|
Manne Siegbahn
Karl Manne Georg Siegbahn (; 3 December 1886 – 26 September 1978) was a Swedish physicist who received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1924 "for his discoveries and research in the field of X-ray spectroscopy". Biography Siegbahn was born in Örebro, Sweden, the son of Georg Siegbahn and his wife, Emma Zetterberg. He graduated in Stockholm 1906 and began his studies at Lund University in the same year. During his education he was secretarial assistant to Johannes Rydberg. In 1908 he studied at the University of Göttingen. He obtained his doctorate (PhD) at the Lund University in 1911, his thesis was titled ''Magnetische Feldmessungen'' (magnetic field measurements). He became acting professor for Rydberg when his (Rydberg's) health was failing, and succeeded him as full professor in 1920. However, in 1922 he left Lund for a professorship at Uppsala University. In 1937, Siegbahn was appointed Director of the Physics Department of the Nobel Institute of the Royal Swedish Academy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Örebro
Örebro ( ; ) is the seventh-largest city in Sweden, the seat of Örebro Municipality, and capital of Örebro County. It is situated by the Närke Plain, near the lake Hjälmaren, a few kilometers inland along the small river Svartån, and has a population of approximately 126,000 in the city proper. It is one of the largest inland hubs of the country, and a major logistic and commercial operating site. Örebro is home to Örebro University, a major university hospital, a medieval castle, the water park Gustavsvik as well as several large shopping malls and the Oset and Rynningeviken Nature Reserve adjacent to lake Hjälmaren. Örebro is a trade and logistics city with a strategic location 200 km from Stockholm, 330 km from Oslo and 280 km from Gothenburg. The city is served by Örebro Airport 10 km (6 mi) southwest of the city, and by Örebro Central Station, serviced by the Mälaren Line and Western Main Line. Etymology The name ''Örebro'' refers to a bridg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Johannes Rydberg
Johannes (Janne) Robert Rydberg (; 8 November 1854 – 28 December 1919) was a Swedish physicist mainly known for devising the Rydberg formula, in 1888, which is used to describe the wavelengths of photons (of visible light and other electromagnetic radiation) emitted by changes in the energy level of an electron in a hydrogen atom. Biography Rydberg was born 8 November 1854 in Halmstad in southern Sweden, the only child of Sven Rydberg and Maria Anderson Rydberg. When he was 4 years old his father died, and the family was forced to live on a small income. In 1873 he graduated from Halmstads elementärläroverk, where he received high grades in maths and physics. Later that year he enrolled in Lund University, and two years later he was awarded his bachelor's degree. In 1879 he was awarded his Doctor of Philosophy with his dissertation "Konstruktioner af kägelsnitt i 3- och 4-punktskontakt". Rydberg began his career as an amanuensis in the institution. He became a docent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Streets At CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research ( CERN) is an international, intergovernmental organisation. Its activities are carried out on land placed at its disposal by the Canton of Geneva, the Swiss Confederation and France France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan .... In accordance with the agreements reached between France, Switzerland and CERN governing the organisation's legal status, the CERN site is placed under the authority and control of the Director-General as the organisation's chief executive officer. The latter is thus empowered to issue internal rules applicable to all persons entering the CERN site and intended to establish thereon the conditions necessary for the exercise of its functions. CERN street names were for a long time an internal matter to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atomic Physics
Atomic physics is the field of physics that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus. Atomic physics typically refers to the study of atomic structure and the interaction between atoms. It is primarily concerned with the way in which electrons are arranged around the nucleus and the processes by which these arrangements change. This comprises ions, neutral atoms and, unless otherwise stated, it can be assumed that the term ''atom'' includes ions. The term ''atomic physics'' can be associated with nuclear power and nuclear weapons, due to the synonymous use of ''atomic'' and ''nuclear'' in standard English. Physicists distinguish between atomic physics—which deals with the atom as a system consisting of a nucleus and electrons—and nuclear physics, which studies nuclear reactions and special properties of atomic nuclei. As with many scientific fields, strict delineation can be highly contrived and atomic physics is often considered in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is the foundation of all quantum physics, which includes quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Quantum mechanics can describe many systems that classical physics cannot. Classical physics can describe many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic and Microscopic scale, (optical) microscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at very small submicroscopic (atomic and subatomic) scales. Classical mechanics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation that is valid at ordinary scales. Quantum systems have Bound state, bound states that are Quantization (physics), quantized to Discrete mathematics, discrete values of energy, momentum, angular momentum, and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electron Shell
In chemistry and atomic physics, an electron shell may be thought of as an orbit that electrons follow around an atom's nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the "1 shell" (also called the "K shell"), followed by the "2 shell" (or "L shell"), then the "3 shell" (or "M shell"), and so on further and further from the nucleus. The shells correspond to the principal quantum numbers (''n'' = 1, 2, 3, 4 ...) or are labeled alphabetically with the letters used in X-ray notation (K, L, M, ...). Each period on the conventional periodic table of elements represents an electron shell. Each shell can contain only a fixed number of electrons: the first shell can hold up to two electrons, the second shell can hold up to eight electrons, the third shell can hold up to 18, continuing as the general formula of the ''n''th shell being able to hold up to 2( ''n''2) electrons. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spectral Line
A spectral line is a weaker or stronger region in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum. It may result from emission (electromagnetic radiation), emission or absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to identify atoms and molecules. These "fingerprints" can be compared to the previously collected ones of atoms and molecules, and are thus used to identify the atomic and molecular components of stars and planets, which would otherwise be impossible. Types of line spectra Spectral lines are the result of interaction between a Quantum mechanics, quantum system (usually atoms, but sometimes molecules or atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei) and a single photon. When a photon has about the right amount of photon energy, energy (which is connected to its frequency) to allow a change in the energy state of the system (in the case of an atom this is usually an electron cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
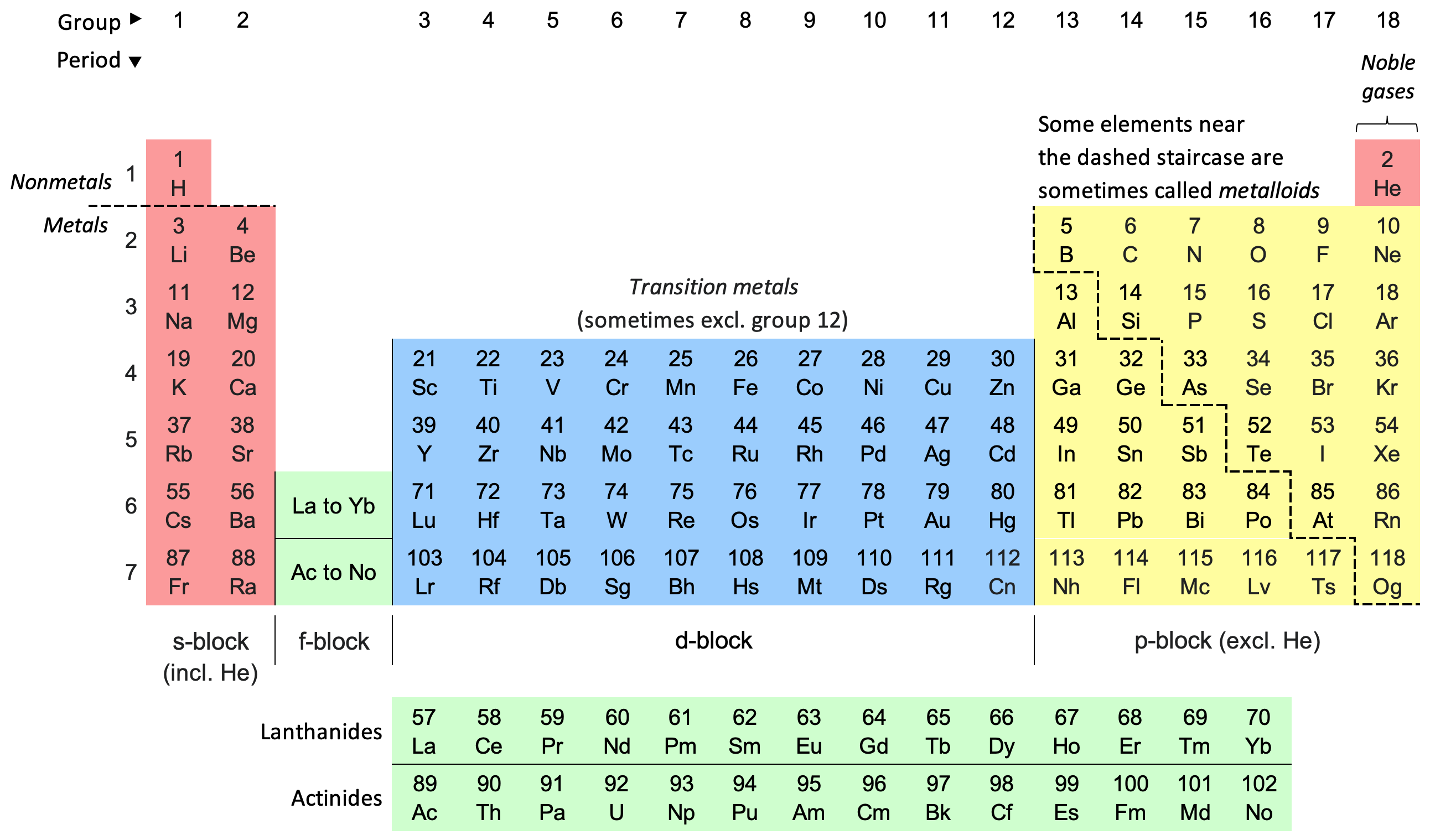
Periodic System
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows ("Period (periodic table), periods") and columns ("Group (periodic table), groups"). It is an Cultural icon, icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the Periodic trends, periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate periodic function, recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called block (periodic table), blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal Periodic trends, trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetal (chemistry), Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chemical Element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its atomic nucleus, nucleus. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, known as isotopes of the element. Two or more atoms can combine to form molecules. Some elements form Homonuclear molecule, molecules of atoms of said element only: e.g. atoms of hydrogen (H) form Diatomic molecule, diatomic molecules (H). Chemical compounds are substances made of atoms of different elements; they can have molecular or non-molecular structure. Mixtures are materials containing different chemical substances; that means (in case of molecular substances) that they contain different types of molecules. Atoms of one element can be transformed into atoms of a different element in nuclear reactions, which change an atom's at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves), phase'' on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings. Wavelength is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The multiplicative inverse, inverse of the wavelength is called the ''spatial frequency''. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter lambda (''λ''). For a modulated wave, ''wavelength'' may refer to the carrier wavelength of the signal. The term ''wavelength'' may also apply to the repeating envelope (mathematics), envelope of modulated waves or waves formed by Interference (wave propagation), interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed phase velocity, wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Henry Moseley
Henry Gwyn Jeffreys Moseley (; 23 November 1887 – 10 August 1915) was an English physicist, whose contribution to the science of physics was the justification from physical laws of the previous empirical and chemical concept of the atomic number. This stemmed from his development of Moseley's law in X-ray spectra. Moseley's law advanced atomic physics, nuclear physics and quantum physics by providing the first experimental evidence in favour of Niels Bohr's theory, aside from the hydrogen atom spectrum which the Bohr theory was designed to reproduce. That theory refined Ernest Rutherford's and Antonius van den Broek's model, which proposed that the atom contains in its nucleus a number of positive nuclear charges that is equal to its (atomic) number in the periodic table. When World War I broke out in Western Europe, Moseley left his research work at the University of Oxford behind to volunteer for the Royal Engineers of the British Army. Moseley was assigned to the force o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |