|
Multimedia Messaging Service
Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) is a standard way to send messages that include multimedia content to and from a mobile phone over a cellular network. Users and providers may refer to such a message as a PXT, a picture message, or a multimedia message. The MMS standard extends the core SMS (Short Message Service) capability, allowing the exchange of text messages greater than 160 characters in length. Unlike text-only SMS, MMS can deliver a variety of media, including up to forty seconds of video, one image, a slideshow of multiple images, or audio. Media companies have utilized MMS on a commercial basis as a method of delivering news and entertainment content, and retailers have deployed it as a tool for delivering scannable coupon codes, product images, videos, and other information. On (mainly) older devices, messages that start off with text, as SMS, are converted to and sent as an MMS when an emoji is added. The commercial introduction of MMS started in March 2002, althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MSISDN
MSISDN ( ) is a number uniquely identifying a subscription in a Global System for Mobile communications or a Universal Mobile Telecommunications System mobile network. It is the mapping of the telephone number to the subscriber identity module in a mobile or cellular phone. This abbreviation has several interpretations, the most common one being "Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number".The conclusion ("most common") is drawn from the recent documentation from 3GPP and Open Mobile Alliance, please see the Abbreviation section above The MSISDN and international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) are two important numbers used for identifying a mobile subscriber. The IMSI is stored in the SIM (the card inserted into the mobile phone), and uniquely identifies the mobile station, its home wireless network, and the home country of the home wireless network. The MSISDN is used for routing calls to the subscriber. The IMSI is often used as a key in the home location re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Charging System
Online charging system (OCS) is a system allowing a communications service provider A telecommunications company is a kind of electronic communications service provider, more precisely a telecommunications service provider (TSP), that provides telecommunications services such as telephony and data communications access. Many t ... to charge their customers, in real time, based on service usage. Architecture Event based charging An event-based charging function (EBCF) is used to charge events based on their occurrence rather than their duration or volume used in the event. Typical events are SMS, MMS, purchase of content (application, game, music, video on demand, etc.). Event-based charging function is used when the CC-Request-Type AVP = 4 i.e. for event request ex: diameter-sms or diameter-..... Let us consider one example of Event-based charging. 1. Cost of one apple is Rupees 25/- You pay the amount, take the apple and go. Similarly, if you send a text message it may cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSM Core Network
Network switching subsystem (NSS) (or GSM core network) is the component of a GSM system that carries out call out and mobility management functions for mobile phones roaming on the network of base stations. It is owned and deployed by mobile phone operators and allows mobile devices to communicate with each other and telephones in the wider public switched telephone network (PSTN). The architecture contains specific features and functions which are needed because the phones are not fixed in one location. The NSS originally consisted of the circuit-switched core network, used for traditional GSM services such as voice calls, SMS, and circuit switched data calls. It was extended with an overlay architecture to provide packet-switched data services known as the GPRS core network. This allows GSM mobile phones to have access to services such as WAP, MMS and the Internet. Mobile switching center (MSC) Description The mobile switching center (MSC) is the primary service d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
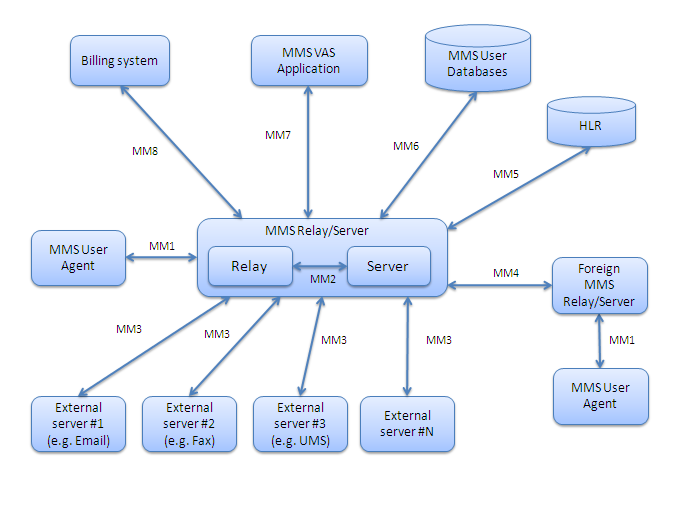
MMS Architecture
The MMS Architecture is the set of standards used by the Multimedia Messaging Service in mobile networks. The standards are prepared by 3GPP. Overview The standard consists of a number of interfaces between components found in the mobile network: * MM1: the interface between MMS User Agent and MMS Center (MMSC, the combination of the MMS Relay & Server). Delivered as HTTP over a packet switched data session. * MM2: the interface between MMS Relay and MMS Server. * MM3: the interface between MMSC and other messaging systems. Using SMTP. * MM4: the interface between MMSC and foreign network providers. Using SMTP. * MM5: the interface between MMSC and HLR. * MM6: the interface between MMSC and user databases. * MM7: the interface between MMS Value-added service applications and MMSC. Typically Content Providers using HTTP / SOAP for delivery. * MM8: the interface between MMSC and the billing systems. * MM9: the interface between MMSC and an online charging system. * MM10: the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ericsson
(), commonly known as Ericsson (), is a Swedish multinational networking and telecommunications company headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden. Ericsson has been a major contributor to the development of the telecommunications industry and is one of the leaders in 5G. Ericsson has over 57,000 granted patents and it is the inventor of Bluetooth technology. The company sells infrastructure, software, and services in information and communications technology for telecommunications service providers and enterprises, including, among others, cellular 4G and 5G equipment, and Internet Protocol (IP) and optical transport systems. The company employs around 100,000 people and operates in more than 180 countries. The company is listed on the Nasdaq Stockholm under the ticker symbols ERIC.A and ERIC.B and on the American Nasdaq under the ticker symbol ERIC. The company was founded in 1876 by Lars Magnus Ericsson and is jointly controlled by the Wallenberg family through its holding company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WAP Push
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is an obsolete technical standard for accessing information over a Cellular network, mobile cellular network. Introduced in 1999, WAP allowed users with compatible mobile devices to browse content such as news, weather and sports scores provided by mobile network operators, specially designed for the limited capabilities of a mobile device. The Japanese i-mode system offered a competing wireless data standard. Before the introduction of WAP, mobile service providers had limited opportunities to offer interactive data services, but needed interactivity to support Internet and WWW, Web applications. Although hyped at launch, WAP suffered from criticism. However the introduction of GPRS networks, offering a faster speed, led to an improvement in the WAP experience. WAP content was accessed using a ''WAP browser'', which is like a standard web browser but designed for reading pages specific for WAP, instead of HTML. By the 2010s it had been largel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Over-the-air Programming
An over-the-air update (or OTA update), also known as over-the-air programming (or OTA programming), is an update to an embedded system that is delivered through a wireless network, such as Wi-Fi or a cellular network. These embedded systems include mobile phones, tablets, set-top boxes, cars and telecommunications equipment. OTA updates for cars and internet of things devices can also be called firmware over-the-air (FOTA). Various components may be updated OTA, including the device's operating system, applications, configuration settings, or parameters like encryption keys. Terminology The term ''over-the-air update'' applies specifically to embedded systems, rather than non-embedded systems like computers. Before OTA updates, embedded devices could only be flashed through direct physical access (with a JTAG) or wired connections (usually through USB or a serial port). Purpose Over-the-air delivery may allow updates to be distributed at larger scales, reduce the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulk Messaging
Bulk messaging is the dissemination of large numbers of SMS messages for delivery to mobile phone terminals. It is used by media companies, banks and other enterprises (for marketing and fraud control) and consumer brands for a variety of purposes including entertainment, enterprise and mobile marketing. Bulk messaging is commonly used for alerts, reminders and marketing, but also information and communication between both staff and customers. Software Software is required for sending and receiving bulk SMS, and various software packages are available. These software packages provide users with the opportunity to add as many phone numbers as required and these phone numbers can be managed in a variety of ways. Most SMS software applications allow the upload of lists of mobile phone numbers using a text file or CSV file. Some sophisticated systems can automatically remove any duplicated or improper numbers, and the mobile numbers may be validated before sending the messages. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
File Transfer Protocol
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard communication protocol used for the transfer of computer files from a server to a client on a computer network. FTP is built on a client–server model architecture using separate control and data connections between the client and the server. FTP users may authenticate themselves with a plain-text sign-in protocol, normally in the form of a username and password, but can connect anonymously if the server is configured to allow it. For secure transmission that protects the username and password, and encrypts the content, FTP is often secured with SSL/TLS (FTPS) or replaced with SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP). The first FTP client applications were command-line programs developed before operating systems had graphical user interfaces, and are still shipped with most Windows, Unix, and Linux operating systems. Many dedicated FTP clients and automation utilities have since been developed for desktops, servers, mobile d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value-added Service
A value-added service (VAS) is a popular telecommunications industry{{cite web, url=https://www.prweb.com/releases/global_mobile_value_added_services_vas_market_worldwide_industry_share_investment_trends_growth_size_strategy_and_forecast_research_report_2013/prweb11284640.htm, title=Global Mobile Value Added Services (VAS) Market: Worldwide Industry Share, Investment Trends, Growth, Size, Strategy And Forecast Research Report 2013, date=3 November 2013, work=PRWeb term for non- core services, or, in short, all services beyond standard voice calls and fax transmissions. However, it can be used in any service industry, for services available at little or no cost, to promote their primary business. In the telecommunications industry, on a conceptual level, value-added services ''add value'' to the standard service offering, spurring subscribers to use their phone more and allowing the operator to drive up their average revenue per user. For mobile phones, technologies like SMS, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |