|
Manfred Böckl
Manfred Böckl (born 2 September 1948) is a German writer who specialises in historical fiction. Since the 1980s, he has written novels that often revolve around Bavaria, crime, abuse of power and historical renegades and seers. He had a local breakthrough in 1991 with a novel about the Bavarian prophet Mühlhiasl. A recurring subject in Böckl's works is Celtic culture and he practices Celtic neopaganism. Early life and education Manfred Böckl was born in Landau an der Isar in Bavaria on 2 September 1948. He had a Catholic father and an Evangelical mother. He studied German studies, geography, jurisprudence, history, philosophy, literature, psychology and theology at the University of Regensburg without finishing a degree. From 1973 to 1976 he worked as an editor at the '' Passauer Neue Presse'' and after that as a freelance writer. Literary career Böckl debuted as a writer in 1966 when he had a novella published. From 1980 to 1984, he published a series of young adult nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landau An Der Isar
] Landau an der Isar (, ; Central Bavarian: ''Landa an da Isar'') is the second-largest town in the Lower Bavaria, Lower Bavarian district, or ''Landkreis'', of Dingolfing-Landau, in the state of Bavaria, Germany. It lies on the river Isar, 120 km downstream from Munich. In 2020, its population was around 14,000. History Landau was founded in 1224 by the Wittelsbach Louis I, Duke of Bavaria, Ludwig I, Duke of Bavaria. The town had been a ''Pflegamt'' for many years and belonged to the Landshut ' of the Electorate-Principality (''Kurfürstentum'') of Bavaria. Landau possessed a town court with broad magisterial powers (Landgericht). Until the Bavarian county reform, or ''Kreisreform'' in German, in 1972, Landau was the district seat (''Kreisstadt'') of its own Landkreis, having the license plate code LAN. In the reform, the former townships of Frammering, Mettenhausen, Reichersdorf and Zeholfing, along with parts of the townships of Kammern and Ganacker, were merged with the tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathias Kneißl
Mathias Kneißl) n English: "Kneissel" known as Robber Kneissl (in German Räuber Kneißl, in Austro-Bavarian Raiba Kneißl), (4 August 1875 in Unterweikertshofen – 21 February 1902) was a German outlaw, poacher and popular antihero in the Bavarian folklore of the Dachau district when the Kingdom of Bavaria was part of the German Empire. Chased by scores of green-uniformed rural policemen, who were already widely considered to be corrupt and who were further disliked for being Franconians who could not speak the local Upper Bavarian dialect, Kneissl became a folk hero to the local population because of his repeated humiliations of the police. According to German forensic scientist Mark Benecke, Mathias Kneissl never saw himself as a Robin Hood figure and was, in reality, "just a man who went astray with no way of getting back." Early life Mathias Kneissl was born on 4 August, 1875, as the eldest of six children of a poor innkeeper. In 1886 his parents, who were later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mittelbayerische Zeitung
''Mittelbayerische Zeitung'' is a regional newspaper for Bavaria, Germany, founded in 1945 by Karl Friedrich Esser. Headquartered in Regensburg, the paper employs 550 and is owned by Mittelbayerischer Verlag KG. The online version can be reached at ''mittelbayerische.de''. There is a paywall A paywall is a method of restricting access to content (media), content, with a purchase or a subscription business model, paid subscription, especially news. Beginning in the mid-2010s, newspapers started implementing paywalls on their website ... installed, but four articles per month are free. References External links * Mittelbayerischer Verlag 1945 establishments in Germany German-language newspapers Mass media in Regensburg Newspapers published in Germany Newspapers established in 1945 {{Germany-newspaper-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angela Merkel
Angela Dorothea Merkel (; ; born 17 July 1954) is a German retired politician who served as Chancellor of Germany from 2005 to 2021. She is the only woman to have held the office. She was Leader of the Opposition from 2002 to 2005 and Leader of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) from 2000 to 2018. Merkel was born in Hamburg in West Germany. Her family moved to East Germany when she was an infant. Merkel obtained a doctorate in quantum chemistry in 1986 and worked as a research scientist until 1989. She then entered politics in the wake of the Revolutions of 1989, briefly serving as deputy spokeswoman for the first democratically elected government of East Germany, led by Lothar de Maizière. Following German reunification in 1990, Merkel was elected to the Bundestag for the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. As the protégée of Chancellor Helmut Kohl, Merkel was appointed as Minister for Women and Youth in 1991, later becoming Minister for the Environment, Nature Conserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
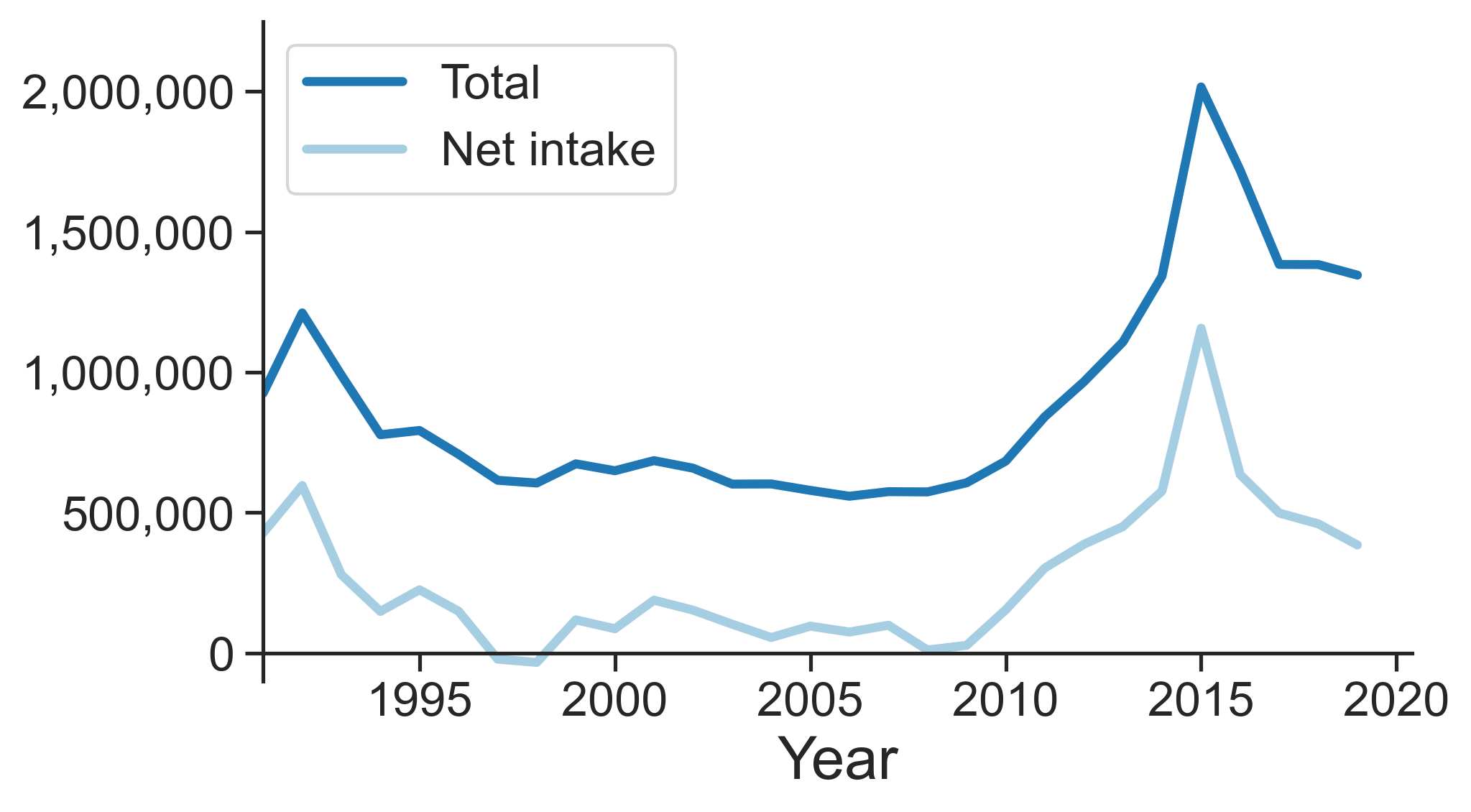
Immigration To Germany
Immigration to Germany, both in the country's modern borders and the many political entities that preceded it, has occurred throughout the country's history. Today, Germany is one of the most popular destinations for immigrants in the world, with well over 1 million people moving there each year since 2013. As of 2024, around List of sovereign states by immigrant and emigrant population, 16.8 million people living in Germany, or about 20% of the population, are Immigrant generations, first-generation immigrants, while the population share with a Migration background, migrant background in the wider sense was almost 30%. Even before Germany's formal Unification of Germany, founding in 1871, its predecessor states, such as the Holy Roman Empire and the German Confederation, were common destinations for the persecuted or migrant workers. Early examples include Protestants seeking religious freedom and refugees from the partitions of Poland. Jewish migrants, mostly from Eastern Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutschlandfunk Kultur
Deutschlandfunk Kultur (; abbreviated to ''DLF Kultur'' or ''DKultur'') is a culture-oriented radio station and part of Deutschlandradio, a set of three national radio stations in Germany. Initially named ''DeutschlandRadio Berlin'', the station was renamed ''Deutschlandradio Kultur'' on 1 April 2005. The present name was adopted on 1 May 2017. The station's studios are in what was the RIAS building at Hans-Rosenthal-Platz in Schöneberg, Berlin. History Deutschlandfunk Kultur's roots go back to the first Deutschlandsender, set up in 1926. After World War II, ''Deutschlandsender'' became the main national radio station of the German Democratic Republic (GDR), with programming aimed at all of Germany. In the 1970s it was merged with the main Berlin station ''Berliner Welle'' and renamed ''Stimme der DDR'' - "Voice of the GDR". It lasted until February 1990 when it again became ''Deutschlandsender'', and in May 1990 it merged with Radio DDR 2. The merged entity was named ''Deu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Druid
A druid was a member of the high-ranking priestly class in ancient Celtic cultures. The druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. While they were reported to have been literate, they are believed to have been prevented by doctrine from recording their knowledge in written form. Their beliefs and practices are attested in some detail by their contemporaries from other cultures, such as the Romans and the Greeks. The earliest known references to the druids date to the 4th century BC. The oldest detailed description comes from Julius Caesar's ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (50s BC). They were described by other Roman writers such as Cicero, Cicero (44) I.XVI.90. Tacitus, and Pliny the Elder. Following the Roman invasion of Gaul, the druid orders were suppressed by the Roman government under the 1st-century AD emperors Tiberius and Claudius, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple Deity
A triple deity is a deity with three apparent forms that function as a singular whole. Such deities may sometimes be referred to as threefold, tripled, triplicate, tripartite, triune, triadic, or as a trinity. The number three has a long history of mythical associations and triple deities are common throughout world mythology. Carl Jung considered the arrangement of deities into triplets an archetype in the history of religion. In classical religious traditions, three separate beings may represent either a triad who typically appear as a group (the Greek Moirai, Charites, and Erinyes; the Norse Norns; or the Irish Morrígan), or a single deity notable for having three aspects (Greek Hecate, Roman Diana).Virgil addresses Hecate as ''tergemina Hecate, tria virginis, ora Dianae'' (''Aeneid'', 4.511). Trinitarian Christianity instead recognizes three " divine persons" in God the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit, which are usually distinguished from the idea of independ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boudica
Boudica or Boudicca (, from Brittonic languages, Brythonic * 'victory, win' + * 'having' suffix, i.e. 'Victorious Woman', known in Latin chronicles as Boadicea or Boudicea, and in Welsh language, Welsh as , ) was a queen of the Iceni, ancient British Iceni tribe, who led a Boudican revolt, failed uprising against the Roman Britain, conquering forces of the Roman Empire in AD 60 or 61. She is considered a British national heroine and a symbol of the struggle for justice and independence. Boudica's husband Prasutagus, with whom she had two daughters, ruled as a nominally independent ally of Rome. He left his kingdom jointly to his daughters and to the Roman emperor in his Will and testament, will. When he died, his will was ignored, and the kingdom was annexed and his property taken. According to the Roman historian Tacitus, Boudica was Flagellation, flogged and her daughters wartime sexual violence, raped. The historian Cassius Dio wrote that previous imperial donations to influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myrddin Wyllt
Myrddin Wyllt (—"Myrddin the Wild", , ) is a figure in medieval Welsh legend. In Middle Welsh poetry he is accounted a chief bard, the speaker of several poems in The Black Book of Carmarthen and The Red Book of Hergest. He is called ''Wyllt''—"the Wild"—by Elis Gruffydd, and elsewhere ''Myrddin Emrys'' ("Ambrosius"), ''Merlinus Caledonensis'' ("of Caledonia") or ''Merlin Sylvestris ''("of the woods").Seymour, Page 9 Myrddin Wylt was born in 540 CE. Although his legend centres on a known Celtic theme, Myrddin's legend is rooted in history, for he is said to have gone mad after the Battle of Arfderydd ( Arthuret) at which Rhydderch Hael of Strathclyde defeated the Brythonic king Gwenddoleu. According to the ''Annales Cambriae'' this took place in 573. Myrddin fled into the forest, lived with the beasts and received the gift of prophecy. Myrddin Wyllt's legend closely resembles that of a north-British figure called Lailoken, which appears in Jocelyn of Furness' 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Süddeutsche Zeitung
The ''Süddeutsche Zeitung'' (; ), published in Munich, Bavaria, is one of the largest and most influential daily newspapers in Germany. The tone of ''SZ'' is mainly described as centre-left, liberal, social-liberal, progressive-liberal, and social-democrat. It is considered one of Germany's newspapers of record. The Süddeutsche Zeitung was one of the first daily newspapers approved by the Allies after World War II and was first published on 6 October 1945. The newspaper is published by ''Süddeutsche Verlag'' in Munich. It is majority owned by investment holdings and a small part by the original publishing family, the Friedmann family. The editors-in-chief are Wolfgang Krach and Judith Wittwer. The chairman of the editorial board is Thomas Schaub. History 20th century On 6 October 1945, five months after the end of World War II in Germany, the ''SZ'' was the first newspaper to receive a license from the U.S. military administration of Bavaria. The first issue was publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig II Of Bavaria
Ludwig II (Ludwig Otto Friedrich Wilhelm; 25 August 1845 – 13 June 1886), also called the Swan King or the Fairy Tale King (), was King of Bavaria from 1864 until his death in 1886. He also held the titles of Count Palatine of the Rhine, Duke of Bavaria, Duke of Franconia, and Duke in Swabia. Outside Germany, he is at times called "the Mad King" or Mad King Ludwig. Ludwig ascended to the throne in 1864 at the age of 18. He increasingly withdrew from day-to-day affairs of state in favour of extravagant artistic and architectural projects. He commissioned the construction of lavish palaces: Neuschwanstein Castle, Linderhof Palace, and Herrenchiemsee. He was also a devoted patron of the composer Richard Wagner. Ludwig spent all his own private royal revenues (although not state funds as is commonly thought) on these projects, borrowed extensively, and defied all attempts by his ministers to restrain him. This extravagance was used against him to declare him insane, a determination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |