Multimedia Messaging Service on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) is a standard way to send messages that include
Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) is a standard way to send messages that include
 If the receiver's handset is not MMS capable, the message is usually delivered to a web-based service from where the content can be viewed from a normal web browser. The URL for the content is usually sent to the receiver's phone in a normal text message. This behavior is usually known as a "legacy experience" since content can still be received by the user.
The method for determining whether a handset is MMS capable is not specified by the standards. A database is usually maintained by the operator, and in it each mobile phone number is marked as being associated with a legacy handset or not. This method is unreliable, however, because customers can independently change their handsets, and many of these databases are not updated dynamically.
MMS does not utilize operator-maintained "data" plans to distribute multimedia content; they are used only if the user clicks links inside the message.
If the receiver's handset is not MMS capable, the message is usually delivered to a web-based service from where the content can be viewed from a normal web browser. The URL for the content is usually sent to the receiver's phone in a normal text message. This behavior is usually known as a "legacy experience" since content can still be received by the user.
The method for determining whether a handset is MMS capable is not specified by the standards. A database is usually maintained by the operator, and in it each mobile phone number is marked as being associated with a legacy handset or not. This method is unreliable, however, because customers can independently change their handsets, and many of these databases are not updated dynamically.
MMS does not utilize operator-maintained "data" plans to distribute multimedia content; they are used only if the user clicks links inside the message.
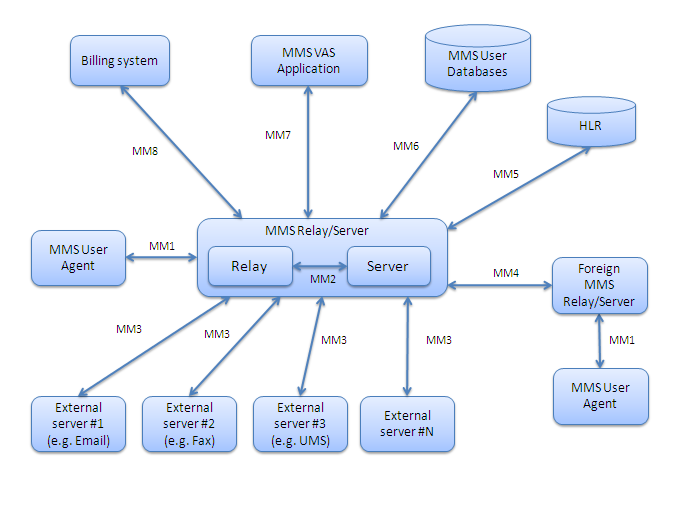 * MM1: the 3GPP interface between MMS User Agent and MMS Center (MMSC, the combination of the MMS Relay & Server)
* MM2: the 3GPP interface between MMS Relay and MMS Server
* MM3: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and external servers
* MM4: the 3GPP interface between different MMSCs
* MM5: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and HLR
* MM6: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and user databases
* MM7: the 3GPP interface between MMS VAS applications and MMSC
* MM8: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and the billing systems
* MM9: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and an
* MM1: the 3GPP interface between MMS User Agent and MMS Center (MMSC, the combination of the MMS Relay & Server)
* MM2: the 3GPP interface between MMS Relay and MMS Server
* MM3: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and external servers
* MM4: the 3GPP interface between different MMSCs
* MM5: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and HLR
* MM6: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and user databases
* MM7: the 3GPP interface between MMS VAS applications and MMSC
* MM8: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and the billing systems
* MM9: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and an
multimedia
Multimedia is a form of communication that uses a combination of different content forms, such as Text (literary theory), writing, Sound, audio, images, animations, or video, into a single presentation. T ...
content to and from a mobile phone
A mobile phone or cell phone is a portable telephone that allows users to make and receive calls over a radio frequency link while moving within a designated telephone service area, unlike fixed-location phones ( landline phones). This rad ...
over a cellular network
A cellular network or mobile network is a telecommunications network where the link to and from end nodes is wireless network, wireless and the network is distributed over land areas called ''cells'', each served by at least one fixed-locatio ...
. Users and providers may refer to such a message as a PXT, a picture message, or a multimedia message. The MMS standard extends the core SMS
Short Message Service, commonly abbreviated as SMS, is a text messaging service component of most telephone, Internet and mobile device systems. It uses standardized communication protocols that let mobile phones exchange short text messages, t ...
(Short Message Service) capability, allowing the exchange of text messages greater than 160 characters in length. Unlike text-only SMS, MMS can deliver a variety of media, including up to forty seconds of video, one image, a slideshow of multiple images, or audio.
Media companies have utilized MMS on a commercial basis as a method of delivering news and entertainment content, and retailers have deployed it as a tool for delivering scannable coupon codes, product images, videos, and other information. On (mainly) older devices, messages that start off with text, as SMS, are converted to and sent as an MMS when an emoji
An emoji ( ; plural emoji or emojis; , ) is a pictogram, logogram, ideogram, or smiley embedded in text and used in electronic messages and web pages. The primary function of modern emoji is to fill in emotional cues otherwise missing from type ...
is added.
The commercial introduction of MMS started in March 2002, although picture messaging had already been established in Japan. It was built using the technology of SMS as a captive technology which enabled service providers to "collect a fee every time anyone snaps a photo." MMS was designed to be able to work on the then-new GPRS
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), also called 2.5G, is a mobile data standard on the 2G cellular communication network's Global System for Mobile Communications, global system for mobile communications (GSM). Networks and mobile devices wit ...
and 3G networks and could be implemented through either a WAP-based or IP-based gateway. The 3GPP
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is an umbrella term for a number of standards organizations which develop protocols for mobile telecommunications. Its best known work is the development and maintenance of:
* GSM and related 2G and ...
and WAP Forum groups fostered the development of the MMS standard, which was then continued by the Open Mobile Alliance
OMA SpecWorks, previously the Open Mobile Alliance (OMA), is a standards organization which develops open, international technical standards for the mobile phone industry. It is a nonprofit Non-governmental organization (NGO), not a formal govern ...
(OMA).
Technical description
MMS messages are delivered in a different way from SMS. The first step is for the sending device to encode the multimedia content in a fashion similar to sending aMIME
A mime artist, or simply mime (from Greek language, Greek , , "imitator, actor"), is a person who uses ''mime'' (also called ''pantomime'' outside of Britain), the acting out of a story through body motions without the use of speech, as a the ...
message (MIME content formats are defined in the MMS Message Encapsulation specification). The message is then forwarded to the carrier's MMS store and forward
Store and forward is a telecommunications technique in which information is sent to an intermediate station where it is kept and sent at a later time to the final destination or to another intermediate station. The intermediate station, or node in ...
server, known as the MMSC (Multimedia Messaging Service Centre). If the receiver is on a carrier different from the sender, then the MMSC acts as a relay, and forwards the message to the MMSC of the recipient's carrier using the Internet.
Once the recipient's MMSC has received a message, it first determines whether the receiver's handset is "MMS capable" or not. If it supports the standards for receiving MMS, the content is extracted and sent to a temporary storage server with an HTTP
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, wher ...
front-end. An SMS "control message" containing the URL
A uniform resource locator (URL), colloquially known as an address on the Web, is a reference to a resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identi ...
of the content is then sent to the recipient's handset to trigger the receiver's WAP browser to open and receive the content from the embedded URL. Several other messages are exchanged to indicate the status of the delivery attempt. Before delivering content, some MMSCs also include a conversion service that will attempt to modify the multimedia content into a format suitable for the receiver. This is known as "content adaptation".
E-mail
Electronic mail (usually shortened to email; alternatively hyphenated e-mail) is a method of transmitting and receiving Digital media, digital messages using electronics, electronic devices over a computer network. It was conceived in the ...
and web-based gateways to the MMS system are common. On the reception side, the content servers can typically receive service requests both from WAP and normal HTTP browsers, so delivery via the web is simple. For sending from external sources to handsets, most carriers allow a MIME
A mime artist, or simply mime (from Greek language, Greek , , "imitator, actor"), is a person who uses ''mime'' (also called ''pantomime'' outside of Britain), the acting out of a story through body motions without the use of speech, as a the ...
encoded message to be sent to the receiver's phone number using a special e-mail address combining the recipient's public phone number and a special domain name, which is typically carrier-specific.
Challenges
There are some challenges with MMS that do not exist with SMS: * Content adaptation: Multimedia content created by one brand of MMS phone may not be entirely compatible with the capabilities of the recipient's MMS phone. In the MMS architecture, the recipient MMSC is responsible for providing for ''content adaptation'' (e.g., image resizing, audio codec transcoding, etc.), if this feature is enabled by the mobile network operator. When content adaptation is supported by a network operator, its MMS subscribers enjoy compatibility with a larger network of MMS users than would otherwise be available. * Distribution lists: Current MMS specifications do not include distribution lists nor methods by which large numbers of recipients can be conveniently addressed, particularly by content providers, called '' Value-added service providers'' (VASPs) in3GPP
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is an umbrella term for a number of standards organizations which develop protocols for mobile telecommunications. Its best known work is the development and maintenance of:
* GSM and related 2G and ...
. Since most SMSC vendors have adopted FTP
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard communication protocol used for the transfer of computer files from a server to a client on a computer network. FTP is built on a client–server model architecture using separate control and dat ...
as an ad-hoc method by which large distribution lists are transferred to the SMSC prior to being used in a bulk-messaging SMS submission, it is expected that MMSC vendors will also adopt FTP.
* Bulk messaging
Bulk messaging is the dissemination of large numbers of SMS messages for delivery to mobile phone terminals. It is used by media companies, banks and other enterprises (for marketing and fraud control) and consumer brands for a variety of purpos ...
: The flow of ''peer-to-peer'' MMS messaging involves several over-the-air transactions that become inefficient when MMS is used to send messages to large numbers of subscribers, as is typically the case for VASPs. For example, when one MMS message is submitted to a very large number of recipients, it is possible to receive a ''delivery report'' and ''read-reply report'' for each and every recipient. Future MMS specification work is likely to optimize and reduce the transactional overhead for the bulk-messaging case.
* Handset configuration: Unlike SMS, MMS requires a number of handset parameters to be set. Poor handset configuration is often blamed as the first point of failure for many users. Service settings are sometimes preconfigured on the handset, but mobile operators are now looking at new device management technologies as a means of delivering the necessary settings for data services (MMS, WAP, etc.) via over-the-air programming
An over-the-air update (or OTA update), also known as over-the-air programming (or OTA programming), is an update to an embedded system that is delivered through a wireless network, such as Wi-Fi or a cellular network.
These embedded systems inc ...
(OTA).
* WAP Push
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is an obsolete technical standard for accessing information over a Cellular network, mobile cellular network. Introduced in 1999, WAP allowed users with compatible mobile devices to browse content such as new ...
: Few mobile network operators offer direct connectivity to their MMSCs for content providers. This has resulted in many content providers using WAP push as the only method available to deliver 'rich content' to mobile handsets. WAP push enables 'rich content' to be delivered to a handset by specifying the URL (via binary SMS) of a pre-compiled MMS, hosted on a content provider's web server. A consequence is that the receiver who pays WAP per kb or minute (as opposed to a flat monthly fee) pays for receiving the MMS, as opposed to only paying for sending one, and also paying a different rate.
Although the standard does not specify a maximum size for a message, 300 kB and 600 kB are the recommended sizes used by networks for compatibility with MMS 1.2 and MMS 1.3 devices respectively. The limit for the first generation of MMS was 50 kB.
Interfaces
 * MM1: the 3GPP interface between MMS User Agent and MMS Center (MMSC, the combination of the MMS Relay & Server)
* MM2: the 3GPP interface between MMS Relay and MMS Server
* MM3: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and external servers
* MM4: the 3GPP interface between different MMSCs
* MM5: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and HLR
* MM6: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and user databases
* MM7: the 3GPP interface between MMS VAS applications and MMSC
* MM8: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and the billing systems
* MM9: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and an
* MM1: the 3GPP interface between MMS User Agent and MMS Center (MMSC, the combination of the MMS Relay & Server)
* MM2: the 3GPP interface between MMS Relay and MMS Server
* MM3: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and external servers
* MM4: the 3GPP interface between different MMSCs
* MM5: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and HLR
* MM6: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and user databases
* MM7: the 3GPP interface between MMS VAS applications and MMSC
* MM8: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and the billing systems
* MM9: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and an online charging system
Online charging system (OCS) is a system allowing a communications service provider
A telecommunications company is a kind of electronic communications service provider, more precisely a telecommunications service provider (TSP), that provides ...
* MM10: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and a message service control function
* MM11: the 3GPP interface between MMSC and an external transcoder
Usage, decline and discontinuation
Verizon
Verizon Communications Inc. ( ), is an American telecommunications company headquartered in New York City. It is the world's second-largest telecommunications company by revenue and its mobile network is the largest wireless carrier in the ...
launched its MMS service in July 2003. Between 2010 and 2013, MMS traffic in the U.S. increased by 70% from 57 billion to 96 billion messages sent. This is due in part to the wide adoption of smartphone
A smartphone is a mobile phone with advanced computing capabilities. It typically has a touchscreen interface, allowing users to access a wide range of applications and services, such as web browsing, email, and social media, as well as multi ...
s. However take-up of MMS never matched the widespread popularity of SMS text messaging.
Due to lower cost and improved functionality provided by modern internet-based instant messengers such as WhatsApp
WhatsApp (officially WhatsApp Messenger) is an American social media, instant messaging (IM), and voice-over-IP (VoIP) service owned by technology conglomerate Meta. It allows users to send text, voice messages and video messages, make vo ...
, Telegram
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pi ...
, and Signal
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
In ...
, MMS usage has declined, and it has been discontinued by several telcos since the early 2020s. Countries with operators
Operator may refer to:
Mathematics
* A symbol indicating a mathematical operation
* Logical operator or logical connective in mathematical logic
* Operator (mathematics), mapping that acts on elements of a space to produce elements of another ...
that have discontinued MMS include: India (BSNL; from 1 November 2015), Philippines (Sun Cellular, Smart Communications, TNT; from 28 September 2018), Singapore (Singtel, M1, Starhub; from 16 November 2021), Kazakhstan (Kcell; from 6 May 2022), Switzerland (Swisscom, Salt Mobile; from 10 January 2023), Germany (Vodafone; from 17 January 2023).
RCS
RCS may refer to:
Organizations Arts and entertainment
* Radio Corporation of Singapore
* Radcliffe Choral Society, a choral ensemble at Harvard University
*RCS MediaGroup (Rizzoli-Corriere della Sera), an Italian publishing group
*Royal Conserva ...
is intended to be the successor technology for MMS and SMS.See also
* Enhanced Messaging Service (EMS) *Rich Communication Services
Rich Communication Services (RCS) is a communication protocol standard for instant messaging, primarily for mobile phones, developed and defined by the GSM Association (GSMA). It aims to be a replacement of SMS and Multimedia Messaging Service, ...
(RCS)
* OTA bitmap, a Nokia specification for picture messaging
* Mobile marketing
Mobile marketing is a multi-channel Online advertising, online marketing technique focused at reaching a specific audience on their smartphones, feature phones, Tablet computer, tablets, or any other related devices through websites, e-mail, SMS ...
* Short code
* Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language
Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language (SMIL ()) is a World Wide Web Consortium recommended Extensible Markup Language (XML) markup language to describe multimedia presentations. It defines markup for timing, layout, animations, visual tr ...
References
External links
* * * * {{Telecommunications 3GPP standards Mobile telecommunication services Mobile telecommunications standards Open Mobile Alliance standards Telecommunications-related introductions in 2002