|
Matilda Caragiu Marioțeanu
Matilda Caragiu Marioțeanu (20 July 1927 – 11 March 2009; ) was a Romanian linguist. She studied in the University of Bucharest, where she became a professor, having also taught at the University of Salzburg and the Goethe University Frankfurt as an invited professor. Caragiu Marioțeanu was the sister of actor Toma Caragiu and sculptor . Caragiu Marioțeanu published a multitude of works about the Romanian and Aromanian languages as well as about the Aromanians in general, having been one herself. Her ''Dodecalogue of the Aromanians'' played an important role for the plot of ''I'm Not Famous but I'm Aromanian'' (2013), the first film in Aromanian. She also collaborated in the publication of several manuals for learning Romanian, translated Aromanian fairy tales and stories into Romanian and wrote two volumes of Aromanian verses. For her research, Caragiu Marioțeanu became a titular member of the Romanian Academy and received the National Order of Merit in 2000. Biograp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argos Orestiko
Argos Orestiko (, before 1926: Χρούπιστα – ''Chroupista''; ) is a town and a municipality in the Kastoria regional unit of Macedonia, Greece. The Kastoria National Airport (also known as Aristotelis Airport) is located in Argos Orestiko. History Antiquity In antiquity, ''Argos Orestikon'' was the main town of the Orestae, in Upper Macedonia. It was said to have been founded by Orestes, the son of Agamemnon, who fled from Argos in the Peloponnese after the murder of his mother. The exact location of classical ''Argos Orestikon'' has not been found. Based on epigraphic evidence, the administrative centre of the Orestae lay near the centre of the present town Argos Orestiko, at a site named "Armenochori". During the campaign of Alexander the Great to the East, settlers from the town founded another Argos Orestikon to distant Scythian steppes during the 4th century BCE. Modern period At least since the 16th century, Argos Orestiko has a notable annual trade fair. Towa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Academy
The Romanian Academy ( ) is a cultural forum founded in Bucharest, Romania, in 1866. It covers the scientific, artistic and literary domains. The academy has 181 active members who are elected for life. According to its bylaws, the academy's main goals are the cultivation of Romanian language and Romanian literature, the study of the national history of Romania and research into major scientific domains. Some of the academy's fundamental projects are the Romanian language dictionary ('' Dicționarul explicativ al limbii române''), the dictionary of Romanian literature, and the treatise on the history of the Romanian people. History On the initiative of C. A. Rosetti, the Academy was founded on April 1, 1866, as ''Societatea Literară Română''. The founding members were illustrious members of the Romanian society of the age. The name changed to ''Societatea Academică Romînă'' in 1867, and finally to ''Academia Română'' in 1879, during the reign of Carol I. The foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
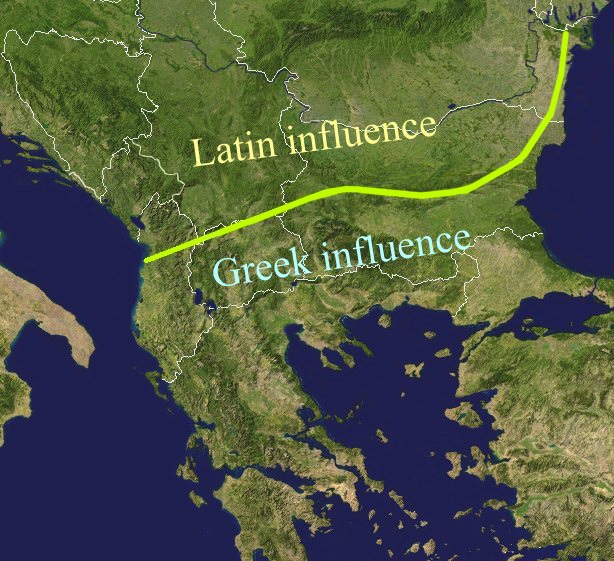
History Of The Romanian Language
The history of the Romanian language started in Roman provinces north of the Jireček Line in Classical antiquity. There are three main hypotheses around its exact territory: the autochthony thesis (it developed in left-Danube Dacia only), the discontinuation thesis (it developed in right-Danube provinces only), and the "as-well-as" thesis that supports the language development on both sides of the Danube. Between the 6th and 8th centuries AD, following the accumulated tendencies inherited from the Vulgar Latin, vernacular Latin and, to a much smaller degree, the influences from an Substrate in Romanian, unidentified substratum, and in the context of a lessened power of the Roman central authority, the language evolved into Common Romanian. This proto-language then came into close contact with the Slavic migrations to the Balkans, Slavic languages and subsequently divided into Aromanian language, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian language, Megleno-Romanian, Istro-Romanian language, Istro- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seminar
A seminar is a form of academic instruction, either at an academic institution or offered by a commercial or professional organization. It has the function of bringing together small groups for recurring meetings, focusing each time on some particular subject, in which everyone present is requested to participate. This is often accomplished through an ongoing Socratic method, Socratic dialogue with a seminar leader or instructor, or through a more formal presentation of research. It is essentially a place where assigned readings are discussed, questions can be raised and debates can be conducted. Etymology The word ''seminar'' was borrowed from German (in which it is capitalized as ), and is ultimately derived from the Latin word , meaning 'seed plot' (an old-fashioned term for 'seedbed'). Its Root (linguistics), root word is (Latin for 'seed'). Overview In some European universities, a ''seminar'' may be a large lecture course, especially when conducted by a renowned thinker ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Course (education)
In higher education, a course is a unit of teaching that typically lasts one academic term, is led by one or more instructors (teachers or professors), and has a fixed roster of students. A course usually covers an individual subject. Courses generally have a fixed program of sessions every week during the term, called lessons or classes. Students may receive a Grading in education, grade and academic Credit (education), credit after completion of the course."course" in ''Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary''. Retrieved 15 August 2008. Courses can either be compulsory material or "elective". An elective is usually not a required course, but there are a certain number of non-specific electives that are required for certain academic major, majors. The entire collection of courses required to complete an academic degree is called a ''undergraduat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silistra
Silistra ( ; ; or ) is a town in Northeastern Bulgaria. The town lies on the southern bank of the lower Danube river, and is also the part of the Romanian border where it stops following the Danube. Silistra is the administrative center of the Silistra Province and one of the important towns of the historical region of Dobruja. Silistra is a major cultural, industrial, transportation, and educational center of Northeastern Bulgaria. There are many historical landmarks including a richly-decorated Late Roman tomb, remains of the medieval fortress, an Ottoman fort, and an art gallery. Etymology The name Silistra is possibly derived from the root of the old Thracian name of the lower part of the Danube " Istrum". The name of the city is given as ''Silistria'' in the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Eleventh Edition. Geography Silistra is in the northeastern part of Bulgaria on the southern bank of the Danube River. It is located in the Bulgarian part of Dobruja. The munici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
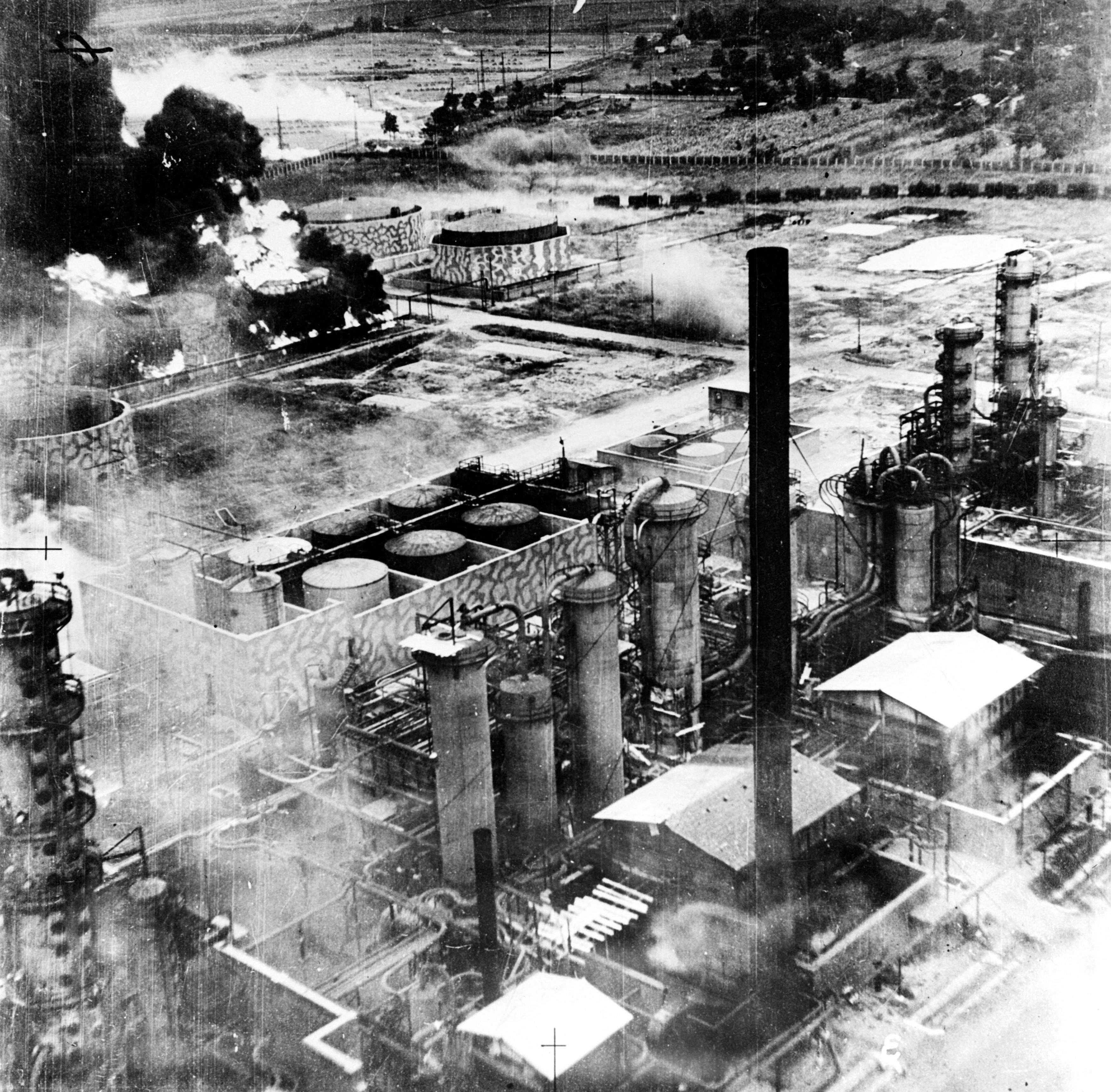
Ploiești
Ploiești ( , , ), formerly spelled Ploești, is a Municipiu, city and county seat in Prahova County, Romania. Part of the historical region of Muntenia, it is located north of Bucharest. The area of Ploiești is around , and it borders the Blejoi commune in the north, Bărcănești, Prahova, Bărcănești and Brazi communes in the south, Târgșoru Vechi commune in the west, and Bucov and Berceni, Prahova, Berceni communes in the east. According to the 2021 Romanian census, 2021 census, Ploiești is the List of cities and towns in Romania, tenth most populous city in the country with a population of 180,540. The city grew beginning with the 17th century on an estate bought by ruler Michael the Brave from the local landlords, gradually replacing nearby Wallachian fairs of Târgșor, Gherghița, and Bucov. Its development was accelerated by heavy industrialisation during the mid-19th century, with the world's first large-scale oil refinery, petroleum refinery being opened between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacău
Bacău ( ; , ; ; ) is the main city in Bacău County, Romania. With a population of 136,087 (as of 2021 census), Bacău is the 14th largest city in Romania. The city is situated in the historical region of Moldavia, at the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains, and on the Bistrița River (which meets the Siret River about to the south of Bacău). The Ghimeș Pass links Bacău to the region of Transylvania. Etymology The town's name, which features in Old Church Slavonic documents as ''Bako'', ''Bakova'' or ''Bakovia'', comes most probably from a personal name of Hungarian origin. Men bearing the name Bakó or Bako are documented in medieval TransylvaniaRădvan 2010, p. 456. and in 15th-century Bulgaria, but according to Victor Spinei the name itself is of Turkicmost probably of Cuman or Pechenegorigin. Nicolae Iorga believes that the city's name is of Hungarian origin (as Adjud and Sascut). Another theory suggests that the town's name has a Slavic origin, pointing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oltenița
Oltenița () is a Municipiu, city in Călărași County, Muntenia, Romania, on the left bank of the river Argeș (river), Argeș, where its waters flow into the Danube. Geography The city is located in the southwestern part of the county; it stands across the Danube from the Bulgarian city of Tutrakan. The Roads in Romania, national road DN4 connects Oltenița to Bucharest, to the northwest. Road connects it to the county seat, Călărași, to the east, and road connects it to Giurgiu, to the west. The Oltenița train station, located near the intersection of those three roads, serves the Căile Ferate Române, CFR Căile Ferate Române Line 800, Line 801, which connects the city to Bucharest (Titan Sud and Obor stations). History Excavations on Gumelnița-Karanovo culture, Gumelnița hill near the city revealed a Neolithic settlement dating from the 4th millennium BC. The first mention of a town bearing the name Oltenița appears in 1515 during the reign of Neagoe Basa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Bulgaria
The Tsardom of Bulgaria (), also known as the Third Bulgarian Tsardom (), usually known in English as the Kingdom of Bulgaria, or simply Bulgaria, was a constitutional monarchy in Southeastern Europe, which was established on , when the Bulgarian state was raised from a Principality of Bulgaria, principality to a tsardom. Prince Ferdinand I of Bulgaria, Ferdinand, founder of the Bulgarian royal family, royal family, was crowned as Tsar of Bulgaria, tsar at the Declaration of Independence, mainly because of his military plans and for seeking options for unification of all lands in the Balkans region with an ethnic Bulgarian majority (lands that had been seized from Bulgaria and given to the Ottoman Empire in the Treaty of Berlin (1878), Treaty of Berlin). He and his successors were reckoned as kings internationally. The state was almost constantly at war throughout its existence, lending to its nickname as "the Balkan Prussia". For several years Bulgaria mobilized an army of more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Exchange Between Bulgaria And Romania
The population exchange between Bulgaria and Romania was a population exchange carried out in 1940 after the transfer of Southern Dobruja to Bulgaria by Romania. It involved 103,711 Romanians, Aromanians and Megleno-Romanians living in Southern Dobruja and 62,278 Bulgarians from Northern Dobruja. After this operation, the application of a population exchange in other cases such as Transylvania was considered. History In 1913, the Kingdom of Romania conquered Southern Dobruja after the Kingdom of Bulgaria, Bulgarian defeat in the Second Balkan War. The country had already acquired Northern Dobruja in 1878. This sparked revisionist feelings in Bulgaria. Following the Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina, occupation of the Romanian regions of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina by the Soviet Union in June 1940, Romania sought protection among the Axis powers, but it was demanded to first resolve its territorial disputes with its neighbors. Thus, on 30 August, Romania ced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Dobruja
Southern Dobruja or South Dobruja ( or simply , ; or , ), also the Quadrilateral (), is an area of north-eastern Bulgaria comprising Dobrich and Silistra provinces, part of the historical region of Dobruja. It has an area of 7,412 square km and a population of 358,000. It is historically noteworthy as a point of contention in Bulgarian-Romanian relations. Part of Bulgaria between 1878 and 1913, the region was annexed by Romania in the Treaty of Bucharest (1913), targeted by Bulgaria during World War I (1914–18), and subsequently remained Romanian until 1940, when Bulgaria regained control in the Treaty of Craiova, which went along with a compulsory population exchange. Southern Dobruja has been part of Bulgaria since 1940. History At the beginning of the modern era, Southern Dobruja had a mixed population of Bulgarians and Turks with several smaller minorities, including Gagauz, Crimean Tatars and Romanians. In 1910, of the 282,007 inhabitants of Southern Dobruja, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |