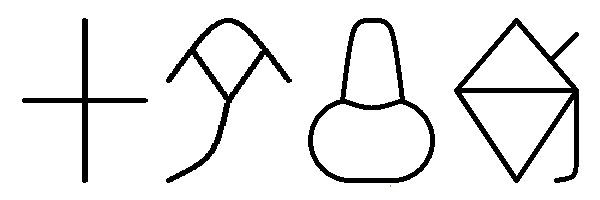|
Maurice Dunand
Maurice Dunand (4 March 1898 – 23 March 1987) was a prominent French archaeologist specializing in the ancient Near East, who served as director of the Mission Archéologique Française in Lebanon. Dunand excavated Byblos from 1924 to 1975, and published a Byblos syllabary in his monograph ''Byblia Grammata'' in 1945. The Neolithic of Lebanon was divided by Dunand into three stages based on the stratified levels of Byblos. From 1963 onwards, Dunand also thoroughly excavated the site of the Temple of Eshmun near Sidon. During the Lebanese Civil War Dunand left Lebanon, taking with him his archives, which he left to the University of Geneva, but which were returned to Lebanon in 2010. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was home to many cradles of civilization, spanning Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran (or Persia), Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. As such, the fields of ancient Near East studies and Near Eastern archaeology are one of the most prominent with regard to research in the realm of ancient history. Historically, the Near East denoted an area roughly encompassing the centre of West Asia, having been focused on the lands between Greece and Egypt in the west and Iran in the east. It therefore largely corresponds with the modern-day geopolitical concept of the Middle East. The history of the ancient Near East begins with the rise of Sumer in the 4th millennium BC, though the date that it ends is a subject of debate among scholars; the term covers the region's developments in the Bronze Age and the Iron Age, and is variously considered to end with either the establishment of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC, the establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west; Cyprus lies a short distance from the coastline. Lebanon has a population of more than five million and an area of . Beirut is the country's capital and largest city. Human habitation in Lebanon dates to 5000 BC. From 3200 to 539 BC, it was part of Phoenicia, a maritime civilization that spanned the Mediterranean Basin. In 64 BC, the region became part of the Roman Empire and the subsequent Byzantine Empire. After the seventh century, it Muslim conquest of the Levant, came under the rule of different Islamic caliphates, including the Rashidun Caliphate, Rashidun, Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid. The 11th century saw the establishment of Christian Crusader states, which fell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
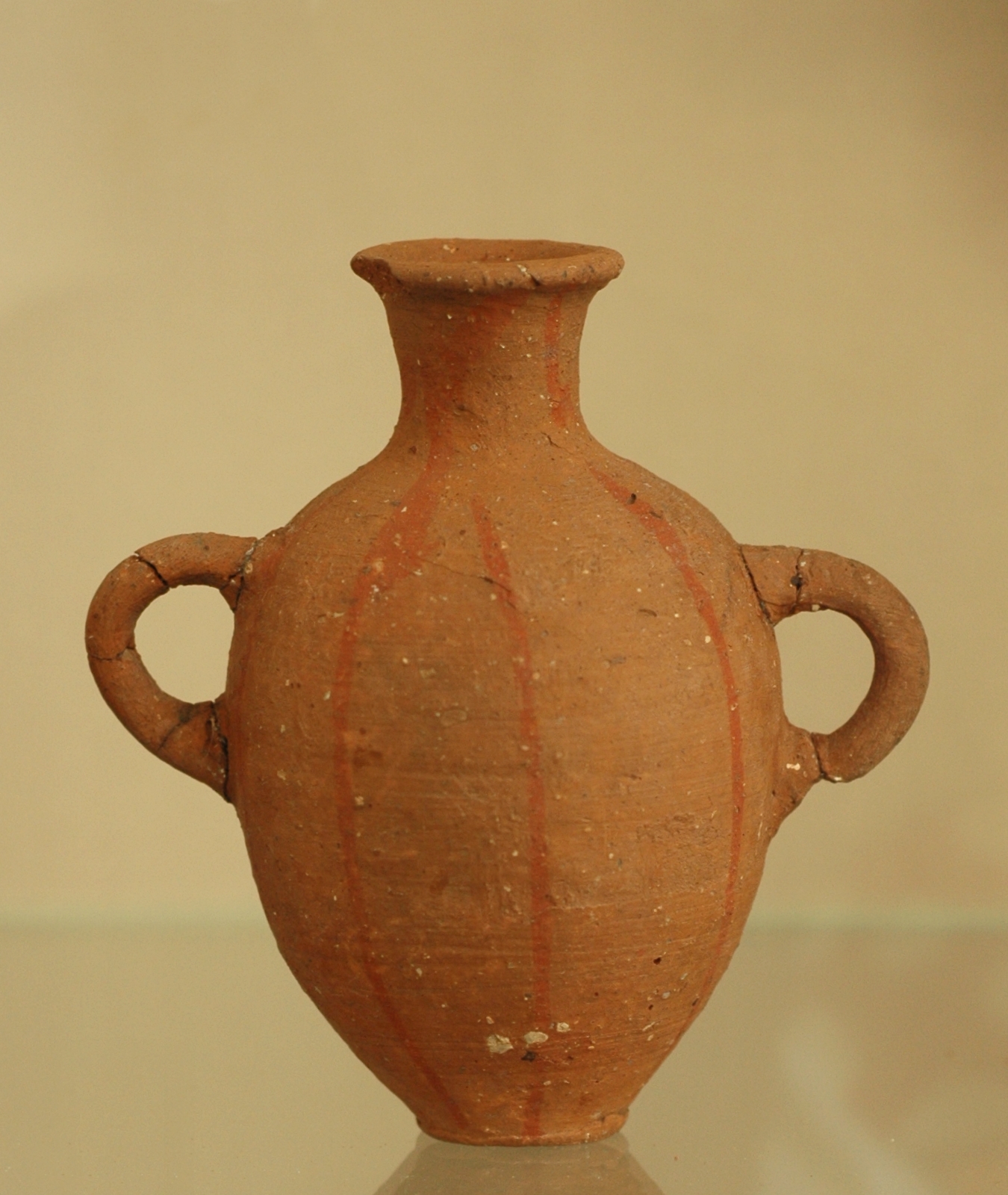
Byblos
Byblos ( ; ), also known as Jebeil, Jbeil or Jubayl (, Lebanese Arabic, locally ), is an ancient city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. The area is believed to have been first settled between 8800 and 7000BC and continuously inhabited since 5000BC. During its history, Byblos was part of numerous cultures including Old Kingdom of Egypt, Egyptian, Phoenician, Assyrian, Achaemenid Empire, Persian, Hellenistic period, Hellenistic, Roman Empire, Roman, Genoese Republic, Genoese, Mamluk Sultanate, Mamluk and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman. Urbanisation is thought to have begun during the third millennium BC when it developed into a city, making it one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, if not the oldest. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It was in Ancient Byblos that the Phoenician alphabet, likely the ancestor of the Greek alphabet, Greek, Latin and all other Western alphabets, was developed. Etymology The name appears as ''Keb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Pierre Thiollet
Jean-Pierre Thiollet (; born 9 December 1956) is a French writer and journalist. He is also affiliated with the European Confederation of Independent Trade Unions, a European trade union. Career Thiollet attended a school in Châtellerault, in Poitiers he attended classes préparatoires aux grandes écoles and acquired a degree in Parisian universities ( Pantheon-Sorbonne University, University of Paris III:Sorbonne Nouvelle, Paris-Sorbonne University). In 1978, he was admitted to Saint-Cyr (Coëtquidan), a French military academy. During the 1980s and early 1990s, he was a member of a French press organization that focused on music halls, the circus, dance and the arts. From 1982 to 1986, his telephone conversations with writer Jean-Edern Hallier were monitored as part of illegal wiretaps conducted during the presidency of François Mitterrand. In the late 1980s, he served as vice president of Amiic, a Geneva-based real estate investment organization. He was a lectur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byblos Syllabary
The Byblos script, also known as the Byblos syllabary, Pseudo-hieroglyphic script, Proto-Byblian, Proto-Byblic, or Byblic, is an undeciphered writing system, known from fourteen inscriptions found in Byblos, a coastal city in Lebanon. The inscriptions are engraved on bronze plates and spatulas, and carved in stone. They were excavated by Maurice Dunand, from 1928 to 1932, and published in 1945 in his monograph ''Byblia Grammata''. The inscriptions are conventionally dated to the second millennium BC, probably between the 18th and 15th centuries BC. Examples of the script have also been discovered in Egypt, Italy, and Megiddo (Garbini, Colless). Description of the script Fourteen inscriptions The Byblos script is usually written from right to left; word dividers are rarely used. Ten inscriptions were described by Dunand in 1945, named ''a'' to ''j'' in their order of discovery. They are: *Two rectangular bronze tablets, documents ''c'' (16×11 cm) and ''d'' (21×12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology Of Lebanon
Archaeology of Lebanon includes thousands of years of history ranging from Lower Palaeolithic, Phoenician, Ancient Rome, Roman, Arabs, Arab, Ottoman Empire, Ottoman, and Crusades periods. Notable findings and sites Lebanon features several important Paleolithic sites associated with Neanderthals. These include Adloun, Chekka Jdidé, El-Masloukh, Ksar Akil, Nahr Ibrahim and Naame.Kipfer, 2000, pp. 623, 632, 637, 647, 655. Byblos is a well-known archaeological site, a Phoenician seaport, where the tomb of Ahiram and the other Byblian royal inscriptions were found. An ancient Phoenician inscription on the tomb dates to between the 13th and 10th centuries BCE.Wedgeworth, 1993, p. 453. Byblos, as well as archaeological sites in Baalbek, Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre, Sidon, and Tripoli, Lebanon, Tripoli, contain artifacts indicating the presence of libraries dating back to the period of Classical antiquity. Industry names Lower Paleolithic industries of Lebanon have shown similarities to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Eshmun
The Temple of Eshmun () is an ancient place of worship dedicated to Eshmun, the Phoenician god of healing. It is located near the Awali (river), Awali river, northeast of Sidon in southwestern Lebanon. The site was occupied from the 7th century BC to the 8th century AD, suggesting an integrated relationship with the nearby city of Sidon. Although originally constructed by Sidonian king Eshmunazar II in the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid era ( 529–333 BC) to celebrate the city's recovered wealth and stature, the temple complex was greatly expanded by Bodashtart, Yatonmilk and later monarchs. Because the continued expansion spanned many centuries of alternating independence and foreign hegemony, the sanctuary features a wealth of different architectural and decorative styles and influences. The sanctuary consists of an esplanade and a grand court limited by a huge limestone terrace wall that supports a monumental podium which was once topped by Eshmun's Greco-Persian styl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidon
Sidon ( ) or better known as Saida ( ; ) is the third-largest city in Lebanon. It is located on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast in the South Governorate, Lebanon, South Governorate, of which it is the capital. Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre, to the south, and the Lebanese capital of Beirut, to the north, are both about away. Sidon has a population of about 80,000 within the city limits, while its metropolitan area has more than a quarter-million inhabitants. Etymology The Phoenician language, Phoenician name (, ) probably meant "fishery" or "fishing town". It is mentioned in Papyrus Anastasi I as ''ḏjdwnꜣ''. It appears in Biblical Hebrew as () and in Classical Syriac, Syriac as (). This was hellenization, Hellenised as (), which was latinization of names, Latinised as and entered English in this form. The name appears in Classical Arabic as () and in Modern Standard Arabic, Modern Arabic as (). As a Colonia (Roman), Roman colony, it was notionally refounded and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanese Civil War
The Lebanese Civil War ( ) was a multifaceted armed conflict that took place from 1975 to 1990. It resulted in an estimated 150,000 fatalities and led to the exodus of almost one million people from Lebanon. The religious diversity of the Lebanese people played a notable role in the lead-up to and during the conflict: Lebanese Christians and Lebanese Sunni Muslims comprised the majority in the coastal cities; Lebanese Shia Muslims were primarily based throughout southern Lebanon and in the Beqaa Valley in the east; and Lebanese Druze, Druze and Christians populated the country's mountainous areas. At the time, the Lebanese government was under the influence of elites within the Maronite Christian community. The link between politics and religion was reinforced under the Greater Lebanon, French Mandate from 1920 to 1943, and the country's parliamentary structure favoured a leading position for Lebanese Christians, who constituted the majority of the population. However, Leban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Geneva
The University of Geneva (French: ''Université de Genève'') is a public university, public research university located in Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded in 1559 by French theologian John Calvin as a Theology, theological seminary. It remained focused on theology until the 17th century, when it became a center for the Enlightenment, enlightenment scholarship. Today, it is the third largest university in Switzerland by number of students. In 1873, it dropped its religious affiliations and became officially secular. In 2009, the University of Geneva celebrated the 450th anniversary of its founding. Almost 40% of the students come from over 150 foreign countries. The university holds and actively pursues teaching, Research university, research, and community service as its primary objectives. The University of Geneva is a member of the League of European Research Universities, 4EU+ Alliance, Coimbra Group, International Forum of Public Universities, and European University A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loisin
Loisin (; ) is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France.Commune de Loisin (74150) INSEE It has approximately 1500 inhabitants. Monuments and places * Saint-Affre ChurchPolitics and administration Administrative situation In 1860 after the annexation from the , Loisin became part of the canton of Douvaine. Since 2015, it belongs to the canton of Sciez after the cantonal redistribution law from 2014. The commu ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |