|
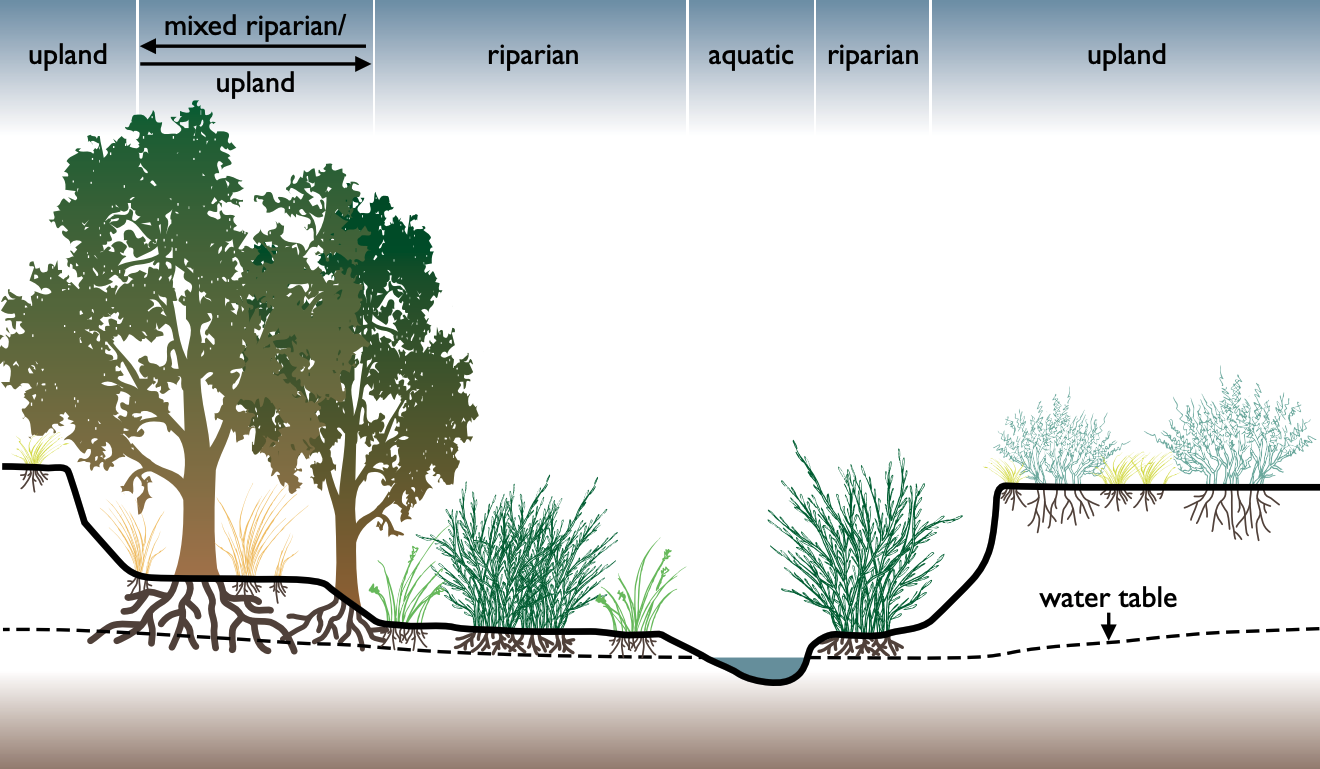
Riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin '' ripa'', meaning " river bank". Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on terrestrial and semiaquatic fauna as well as aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, and even non-vegetative areas. Riparian zones may be natural or engineered for soil stabilization or restoration. These zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riparian Buffer
A riparian buffer or stream buffer is a vegetated area (a " buffer strip") near a stream, usually forested, which helps shade and partially protect the stream from the impact of adjacent land uses. It plays a key role in increasing water quality in associated streams, rivers, and lakes, thus providing environmental benefits. With the decline of many aquatic ecosystems due to agriculture, riparian buffers have become a very common conservation practice aimed at increasing water quality and reducing pollution. Benefits Riparian buffers act to intercept sediment, nutrients, pesticides, and other materials in surface runoff and reduce nutrients and other pollutants in shallow subsurface water flow. They also serve to provide habitat and wildlife corridors in primarily agricultural areas. They can also be key in reducing erosion by providing stream bank stabilization. Large scale results have demonstrated that the expansion of riparian buffers through the deployment of plantati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riparian Forest
A riparian forest or riparian woodland is a forested or wooded area of land adjacent to a body of water such as a river, stream, pond, lake, marshland, estuary, canal, Sink (geography), sink, or reservoir. Due to the broad nature of the definition, riparian woodlands have a huge diversity of characteristics including but not limited to soil composition, microclimates, and vegetative structures. However, among the varied range and landscapes, one factor stays constant: a high rate of Primary production, primary productivity. This makes riparian forests hugely important centers of nutrient recycling. Etymology The term riparian comes from the Latin word ''ripa'', 'river bank'; technically it refers only to areas adjacent to flowing bodies of water such as rivers, streams, Swamp, sloughs and estuaries. However, the terms ''riparian forest'' and ''riparian zone'' have come to include areas adjacent to non-flowing bodies of water such as ponds, lakes, playas and reservoirs. Charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stream
A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to by a variety of local or regional names. Long, large streams are usually called rivers, while smaller, less voluminous and more intermittent river, intermittent streams are known, amongst others, as brook, creek, rivulet, rill, run, tributary, feeder, freshet, narrow river, and streamlet. The flow of a stream is controlled by three inputs – surface runoff (from precipitation or meltwater), daylighting (streams), daylighted subterranean river, subterranean water, and surfaced groundwater (Spring (hydrology), spring water). The surface and subterranean water are highly variable between periods of rainfall. Groundwater, on the other hand, has a relatively constant input and is controlled more by long-term patterns of pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially in the soils. Wetlands form a transitional zone between waterbodies and dry lands, and are different from other terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems due to their vegetation's roots having adapted to oxygen-poor waterlogged soils. They are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as habitats to a wide range of aquatic and semi-aquatic plants and animals, with often improved water quality due to plant removal of excess nutrients such as nitrates and phosphorus. Wetlands exist on every continent, except Antarctica. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main types of wetland are defined based on the dominant plants and the source of the water. For example, ''marshes'' ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the Runoff (hydrology), runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth. Rivers flow in channeled watercourses and merge in confluences to form drainage basins, or catchments, areas where surface water eventually flows to a common outlet. Rivers have a great effect on the landscape around them. They may regularly overflow their Bank (geography), banks and flood the surrounding area, spreading nutrients to the surrounding area. Sedime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silviculture
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the growth, composition/structure, as well as quality of forests to meet values and needs, specifically timber production. The name comes from the Latin ('forest') and ('growing'). The study of forests and woods is termed ''silvology''. Silviculture also focuses on making sure that the treatment(s) of Stand level modelling, forest stands are used to conserve and improve their productivity. Generally, silviculture is the science and art of growing and cultivating forest crops based on a knowledge of silvics, the study of the life history and general characteristics of forest trees and stands, with reference to local/regional factors. The focus of silviculture is the control, establishment and management of forest stands. The distinction between forestry and silviculture is that silviculture is applied at the Stand level modelling, stand-level, while forestry is a broader concept. Adaptive management is common in silviculture, while fores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Plant
Aquatic plants, also referred to as hydrophytes, are vascular plants and Non-vascular plant, non-vascular plants that have adapted to live in aquatic ecosystem, aquatic environments (marine ecosystem, saltwater or freshwater ecosystem, freshwater). In lakes, rivers and wetlands, aquatic vegetations provide cover for aquatic animals such as fish, amphibians and aquatic insects, create substrate (marine biology), substrate for benthic invertebrates, produce oxygen via photosynthesis, and serve as food for some herbivorous wildlife. Familiar examples of aquatic plants include Nymphaeaceae, waterlily, Nelumbo, lotus, duckweeds, mosquito fern, floating heart, water milfoils, Hippuris, mare's tail, water lettuce, water hyacinth, and algae. Aquatic plants require special adaptation (biology), adaptations for prolonged inundation in water, and for buoyancy, floating at the water surface. The most common adaptation is the presence of lightweight internal packing cells, aerenchyma, but floa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biofilter
Biofiltration is a pollution control technique using a bioreactor containing living material to capture and biologically degrade pollutants. Common uses include processing waste water, capturing harmful chemicals or silt from surface runoff, and microbiotic oxidation of contaminants in air. Industrial biofiltration can be classified as the process of utilizing biological oxidation to remove volatile organic compounds, odors, and hydrocarbons. Examples of biofiltration Examples of biofiltration include: * Bioswales, biostrips, biobags, bioscrubbers, Vermifilters and trickling filters * Constructed wetlands and natural wetlands * Slow sand filters * Treatment ponds * Green belts * Green walls * Riparian zones, riparian forests, bosques * Bivalve bioaccumulation Control of air pollution When applied to air filtration and purification, biofilters use microorganisms to remove air pollution. The air flows through a packed bed and the pollutant transfers into a thin biofil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance (ecology), abundance, biomass (ecology), biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; ecological succession, successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with woody plants (trees and shrubs), or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see differences between British, American and Australian English explained below). Some savannas may also be woodlands, such as ''savanna woodland'', where trees and shrubs form a light canopy. Woodlands may support an understory of shrubs and herbaceous plants including grasses. Woodland may form a transition to shrubland under drier conditions or during early stages of primary or secondary succession. Higher-density areas of trees with a largely closed canopy that provides extensive and nearly continuous shade are often referred to as forests. Extensive efforts by conservationist groups have been made to preserve woodlands from urbanization and agriculture. For example, the woodlands of Northwest Indiana ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Animal
An aquatic animal is any animal, whether vertebrate or invertebrate, that lives in a body of water for all or most of its lifetime. Aquatic animals generally conduct gas exchange in water by extracting dissolved oxygen via specialised respiratory system, respiratory organ (biology), organs called gills, cutaneous respiration, through the skin or enteral respiration, across enteral mucosae, although some are evolution, evolved from terrestrial ancestors that re-adaptation, adapted to aquatic environments (e.g. marine reptiles and marine mammals), in which case they actually use lungs to breathing, breathe air and are essentially apnea, holding their breath when living in water. Some species of gastropod mollusc, such as the Elysia chlorotica, eastern emerald sea slug, are even capable of kleptoplastic photosynthesis via endosymbiosis with ingested yellow-green algae. Almost all aquatic animals reproduce in water, either oviparously or viviparously, and many species routinely fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank (geography)
In geography, a bank is the land alongside a body of water. Different structures are referred to as ''banks'' in different fields of geography. In limnology (the study of inland waters), a stream bank or river bank is the terrain alongside the Stream bed, bed of a river, creek, or stream. The bank consists of the sides of the channel (geography), channel, between which the streamflow, flow is confined. Stream banks are of particular interest in fluvial geography, which studies the processes associated with rivers and streams and the Deposition (geology), deposits and landforms created by them. Bankfull discharge is a Discharge (hydrology), discharge great enough to fill the channel and overtop the banks. The descriptive terms ''left bank'' and ''right bank'' refer to the perspective of an observer looking current (stream), downstream; a well-known example of this being the southern Rive Gauche, left bank and the northern Rive Droite, right bank of the river Seine definin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |