|
Magnús Óláfsson (died 1103)
Magnus III Olafsson (Old Norse: ''Magnús Óláfsson'', Norwegian language, Norwegian: ''Magnus Olavsson''; 1073 – 24 August 1103), better known as Magnus Barefoot (Old Norse: ''Magnús berfœttr'', Norwegian: ''Magnus Berrføtt''), was the King of Norway from 1093 until his death in 1103. His reign was marked by aggressive military campaigns and conquest, particularly in the Norse-dominated parts of the British Isles, where he extended his rule to the Kingdom of the Isles and Kingdom of Dublin, Dublin. As the only son of King Olaf III of Norway, Olaf Kyrre, Magnus was Coronations in Norway#Early coronations, proclaimed king in southeastern Norway shortly after his father's death in 1093. In the north his claim was contested by his cousin, Haakon Toresfostre, Haakon Magnusson (son of King Magnus II of Norway, Magnus Haraldsson), and the two co-ruled uneasily until Haakon's death in 1095. Disgruntled members of the nobility refused to recognise Magnus after his cousin's de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Penning
The penning was the dominant currency of the Norwegian coin system in the period 995–1387. Minted in Norway by the kings of Norway from Olaf Tryggvason (995-1000) and up to Olaf Haakonsson (1380-1387), it remained as a unit of account in the kingdom until 1513. It was introduced the year 995 in the image of the Anglo-Saxon coinage, and was the first and oldest currency of Norway. The coin system was later adapted in both Sweden and Denmark. The name lives on in the North Germanic languages in the contracted form of the plural, ''penger/pengar'', which means money. In the old Norwegian weight system it entered into units as ertog, øre and mark. Penning amended standard on several occasions through the Middle Ages. Both coin image, inscriptions, size, weight, and the silver content could vary considerably. The penning was minted in imitation of the pennies, pfennig and deniers issued elsewhere in Europe. However, although based on these coins, the accounting system wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Language
Norwegian ( ) is a North Germanic language from the Indo-European language family spoken mainly in Norway, where it is an official language. Along with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a dialect continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional varieties; some Norwegian and Swedish dialects, in particular, are very close. These Scandinavian languages, together with Faroese and Icelandic as well as some extinct languages, constitute the North Germanic languages. Faroese and Icelandic are not mutually intelligible with Norwegian in their spoken form because continental Scandinavian has diverged from them. While the two Germanic languages with the greatest numbers of speakers, English and German, have close similarities with Norwegian, neither is mutually intelligible with it. Norwegian is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. Today there are two official forms of ''written'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
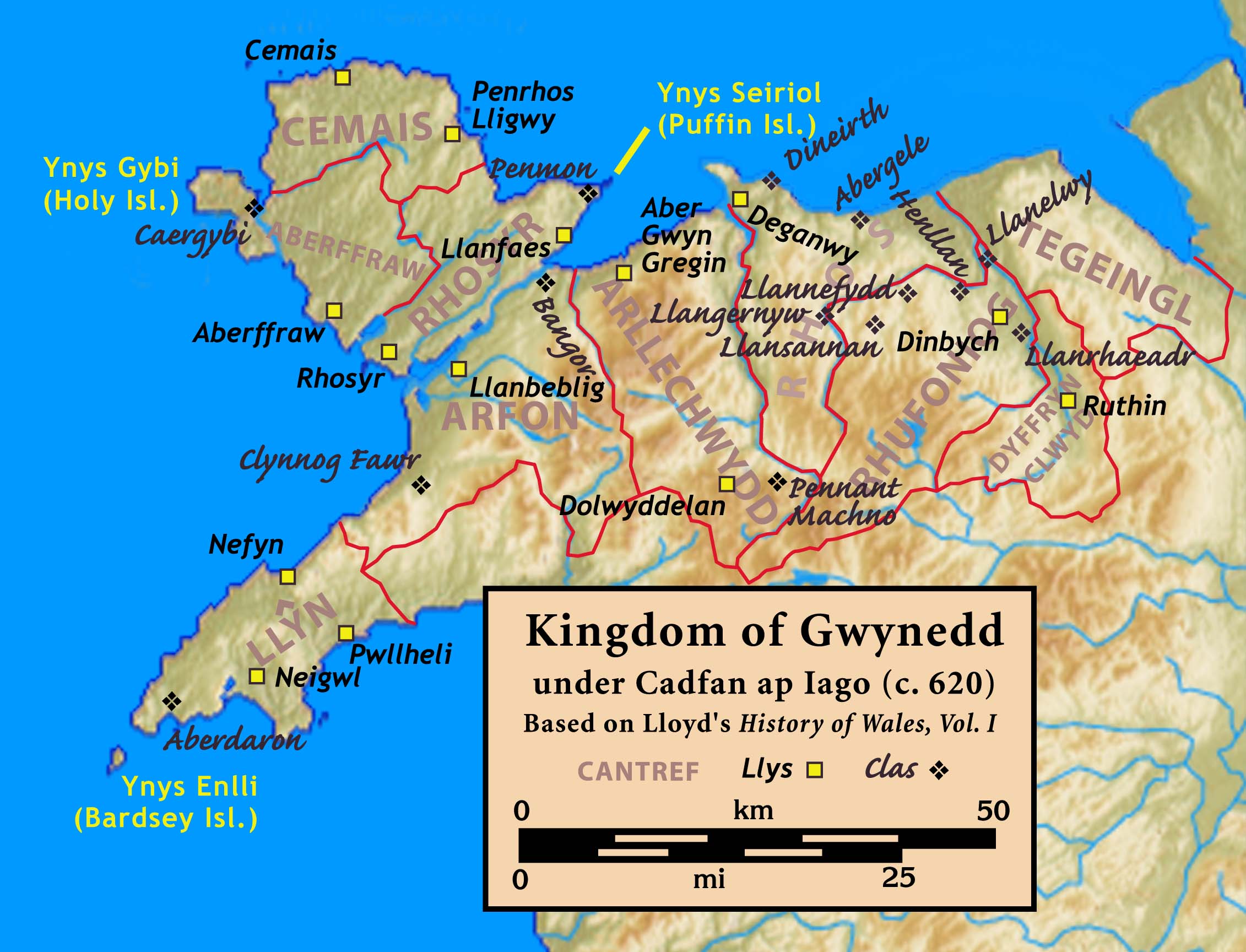
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Wales in the Early Middle Ages, Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire Succession of states, successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the list of rulers of Gwynedd, rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as "King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Timeline of conflict in Anglo-Saxon Britain, Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llywelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglesey
Anglesey ( ; ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms the bulk of the Principal areas of Wales, county known as the Isle of Anglesey, which also includes Holy Island, Anglesey, Holy Island () and some islets and Skerry, skerries. The county borders Gwynedd across the Menai Strait to the southeast, and is otherwise surrounded by the Irish Sea. Holyhead is the largest town, and the administrative centre is Llangefni. The county is part of the Preserved counties of Wales, preserved county of Gwynedd. Anglesey is the northernmost county in Wales. The Isle of Anglesey has an area of and a population of in . After Holyhead (12,103), the largest settlements are Llangefni (5,500) and Amlwch (3,967). The economy of the county is mostly based on agriculture, energy, and tourism, the latter especially on the coast. Holyhead is also a major ferry port for Dublin, Ireland. The county has the second-highest percentage of Welsh language, Welsh speakers in Wales, at 57.2%, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galloway
Galloway ( ; ; ) is a region in southwestern Scotland comprising the counties of Scotland, historic counties of Wigtownshire and Kirkcudbrightshire. It is administered as part of the council areas of Scotland, council area of Dumfries and Galloway. Galloway is bounded by sea to the west and south, the Galloway Hills to the north, and the River Nith to the east; the border between Kirkcudbrightshire and Wigtownshire is marked by the River Cree. The definition has, however, fluctuated greatly in size over history. A native or inhabitant of Galloway is called a Gallovidian. The region takes its name from the ''Gall-Gàidheil'', or "stranger Gaels", Norse–Gaels, a people of mixed Gaelic and Norse descent who seem to have settled here in the 10th century. Galloway remained a Gàidhealtachd area for much longer than other regions of the Scottish Lowlands and a Galwegian Gaelic, distinct local dialect of the Scottish Gaelic language survived into at least the 18th century. A hardy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Isles
The Northern Isles (; ; ) are a chain (or archipelago) of Island, islands of Scotland, located off the north coast of the Scottish mainland. The climate is cool and temperate and highly influenced by the surrounding seas. There are two main island groups: Shetland and Orkney. There are a total of 36 inhabited islands, with the fertile agricultural islands of Orkney contrasting with the more rugged Shetland islands to the north, where the economy is more dependent on fishing and the oil wealth of the surrounding seas. Both archipelagos have a developing renewable energy industry. They share a common Picts, Pictish and Norse activity in the British Isles, Norse history, and were part of the Kingdom of Norway (872–1397), Kingdom of Norway before being absorbed into the Kingdom of Scotland in the 15th century. The islands played a significant naval role during the World war, world wars of the 20th century. Tourism is important to both archipelagos, with their distinctive prehisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Man
The Isle of Man ( , also ), or Mann ( ), is a self-governing British Crown Dependency in the Irish Sea, between Great Britain and Ireland. As head of state, Charles III holds the title Lord of Mann and is represented by a Lieutenant Governor. The government of the United Kingdom is responsible for the Isle of Man's military defence and represents it abroad, but the Isle of Man still has a separate international identity. Humans have lived on the island since before 6500 BC. Gaelic cultural influence began in the 5th century AD, when Irish missionaries following the teaching of St Patrick began settling the island, and the Manx language, a branch of the Goidelic languages, emerged. In 627, King Edwin of Northumbria conquered the Isle of Man along with most of Mercia. In the 9th century, Norsemen established the thalassocratic Kingdom of the Isles, which included the Hebrides and the Northern Isles, along with the Isle of Man as the southernmost island. Magnus Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrides
The Hebrides ( ; , ; ) are the largest archipelago in the United Kingdom, off the west coast of the Scotland, Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebrides. These islands have a long history of occupation (dating back to the Mesolithic period), and the culture of the inhabitants has been successively influenced by the cultures of Celtic language, Celtic-speaking, Old Norse language, Norse-speaking, and English language, English-speaking peoples. This diversity is reflected in the various names given to the islands, which are derived from the different languages that have been spoken there at various points in their history. The Hebrides are where much of Scottish Gaelic literature and Gaelic music has historically originated. Today, the economy of the islands is dependent on crofting, fishing, tourism, the oil industry, and renewable energy. The Hebrides have less biodiversity t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orkney
Orkney (), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago off the north coast of mainland Scotland. The plural name the Orkneys is also sometimes used, but locals now consider it outdated. Part of the Northern Isles along with Shetland, Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north of Caithness and has about 70 islands, of which 20 are inhabited.Haswell-Smith (2004) pp. 336–403. The largest island, the Mainland, Orkney, Mainland, has an area of , making it the List of islands of Scotland, sixth-largest Scottish island and the List of islands of the British Isles, tenth-largest island in the British Isles. Orkney's largest settlement, and also its administrative centre, is Kirkwall. Orkney is one of the 32 Subdivisions of Scotland, council areas of Scotland, as well as a Orkney (Scottish Parliament constituency), constituency of the Scottish Parliament, a Lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area, and an counties of Scotland, historic county. The local council is Orkney I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Sea
The Irish Sea is a body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Celtic Sea in the south by St George's Channel and to the Inner Seas off the West Coast of Scotland in the north by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel. Anglesey, North Wales, is the largest island in the Irish Sea, followed by the Isle of Man. The term ''Manx Sea'' may occasionally be encountered (, , ). On its shoreline are Scotland to the north, England to the east, Wales to the southeast, Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland to the west. The Irish Sea is of significant economic importance to regional trade, shipping and transport, as well as fishing and power generation in the form of wind power and nuclear power plants. Annual traffic between Great Britain and Ireland is over 12 million passengers and of traded goods. Topography The Irish Sea joins the North Atlantic at both its northern and southern ends. To the north, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnus II Of Norway
Magnus Haraldsson (Old Norse: ''Magnús Haraldsson''; – 28 April 1069) was King of Norway from 1066 to 1069, jointly with his brother Olaf Kyrre from 1067. He was not included in official Norwegian regnal lists until modern times, but has since been counted as Magnus II. A son of King Harald Hardrada, Magnus was in 1058 appointed nominal leader of an expedition into the Irish Sea while still only a child. He appears to have assisted Welsh ruler Gruffydd ap Llywelyn and Ælfgar, Earl of Mercia in their struggles against Wessex, although his primary objective may have been to assert control over Orkney. He later accompanied his father in Harald's campaign against Denmark in 1062, and was appointed regent and made king before Harald's fatal invasion of England in 1066. Magnus briefly ruled Norway alone thereafter, until his younger brother Olaf returned from England in 1067. Magnus co-ruled with Olaf following his brother's return to Norway, but less than three years i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronations In Norway
Coronations were held in Norway from 1164 to 1906, mostly in the Nidaros Cathedral in Trondheim. Although a crowning ceremony was formerly mandated by the nation's constitution, this requirement was eliminated in 1908. However, Norwegian kings have since chosen voluntarily to take part in a ritual of "benediction" to mark their accession to the throne, during which the crown is present, but not physically bestowed upon the sovereign. The new ceremony retains some of the religious elements of earlier rites, while eliminating other features now considered to be "undemocratic". There is no law preventing a coronation from occurring so any future monarch of Norway can choose to have one. Consecration from the Official Website of the Norwegian Royal Family. Retrieved on 2009-09-16. History [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |