|
Lower Colorado River Valley
The Lower Colorado River Valley (LCRV) is the river region of the lower Colorado River of the southwestern United States in North America that rises in the Rocky Mountains and has its outlet at the Colorado River Delta in the northern Gulf of California in northwestern Mexico, between the states of Baja California and Sonora. This north–south stretch of the Colorado River forms the border between the U.S. states of California/Arizona and Nevada/Arizona, and between the Mexican states of Baja California/Sonora. It is commonly defined as the region from below Hoover Dam and Lake Mead to its outlet at the northern Gulf of California (Sea of Cortez); it includes the Colorado River proper, canyons, the valley, mountain ranges with wilderness areas, and the floodplain and associated riparian environments. It is home to recreation activities from the river, the lakes created by dams, agriculture, and the home of various cities, communities, and towns along the river, or associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
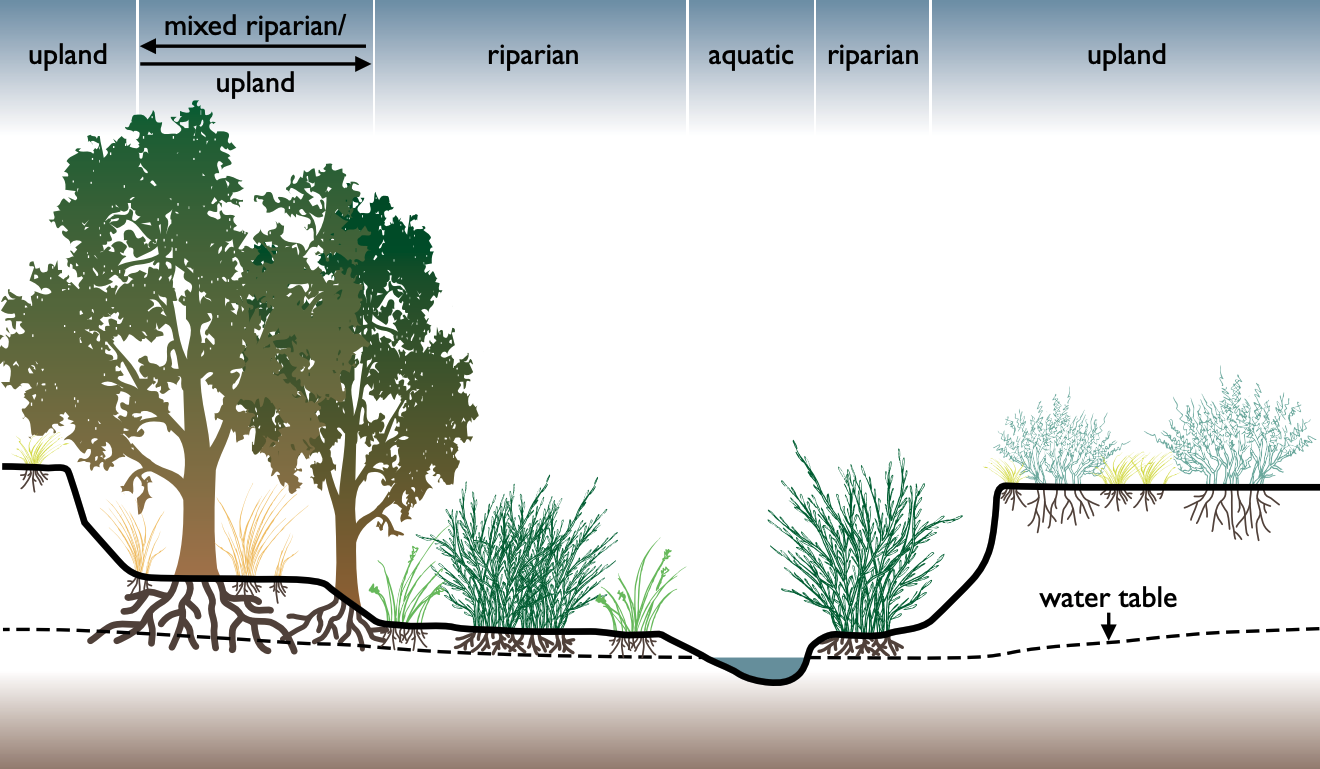
Riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin '' ripa'', meaning " river bank". Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on terrestrial and semiaquatic fauna as well as aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, and even non-vegetative areas. Riparian zones may be natural or engineered for soil stabilization or restoration. These zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Havasu City
Lake Havasu City (, ) is a city in Mohave County, Arizona, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 57,144, up from 52,527 in 2010. It is served by Lake Havasu City Airport. History The community first started during World War II as Site Six, an Army Air Corps rest camp on the shores of Lake Havasu. In 1958, American businessman Robert P. McCulloch purchased of property on the east side of the lake along Pittsburgh Point, a peninsula that would eventually be transformed into an island. After four years of planning, McCulloch Properties acquired another of federal land in the surrounding area. Lake Havasu City was established on September 30, 1963, by a resolution of the Mohave County Board of Supervisors, as the Lake Havasu Irrigation and Drainage District, making it a legal entity (the act is referenced in resolution #63-12-1). McCulloch Properties flew in prospective residents from around the United States for free in what became a substanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullhead City, Arizona
Bullhead City is a city located on the Colorado River in Mohave County, Arizona, Mohave County, Arizona, United States, south of Las Vegas, Nevada, and directly across the Colorado River from Laughlin, Nevada, whose casinos and ancillary services supply much of the employment for Bullhead City. Bullhead City is located at the southern end of Lake Mohave. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population of Bullhead City was 41,348. The nearby communities of Laughlin, Nevada, Laughlin, Needles, California, Needles, Fort Mohave, Arizona, Fort Mohave and Mohave Valley, Arizona, Mohave Valley bring the Bullhead area's total population to over 77,000, making it the largest economic region in Mohave County. With over , Bullhead City is the largest city in Mohave County in terms of total land area. History The earliest inhabitants of the Colorado River Valley were the Mojave people. The rich soil and plentiful water provided the valley's natives with the necessities t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Valley
Death Valley is a desert valley in Eastern California, in the northern Mojave Desert, bordering the Great Basin Desert. It is thought to be the Highest temperature recorded on Earth, hottest place on Earth during summer. Death Valley's Badwater Basin is the point of lowest elevation in North America, at below sea level. It is east-southeast of Mount Whitney – the highest point in the contiguous United States, with an elevation of 14,505 feet (4,421 m). On the afternoon of July10, 1913, the National Weather Service, United States Weather Bureau recorded a high temperature of 134 °F (56.7 °C) at Furnace Creek, California, Furnace Creek in Death Valley, which stands as the Highest temperature recorded on Earth, highest ambient air temperature ever recorded on the surface of the Earth. This reading, however, and several others taken in that period are disputed by some modern experts. Lying mostly in Inyo County, California, near the border of California and Nevada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
View Of Trigo Mountains Wilderness, AZ
Acornsoft was the software arm of Acorn Computers, and a major publisher of software for the BBC Micro and Acorn Electron. As well as games, it also produced a large number of educational titles, extra computer languages and business and utility packages – these included word processor ''VIEW'' and the spreadsheet ''ViewSheet'' supplied on ROM and cartridge for the BBC Micro/Acorn Electron and included as standard in the BBC Master and Acorn Business Computer. History Acornsoft was formed in late 1980 by Acorn Computers directors Hermann Hauser and Chris Curry, and David Johnson-Davies, author of the first game for a UK personal computer and of the official Acorn Atom manual "Atomic Theory and Practice". David Johnson-Davies was managing director and in early 1981 was joined by Tim Dobson, Programmer and Chris Jordan (designer), Chris Jordan, Publications Editor. While some of their games were clones or remakes of popular arcade games (e.g. ''Hopper'' is a clone of Sega's ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocopah
The Cocopah ( Cocopah: Xawiƚƚ Kwñchawaay) are Native Americans who live in Baja California, Mexico, and Arizona, United States. In the United States, Cocopah people belong to the federally recognized Cocopah Tribe of Arizona. Name The Cocopah are also called the Cucapá (in Cocopa: Kwapa or Kwii Capáy). Language The Cocopah language belongs to the Delta–California branch of the Yuman family. Their self-designation is Xawiƚƚ kwñchawaay, translating to “Those Who Live on the Cloudy River” (from ''Xawíƚƚy'' - "river", ''kwii'' - "cloud", ''(ny)way'' - "to live", ''llyay/nyaam'' - "many"). According to the U.S. Census, there were 1,009 Cocopah in 2010. Alternate spellings of Cocopah in Spanish documents include: Cócopa, Cócapa, Cócope, Cósopa, Cúcapa. History Precontact Ancestors of the Cocopah inhabited parts of present-day Arizona, California, and Baja California and are known by western academics as belonging to the Patayan culture. Patayan is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechan
The Quechan ( Quechan: ''Kwatsáan'' 'those who descended'), or Yuma, are a Native American tribe who live on the Fort Yuma Indian Reservation on the lower Colorado River in Arizona and California just north of the Mexican border. Despite their name, they are not related to the Quechua people of the Andes. Members are enrolled in the Quechan Tribe of the Fort Yuma Indian Reservation. The federally recognized Quechan tribe's main office is located in Winterhaven, California. Its operations and the majority of its reservation land are located in California, United States. History The historic Yuman-speaking people in this region were skilled warriors and active traders, maintaining exchange networks with the Pima in southern Arizona, New Mexico, and with peoples of the Pacific coast. The first significant contact of the Quechan with Europeans was with the Spanish explorer Juan Bautista de Anza and his party in the winter of 1774. Relations were friendly. On Anza's retur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado River Indian Reservation
The Colorado River Indian Tribes (, ) is a federally recognized tribe consisting of the four distinct ethnic groups associated with the Colorado River Indian Reservation: the Mohave, Chemehuevi, Hopi, and Navajo. The tribe has about 4,277 enrolled members. A total population of 9,485 currently resides within the tribal reservation according to the 2012-2016 American Community Survey data. History The reservation was established on March 3, 1865, for "Indians of said river and its tributaries." Initially, these were the Mohave and Chemehuevi, but Hopi and Navajo people were relocated to the reservation in 1945. In 1942, land within the reservation was chosen - against the wishes of the tribal council - as the site of Poston War Relocation Center during World War II. Office of Indian Affairs officials saw the Japanese-American Internment camp as a way to bring infrastructure to the reservation without having to fund it themselves. The camp closed in 1945 and the land and remainin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Mojave Indian Reservation
The Fort Mohave Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation along the Colorado River, currently encompassing in Arizona, in California, and in the southernmost point of Nevada. Located around the tri-point of the three states, the reservation is home to approximately 1,100 members of the federally recognized Fort Mojave Indian Tribe of Arizona, California, and Nevada (), a federally recognized tribe of Mohave people. Native Americans occupy less than 50 percent of the Mojave reservation. The Mohave people have leased much of their land to cotton, maize, and soybean farming companies, which employ a large population of resident white and Mexican Americans. The site of the former Fort Mohave and the eastern terminus of the Mojave Road are situated within the Fort Mojave Indian Reservation. History These lands were occupied for thousands of years by succeeding cultures of Indigenous peoples. The property covers areas along the Colorado River of the three adjacent states of Ari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemehuevi Indian Reservation
The Chemehuevi Indian Tribe of the Chemehuevi Reservation (Colorado River Numic language: Nüwüwü) is a federally recognized tribe of Chemehuevi people, who are the southernmost branch of Southern Paiute people. To celebrate their organization under the Indian Reorganization Act, tribal recognition, and ratifying their constitution, the tribe hosts Nuwuvi Days, an annual festival held during the first weekend in June. Reservation The Chemehuevi Reservation () is located in San Bernardino County, California, bordering Lake Havasu for and along the Colorado River. The reservation is large and has a population of 345. Government The Chemehuevi Indian Tribe's headquarters is located in Havasu Lake, California. The tribe is governed by a democratically elected, nine-member tribal council. Economic development The tribe owns and operates Havasu Landing Resort, Casino and Hotel on Lake Havasu Lake Havasu () is a large reservoir formed by Parker Dam on the Colorado River, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in the cities. While humans started gathering grains at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers only began planting them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs, and cattle were domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. In the 20th century, industrial agriculture based on large-scale monocultures came to dominate agricultural output. , small farms produce about one-third of the world's food, but large farms are prevalent. The largest 1% of farms in the world are greater than and operate more than 70% of the world's farmland. Nearly 40% of agricultural land is found on farms larger than . However, five of every six farm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |