2) agonists, which are used to treat high blood pressure and asthma, for example. Many cells have these receptors, and the binding of a catecholamine to the receptor will generally stimulate the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). The SNS is responsible for the fight-or-flight response, which is triggered by experiences such as exercise or fear-causing situations. This response dilates pupils, increases heart rate, mobilizes energy, and diverts blood flow from non-essential organs to skeletal muscle. These effects together tend to increase physical performance momentarily. History By the turn of the 19th century, it was agreed that the stimulation of sympathetic nerves could cause di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pupillary Light Reflex
The pupillary light reflex (PLR) or photopupillary reflex is a reflex that controls the diameter of the pupil, in response to the intensity ( luminance) of light that falls on the retinal ganglion cells of the retina in the back of the eye, thereby assisting in adaptation of vision to various levels of lightness/darkness. A greater intensity of light causes the pupil to constrict ( miosis/myosis; thereby allowing less light in), whereas a lower intensity of light causes the pupil to dilate ( mydriasis, expansion; thereby allowing more light in). Thus, the pupillary light reflex regulates the intensity of light entering the eye. Light shone into one eye will cause both pupils to constrict. Terminology The pupil is the dark circular opening in the center of the iris and is where light enters the eye. By analogy with a camera, the pupil is equivalent to aperture, whereas the iris is equivalent to the diaphragm. It may be helpful to consider the ''Pupillary reflex'' as an Iris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anisocoria
Anisocoria is a condition characterized by an unequal size of the eyes' pupils. Affecting up to 20% of the population, anisocoria is often entirely harmless, but can be a sign of more serious medical problems. Causes Anisocoria is a common condition, defined by a diameter difference of 0.4 mm or more between the sizes of the pupils of the eyes. Anisocoria has various causes: * Physiological anisocoria: About 20% of the population has a slight difference in pupil size, which is known as physiological anisocoria. In this condition, the difference between pupils is usually less than 1 mm. * Horner's syndrome * Mechanical anisocoria: Occasionally, previous trauma, eye surgery, or inflammation ( uveitis, angle closure glaucoma) can lead to adhesions between the iris and the lens. * Adie tonic pupil: Tonic pupil is usually an isolated benign entity, presenting in young women. It may be associated with loss of deep tendon reflex (Adie's syndrome). Tonic pupil is charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Miosis
Miosis, or myosis (), is excessive constriction of the pupil. citing: Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th ed. The opposite condition, mydriasis, is the dilation of the pupil. Anisocoria is the condition of one pupil being more dilated than the other. Causes Age * Senile miosis (a reduction in the size of a person's pupil in old age)Diseases *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dilated Fundus Examination
Dilated fundus examination (DFE) is a diagnostic procedure that uses mydriatic eye drops to dilate or enlarge the pupil in order to obtain a better view of the fundus of the eye. Once the pupil is dilated, examiners use ophthalmoscopy to view the eye's interior, which makes it easier to assess the retina, optic nerve head, blood vessels, and other important features. DFE has been found to be a more effective method for evaluating eye health when compared to non-dilated examination, and is the best method of evaluating structures behind the iris. It is frequently performed by ophthalmologists and optometrists as part of an eye examination. Examination The most common agents used to dilate the pupil are phenylephrine (2.5% in pediatrics or 10% in adults) and tropicamide (0.5% or 1%). While phenylephrine stimulates receptors that contract the dilator muscle of the pupil, tropicamide blocks stimulation of the pupillary sphincter muscle to allow for relaxation. As the insertio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pupillary Response
Pupillary response is a physiological response that varies the size of the pupil between 1.5 mm and 8 mm, via the optic and oculomotor cranial nerve. A constriction response (miosis), is the narrowing of the pupil, which may be caused by scleral buckles or drugs such as opiates/ opioids or anti-hypertension medications. Constriction of the pupil occurs when the circular muscle, controlled by the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS), contracts, and also to an extent when the radial muscle relaxes. A dilation response (mydriasis), is the widening of the pupil and may be caused by adrenaline; anticholinergic agents; stimulant drugs such as MDMA, cocaine, and amphetamines; and some hallucinogenics (e.g. LSD). Dilation of the pupil occurs when the smooth cells of the radial muscle, controlled by the sympathetic nervous system (SNS), contract, and also when the cells of the iris sphincter muscle relax. The responses can have a variety of causes, from an involuntary reflex reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug injection, injection, smoking, ingestion, absorption (skin), absorption via a dermal patch, patch on the skin, suppository, or sublingual administration, dissolution under the tongue. In pharmacology, a drug is a chemical substance, typically of known structure, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. A pharmaceutical drug, also called a medication or medicine, is a chemical substance used to pharmacotherapy, treat, cure, preventive healthcare, prevent, or medical diagnosis, diagnose a disease or to promote well-being. Traditionally drugs were obtained through extraction from medicinal plants, but more recently also by organic synthesis. Pharmaceutical drugs may be used for a limited duration, or on a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |