|
Monte Grappa
Monte Grappa () (1,775 m) is a mountain of the Venetian Prealps in Veneto, Italy. It lies between the Venetian plain to the south and the central alpine areas to the north. To the west, it is parted from the Asiago upland by the Brenta river, and to the east it is separated from the Cesen-Visentin massif by the Piave river. To the north lie Corlo lake and Feltre valley. In the past, the mountain was called ''Alpe Madre'' (''Mother Alp''), and is currently divided among three provinces: Vicenza to the west, Treviso to the south and Belluno to the northeast. It is the highest peak of a small massif, which also includes many other peaks such as Col Moschin, Colle della Berretta, Monte Asolone, Monte Pertica, Prassolan, Monti Solaroli, Fontana Secca, Monte Peurna, Monte Santo, Monte Tomatico, Meatte, Monte Pallon, and Monte Tomba. In September 2021, UNESCO announced that Monte Grappa would become one of 20 new biosphere reserves as part of their Man and the Biosphere Programme. Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venetian Prealps '' - IGM); on-lin ...
The Venetian Prealps (''Prealpi Venete'' in Italian) are a mountain range in the south-eastern part of the Alps. They are located in Triveneto, in the north-eastern part of Italy. Geography Administratively the range is divided between the Italian provinces of Trento (in the region of Trentino Alto Adige), Verona, Vicenza, Treviso, Belluno (in the Region of Veneto) and Pordenone (in the region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia). The Venetian Prealps are drained by the rivers Adige, Brenta, Piave and other minor rivers and streams, all of them tributaries of the Adriatic Sea. Summits The chief summits of the Venetian prealps are: Maps * Italian official cartography (''Istituto Geografico Militare The ''Istituto Geografico Militare'' (IGM), or Military Geographic Institute, is an Italian public organization, dependent on the Italian Army general staff (''Stato Maggiore dell'Esercito''). It is the national mapping agency for Italy. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalactites
A stalactite (, ; , ) is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is capable of being melted, may form a stalactite. Stalactites may be composed of lava, minerals, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). A stalactite is not necessarily a speleothem, though speleothems are the most common form of stalactite because of the abundance of limestone caves. The corresponding formation on the floor of the cave is known as a stalagmite. Formation and type Limestone stalactites The most common stalactites are speleothems, which occur in limestone caves. They form through deposition of calcium carbonate and other minerals, which is precipitated from mineralized water solutions. Limestone is the chief form of calcium carbonate rock which is dissolved by water that con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globularia Nudicaulis
''Globularia'' is a genus of about 22 species of flowering plants in the family Plantaginaceae, native to central and southern Europe, Macaronesia, northwest Africa and southwest Asia. They are dense low evergreen mat-forming perennials or subshrubs, with leathery oval leaves 1–10 cm long. The flowers are produced in dense inflorescences ( capitula) held above the plant on a 1–30 cm tall stem; the capitula is 1–3 cm in diameter, with numerous tightly packed purple, violet, pink or white flowers. ''Globularia'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including '' Coleophora virgatella''. Several members of the genus, such as '' Globularia cordifolia'' and '' Globularia punctata'', are cultivated and sold for garden use. Under the old Cronquist system of plant classification, they were treated in their own family, Globulariaceae, but genetic evidence has shown that the genus belongs in the family Plantaginaceae. Most specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knautia Persicina
''Knautia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Caprifoliaceae. It includes 55 species native to Europe, North Africa, Western and Central Asia, and Siberia. The common names are variants of "widow flower". Others are given the name "scabious", which properly belongs to the related genus (''Scabiosa''). The name ''Knautia'' comes from the 17th-century German botanists, Drs. Christoph and Christian Knaut. by Julia Brittain Species 55 species are accepted. *'' Knautia adriatica'' *'' Knautia albanic ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leontodon Tenuiflorus
''Leontodon'' is a genus of plants in the tribe Cichorieae within the family Asteraceae, commonly known as hawkbits. Their English name derives from the mediaeval belief that hawks ate the plant to improve their eyesight. Although originally only native to Eurasia and North Africa, some species have since become established in other countries, including the United States and New Zealand. Recent research has shown that the genus ''Leontodon'' in the traditional delimitation is polyphyletic. Therefore, the former ''Leontodon'' subgenus ''Oporinia'' was raised to generic level. According to the nomenclatural rules the name '' Scorzoneroides'' has priority at generic level and therefore, the members of ''Leontodon'' subgenus ''Oporinia'' were transferred to the re-erected genus ''Scorzoneroides''. Ecology Seeds of ''Leontodon'' species are an important food source for certain bird species. Uses In Crete, the roots of the species '' Leontodon tuberosus'' are eaten raw and its leav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beech Tree
Beech (genus ''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to subtropical (accessory forest element) and temperate (as dominant element of mesophytic forests) Eurasia and North America. There are 14 accepted species in two distinct subgenera, ''Englerianae'' and ''Fagus''. The subgenus ''Englerianae'' is found only in East Asia, distinctive for its low branches, often made up of several major trunks with yellowish bark. The better known species of subgenus ''Fagus'' are native to Europe, western and eastern Asia and eastern North America. They are high-branching trees with tall, stout trunks and smooth silver-grey bark. The European beech ''Fagus sylvatica'' is the most commonly cultivated species, yielding a utility timber used for furniture construction, flooring and engineering purposes, in plywood, and household items. The timber can be used to build homes. Beechwood makes excellent firewood. Slats of washed beech wood are spread around the bottom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
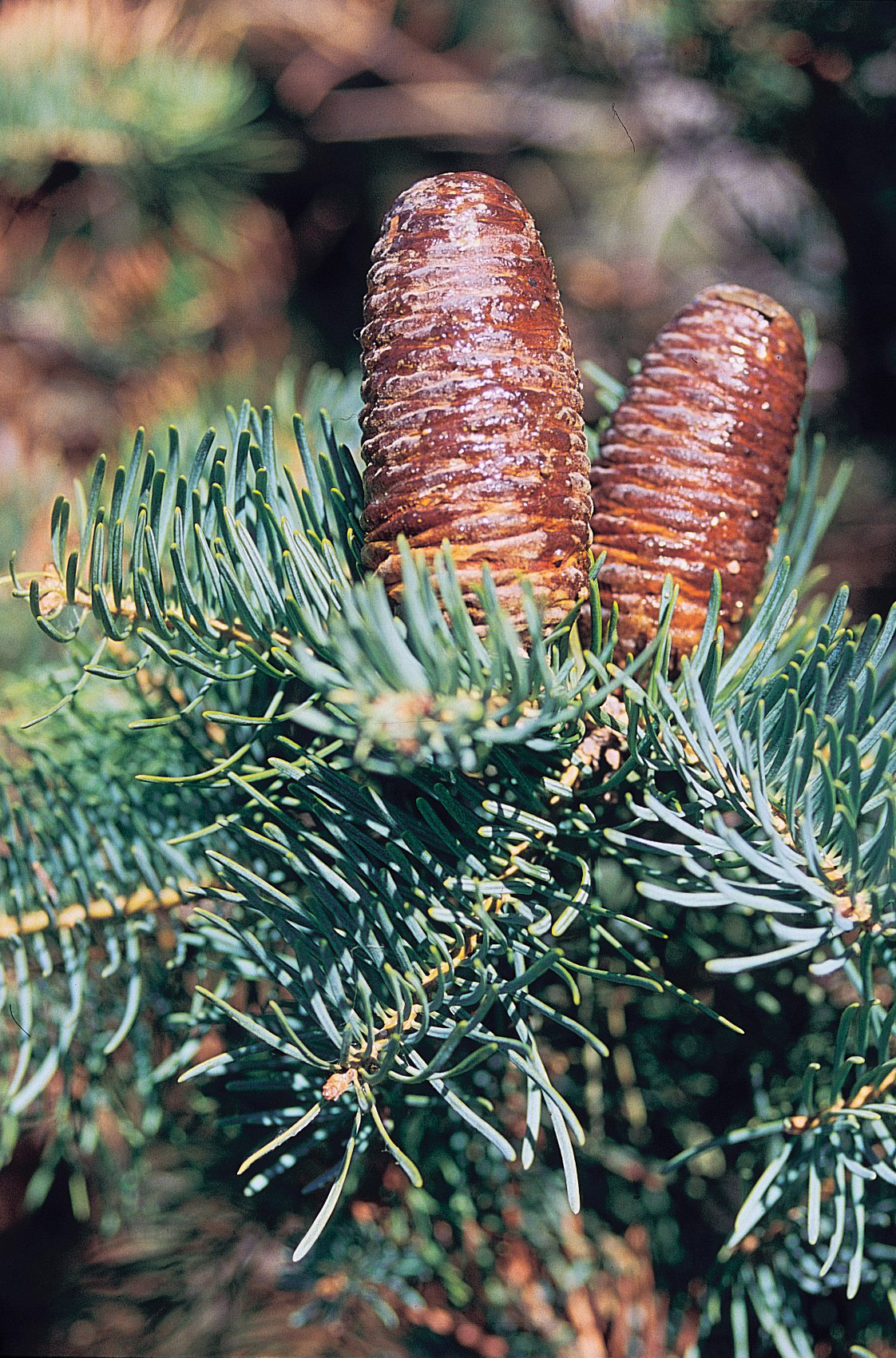
Spruce Fir
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' ( ), a genus of about 40 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Northern hemisphere. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Piceoideae. Spruces are large trees, from about 20 to 60 m (about 60–200 ft) tall when mature, and have whorled branches and conical form. Spruces can be distinguished from other genera of the family Pinaceae by their needles (leaves), which are four-sided and attached singly to small persistent peg-like structures ( pulvini or sterigmata) on the branches, and by their cones (without any protruding bracts), which hang downwards after they are pollinated. The needles are shed when 4–10 years old, leaving the branches rough with the retained pegs. In other similar genera, the branches are fairly smooth. Spruce are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera (moth and butterfly) species, such as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abies Concolor
''Abies concolor'', the white fir, concolor fir, or Colorado fir, is a coniferous tree in the pine family Pinaceae. This tree is native to the mountains of western North America, including the Sierra Nevada and southern Rocky Mountains, and into the isolated mountain ranges of southern Arizona, New Mexico, and Northern Mexico. It naturally occurs at elevations between . It is popular as an ornamental landscaping tree and as a Christmas tree. Description This large evergreen conifer grows best in the central Sierra Nevada of California, where the record specimen was recorded as tall and measured in diameter at breast height (dbh) in Yosemite National Park.American Forestry Association. 1978. National register of big trees. American Forests 84(4):19-47 The typical size of white fir ranges from tall and up to dbh. The largest specimens are found in the central Sierra Nevada, where the largest diameter recorded was found in Sierra National Forest at (1972); the west slope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tilia Platyphyllos
''Tilia platyphyllos'', the large-leaved lime or large-leaved linden, is a species of flowering plant in the family (biology), family Malvaceae (Tiliaceae). It is a deciduous tree, native plant, native to much of continental Europe as well as southwestern Great Britain, growing on Lime (mineral), lime-rich soils. The common names largeleaf linden and large-leaved linden are in standard use throughout the English-speaking world except in the British Isles, where it is known as large-leaved lime. The name "lime", possibly a corruption of "line" originally from "lind", has been in use for centuries and also attaches to other species of ''Tilia''. It is not, however, closely related to the lime (fruit), lime fruit tree, a species of citrus. The Binomial nomenclature, specific epithet ''platyphyllos'' (greek: πλατύφυλλος) means in greek "with broad leaves". Description ''Tilia platyphyllos'' is a narrowly domed tree with a moderate growth rate, and can eventually attain a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
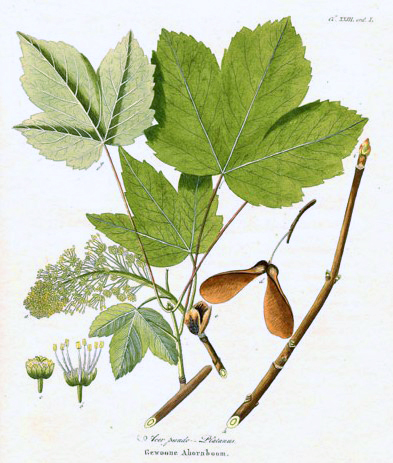
Acer Pseudoplatanus
''Acer pseudoplatanus'', known as the sycamore in the British Isles and as the sycamore maple in the United States, is a species of maple native to Central Europe and Western Asia. It is a large deciduous, broad-leaved tree, tolerant of wind and coastal exposure. Although native to an area ranging from France eastward to Ukraine, northern Turkey and the Caucasus, and southward to the mountains of Italy and northern Iberia, the sycamore establishes itself easily from seed and was introduced to the British Isles by 1500. It is now Naturalisation (biology), naturalised there and in other parts of Europe, North America, Australia and New Zealand, where it may become an invasive species. The sycamore can grow to a height of about and the branches form a broad, rounded Crown (botany), crown. The Bark (botany), bark is grey, smooth when young and later flaking in irregular patches. The leaves grow on long Petiole (botany), leafstalks and are large and List of botanical terms#palmate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conifers
Conifers () are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extant conifers are perennial woody plants with secondary growth. The majority are trees, though a few are shrubs. Examples include cedars, Douglas-firs, cypresses, firs, junipers, kauri, larches, pines, hemlocks, redwoods, spruces, and yews.Campbell, Reece, "Phylum Coniferophyta". ''Biology''. 7th ed. 2005. Print. p. 595. As of 2002, Pinophyta contained seven families, 60 to 65 genera, and more than 600 living species. Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are ecologically important. They are the dominant plants over large areas of land, most notably the taiga of the Northern Hemisphere, but also in similar cool climates in mountains further south. Boreal conifers have many wintertime adaptations. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Vegetation
Alpine plants are plants that grow in an alpine climate, which occurs at high elevation and above the tree line. There are many different plant species and taxa that grow as a plant community in these alpine tundra. These include perennial grasses, sedges, forbs, cushion plants, mosses, and lichens.. Alpine plants are adapted to the harsh conditions of the alpine environment, which include low temperatures, dryness, ultraviolet radiation, wind, drought, poor nutritional soil, and a short growing season. Some alpine plants serve as medicinal plants. Ecology Alpine plants occur in a tundra: a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees. Alpine tundra occurs in mountains worldwide. It transitions to subalpine forests below the tree line; stunted forests occurring at the forest-tundra ecotone are known as ''Krummholz''. With increasing elevation, it ends at the snow line where snow and ice persist through summer, also known as the Nival Zone. Alpine plants are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |