|
Mahmud I
Mahmud I (, ; 2 August 1696 13 December 1754), known as Mahmud the Hunchback, was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1730 to 1754. He took over the throne after the quelling of the Patrona Halil rebellion. His reign was marked by wars in Persia and conflicts in Europe. He delegated government affairs to his viziers and devoted time to writing poetry. Nader Shah's devastating campaign weakened the Mughal Empire and created the opportunity for Mahmud I to initiate war with cooperation from Muhammad Shah. The alliance ended with the latter's death, leading to tensions between the Afsharids and the Ottomans. In 1748, he outlawed Freemasonry within the Ottoman Empire.Layiktez, CecilFreemasonry in the Islamic World, Pietre-Stones Review of Freemasonry, 1996 Early life He was born at Edirne Palace on 2 August 1696, the son of Mustafa II (1664–1703); his mother was Saliha Sultan (mother of Mahmud I), Saliha Sultan. Mahmud I was the older half-brother of Osman III (1754–57). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Custodian Of The Two Holy Mosques
His Majesty the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques (abbreviated as CTHM; ), or Protector of the Two Holy Cities, is a Royal and noble styles, royal style that has been used officially by the King of Saudi Arabia, monarchs of Saudi Arabia since 1986. The title has historically been used by many Muslim rulers in the past, including the Ayyubid dynasty, Ayyubids, the Mamluk Sultanate, Mamluks, the List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans and the Sharifate of Mecca, Sharifain rulers of Hejaz. The title was sometimes regarded to denote the ''de facto'' Caliph of Islam, but it mainly refers to the ruler taking the responsibility of guarding and maintaining the two Holiest sites in Islam, holiest mosques in Islam: Masjid al-Haram, Al-Haram Mosque (, 'The Sacred Mosque') in Mecca and the Prophet's Mosque () in Medina, both of which are in the Hejazi region of Saudi Arabia. The Custodian has been named the most powerful and influential person in Islam and the Sunni branch of Islam by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
New Mosque (Istanbul)
The New Mosque (, , originally named the Valide Sultan Mosque, ) and later New Valide Sultan Mosque () after its partial reconstruction and completion between 1660 and 1665, is an Ottoman imperial mosque located in the Eminönü quarter of Istanbul, Turkey. It is situated on the Golden Horn, at the southern end of the Galata Bridge, and is a notable Istanbul landmark marking the crossing from the old historic core of the city to the Beyoğlu (Pera) district. The mosque is a notable example of the Sultanate of Women period in Ottoman Empire. History Valide Sultan Mosque The construction of the mosque began in 1597. It was ordered by Safiye Sultan (wife of Murad III), Safiye Sultan, who was the wife of Sultan Murad III and later Valide sultan, Valide Sultan (Queen Mother) of Sultan Mehmed III. She ordered the mosque in her capacity as ''Valide Sultan'', two years after Mehmed III's ascension to the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman throne in 1595, hence the original formal name "Valide Sult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kafes
The Kafes (, from ), literally "cage", was the part of the Imperial Harem of the Ottoman Palace where possible successors to the throne were kept under a form of house-arrest and constant surveillance by the palace guards. The early history of the Ottoman Empire is littered with succession wars between rival sons of the deceased sultan. It was common for a new sultan to have his brothers killed, including infants,{{cite book , last=Meyer , first=G. J. , author-link=G. J. Meyer , date=May 30, 2006 , title=A World Undone: The Story of the Great War, 1914 to 1918 , publisher=Delacorte Press , page=89 , isbn=0553803549 sometimes dozens of them at once. This practice reduced the number of claimants to the throne, leading to several occasions where the Ottoman line seemed destined to end. The confinement of heirs provided security for an incumbent sultan and continuity of the dynasty. First use When Ahmed I died in 1617, his eldest son was only 13 years old, and for the first time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
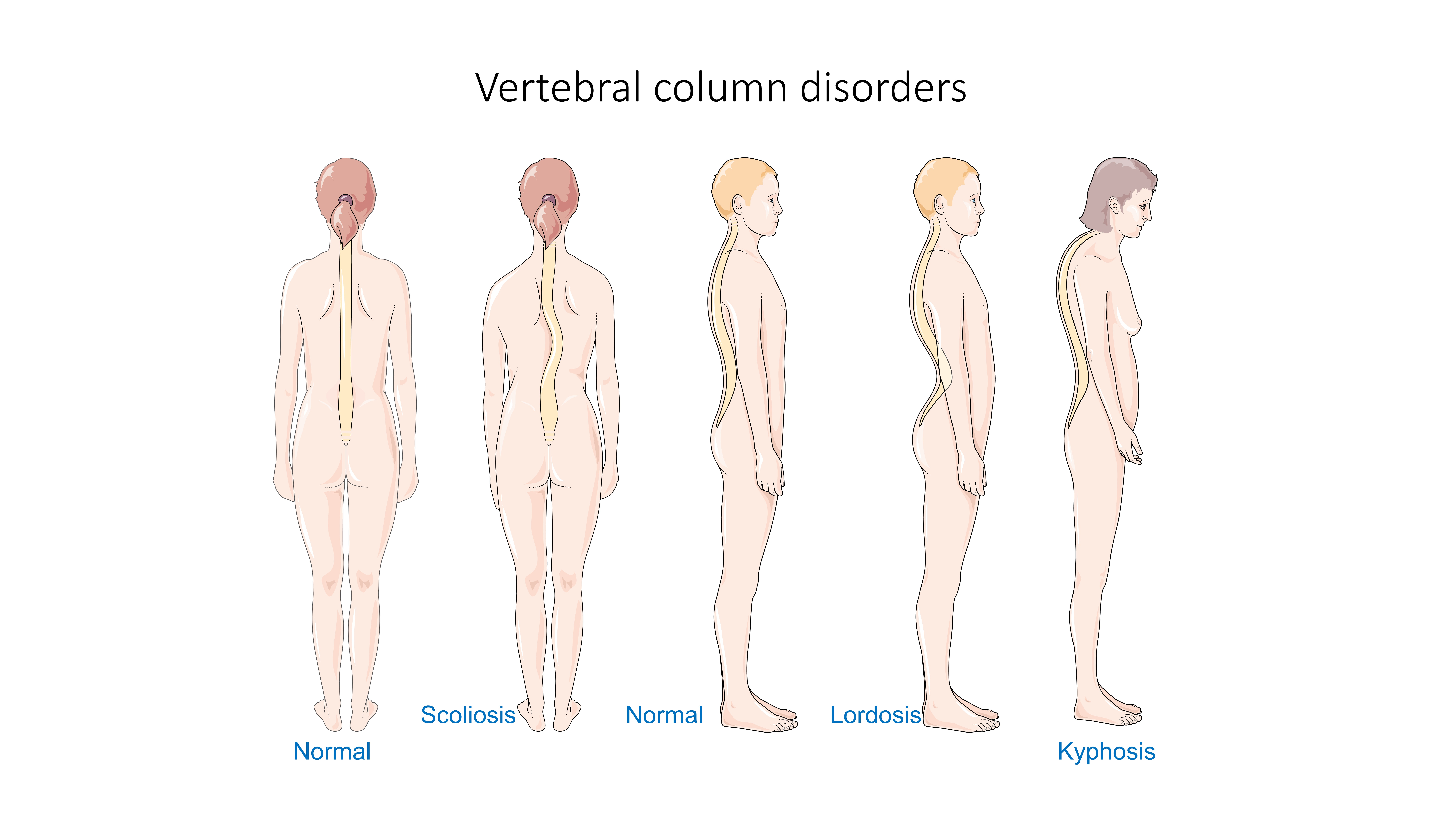
Kyphosis
Kyphosis () is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the Spinal column, spine as it occurs in the Thoracic spine, thoracic and sacrum, sacral regions. Abnormal inward concave ''lordotic'' curving of the Cervical spine, cervical and Lumbar spine, lumbar regions of the spine is called lordosis. It can result from degenerative disc disease; developmental abnormalities, most commonly Scheuermann's disease; Copenhagen disease, osteoporosis with compression fractures of the vertebra; multiple myeloma; or trauma. A normal thoracic spine extends from the 1st thoracic to the 12th thoracic vertebra and should have a slight kyphotic angle, ranging from 20° to 45°. When the "roundness" of the upper spine increases past 45° it is called kyphosis or "hyperkyphosis". Scheuermann's kyphosis is the most classic form of hyperkyphosis and is the result of wedged vertebrae that develop during adolescence. The cause is not currently known and the condition appears to be multifactorial a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Freemasonry
Freemasonry (sometimes spelled Free-Masonry) consists of fraternal groups that trace their origins to the medieval guilds of stonemasons. Freemasonry is the oldest secular fraternity in the world and among the oldest still-existing organizations in history. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of three main traditions: *Anglo-American Freemasonry, Anglo-American style Freemasonry, which insists that a "volume of sacred law", such as the Bible, Quran, or other religious text be open in a working Masonic lodge, lodge, that every member professes belief in a God, supreme being, that only men be admitted, and discussion of religion or politics does not take place within the lodge. *Continental Freemasonry or Liberal Freemasonry which has continued to evolve beyond these restrictions, particularly regarding religious belief and political discussion. *Co-Freemasonry, Women Freemasonry or Co-Freemasonry, which includes organizations that either admit women exclusively (such as the Ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Muhammad Shah
Mirza Nasir-ud-Din Muḥammad Shah (born Roshan Akhtar; 7 August 1702 – 26 April 1748) was the thirteenth Mughal emperor from 1719 to 1748. He was son of Khujista Akhtar, the fourth son of Bahadur Shah I. After being chosen by the Sayyid Brothers of Barha, he ascended the throne at the young age of 16, under their strict supervision. He later got rid of them with the help of Nizam-ul-Mulk, Asaf Jah I – Syed Hussain Ali Khan was murdered at Fatehpur Sikri in 1720 and Sayyid Hassan Ali Khan Barha was captured in battle in 1720 and fatally poisoned in 1722. Muhammad Shah was a great patron of the arts, including musical, cultural and administrative developments, he is thus often referred to as Muhammad Shah Rangila (). His pen-name was "Sadrang" and he is also sometimes referred to as "Bahadur Shah Rangila" after his grand father Bahadur Shah I. Muhammad Shah's reign was marked by rapid and irreversible decline of the Mughal Empire that was exacerbated by Nader Shah's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ottoman–Persian War (1743–1746)
The Ottoman–Persian War of 1743–1746 or Ottoman–Iranian War of 1743–1746 was fought between the Ottoman Empire and Afsharid Iran. Background Persia attempted to ratify the Treaty of Constantinople (1736), Treaty of Constantinople, by demanding that the Ja'fari, also known as the Imamiyyah was to be accepted as a fifth legal Islamic schools and branches, sect of Islam. In 1743, Nader Shah declared war on the Ottoman Empire. He demanded the surrender of Baghdad. The Persians had captured Baghdad in 1623 and Mosul in 1624, but the Ottomans had recaptured Mosul in 1625 and Baghdad in 1638. The Treaty of Zuhab in 1639 between the Ottoman Empire and the Safavid Iran, Safavid Empire had resulted in peace for 85 years. During the fall of the Safavid dynasty, Russia and the Ottoman Empire agreed to divide the northwest and the Caspian region of Persia, but with the advent of Nader Shah, the Russians and the Turks withdrew from the region. Nader Shah waged war against the Ottoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nader Shah's Invasion Of India
In May 1738, Nader Shah, the ruler of Iran (1736–1747) and the founder of the Afsharid dynasty, invaded Northern India, eventually attacking Delhi in March 1739. His army easily defeated the Mughals at the Battle of Karnal and then occupied the Mughal capital. Nader Shah's victory against the weak and crumbling Mughal Empire in the far east meant that he could afford to turn back and resume war against Persia's archrival, the neighbouring Ottoman Empire, as well as launch further campaigns in the North Caucasus and Central Asia. The loss of the Mughal treasury, which was carried back to Persia, dealt the final blow to the effective power of the Mughal Empire in India. Prelude By the end of 1736, Nadir Shah had consolidated his rule over Iran and dealt with the internal uprisings that had developed over the three years before that. He now shifted his focus towards the Afghan Ghilji tribe, who had been reorganised by their new leader Hussain Hotak (), a cousin of As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nader Shah
Nader Shah Afshar (; 6 August 1698 or 22 October 1688 – 20 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian history, ruling as shah of Iran (Persia) from 1736 to 1747, when he was assassinated during a rebellion. He fought numerous campaigns throughout the Middle East, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and South Asia, emerging victorious from the battles of Herat, Mihmandust, Murche-Khort, Kirkuk, Yeghevārd, Khyber Pass, Karnal, and Kars. Because of his military genius,The Sword of Persia: Nader Shah, from Tribal Warrior to Conquering Tyrant "Nader commanded the most powerful military force in Asia, if not the world" (quote from publisher's summary) some historians have described him as the '' |
Patrona Halil Rebellion
Patrona was a military rank of the Ottoman Navy equivalent to a Vice admiral or modern Turkish ''Tümamiral''. The word ''Patrona'' was originally Italian as term for the Admiral's galley. The Ottoman Patrona was the second commander of the Ottoman fleet, junior to the Kapudan Pasha The Kapudan Pasha (, modern Turkish: ), also known as the (, modern: , "Captain of the Sea") was the grand admiral of the Ottoman Navy. Typically, he was based at Galata and Gallipoli during the winter and charged with annual sailings durin ... (Admiral). The rank was used since 17th century but abolished in 1855 and replaced by '' Ferik Amiral''. The Patrona's flag was the red Ottoman flag (including white crescent and star) with a silver cannon on the red ground. Sources *Ernst von Skork: ''Das Volk und Reich der Osmanen, in besonderer Darstellung ihrer Kriegsverfassung und Kriegswesens'', p. 262ff. Friese, Pirna 1829 *First ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' (1913-1936), Vol. VI, p. 1164. Brill, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sultan Of The Ottoman Empire
The sultans of the Ottoman Empire (), who were all members of the Ottoman dynasty (House of Osman), ruled over the Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental empire from its perceived inception in 1299 to Dissolution of the Ottoman Empire, its dissolution in 1922. At its height, the Ottoman Empire spanned an area from Budin Eyalet, Hungary in the north to Yemen Eyalet, Yemen in the south and from Ottoman Algeria, Algeria in the west to Ottoman Iraq, Iraq in the east. Administered at first from the city of Söğüt since before 1280 and then from the city of Bursa since 1323 or 1324, the empire's capital was moved to Adrianople (now known as Edirne in English) in 1363 following Ottoman conquest of Adrianople, its conquest by Murad I and then to Constantinople (present-day Istanbul) in 1453 following Fall of Constantinople, its conquest by Mehmed the Conqueror, Mehmed II. The Rise of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Empire's early years have been the subject of varying narrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |