|
Love At First Sight
Love at first sight is a personal experience and a common theme in creative works: a person or character feels an instant, extreme, and ultimately long-lasting romantic attraction for a stranger upon first seeing that stranger. It has been described by poets and critics since the emergence of ancient Greece. Historical conceptions Greek In the classical world, the phenomenon of "love at first sight" was understood within the context of a more general conception of passionate love, a kind of madness or, as the Greeks put it, ''theia mania'' ("madness from the gods"). This love passion was described through an elaborate metaphoric and mythological psychological effect involving "love's arrows" or "love darts," the source of which was often given as the mythological Eros or Cupid, sometimes by other mythological deities, such as Pheme. At times, the source of the arrows was said to be the image of the beautiful love object itself. If these arrows arrived at the lover's eyes, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trope (literature)
A literary trope is an artistic effect realized with figurative language – word, phrase, image – such as a rhetorical figure. In editorial practice, a ''trope'' is "a substitution of a word or phrase by a less literal word or phrase". Semantic change has expanded the definition of the literary term ''trope'' to also describe a writer's usage of commonly recurring or overused literary techniques and rhetorical devices (characters and situations), motifs, and clichés in a work of creative literature. Origins The term ''trope'' derives from the Greek (), 'a turn, a change', related to the root of the verb (), 'to turn, to direct, to alter, to change'; this means that the term is used metaphorically to denote, among other things, metaphorical language. Tropes and their classification were an important field in classical rhetoric. The study of tropes has been taken up again in modern criticism, especially in deconstruction. Tropological criticism (not to be confused with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John J
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died ), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (died ), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus Christ * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope John ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hero And Leander (poem)
''Hero and Leander'' is a poem by Christopher Marlowe that retells the Greek myth of Hero and Leander. After Marlowe's untimely death, it was completed by George Chapman. The minor poet Henry Petowe published an alternative completion to the poem. The poem was first published five years after Marlowe's demise. Publication Two editions of the poem were issued in quarto in 1598 (see 1598 in poetry); one, printed by Adam Islip for the bookseller Edward Blount, contained only Marlowe's original, while the other, printed by Felix Kingston for Paul Linley, included both the original and Chapman's continuation. A third edition in 1600, published by John Flasket, printed a title-page advertising the addition of Marlowe's translation of Book I of Lucan's ''Pharsalia'' to the original poem, though the book itself merely adds Chapman's portion. The fourth edition of 1606, again from Flasket, abandoned any pretence of including the Lucan and once again joined Marlowe's and Chapman's po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Marlowe
Christopher Marlowe ( ; Baptism, baptised 26 February 156430 May 1593), also known as Kit Marlowe, was an English playwright, poet, and translator of the Elizabethan era. Marlowe is among the most famous of the English Renaissance theatre, Elizabethan playwrights. Based upon the "many imitations" of his play ''Tamburlaine'', modern scholars consider him to have been the foremost dramatist in London in the years just before his mysterious early death. Some scholars also believe that he greatly influenced William Shakespeare, who was baptised in the same year as Marlowe and later succeeded him as the preeminent Elizabethan playwright. Marlowe was the first to achieve critical reputation for his use of blank verse, which became the standard for the era. His plays are distinguished by their overreaching protagonists. Themes found within Marlowe's literary works have been noted as humanistic with realistic emotions, which some scholars find difficult to reconcile with Marlowe's "anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 23 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of River Avon, Warwickshire, Avon" or simply "the Bard". His extant works, including William Shakespeare's collaborations, collaborations, consist of some Shakespeare's plays, 39 plays, Shakespeare's sonnets, 154 sonnets, three long narrative poems and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays List of translations of works by William Shakespeare, have been translated into every major modern language, living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright. Shakespeare remains arguably the most influential writer in the English language, and his works continue to be studied and reinterpreted. Shakespeare was born and raised in Stratford-upon-Avon, Warwickshire. At the age of 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troilus
Troilus ( or ; ; ) is a legendary character associated with the story of the Trojan War. The first surviving reference to him is in Homer's ''Iliad,'' composed in the late 8th century BC. In Greek mythology, Troilus is a young Troy, Trojan prince, one of the sons of King Priam (or Apollo) and Hecuba. Prophecies link Troilus' fate to that of Troy and so he is ambushed and murdered by Achilles. Sophocles was one of the writers to tell this tale. It was also a popular theme among artists of the time. Ancient writers treated Troilus as the epitome of a dead child mourned by his parents. He was also regarded as a wikt:paragon, paragon of youthful male beauty. In Western European medieval and Renaissance versions of the legend, Troilus is the youngest of Priam's five legitimate sons by Hecuba. Despite his youth he is one of the main Trojan war leaders. He dies in battle at Achilles' hands. In a popular addition to the story, originating in the 12th century, Troilus falls in love with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
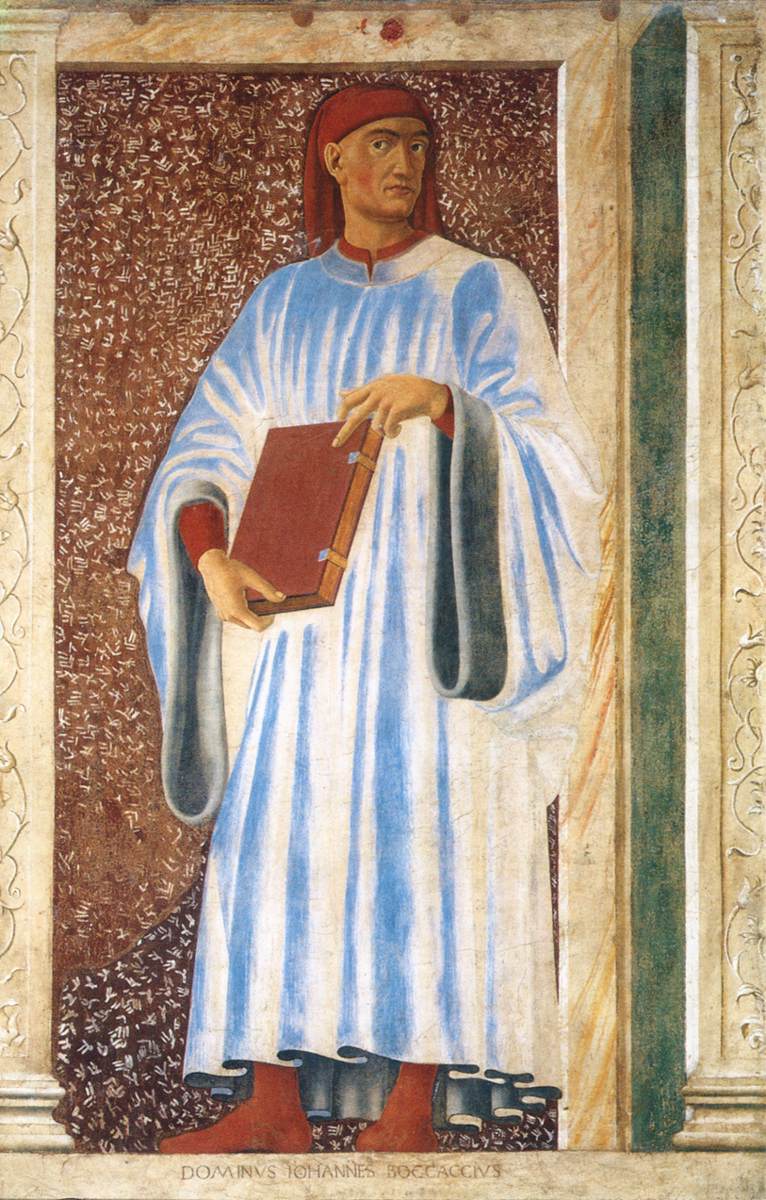
Giovanni Boccaccio
Giovanni Boccaccio ( , ; ; 16 June 1313 – 21 December 1375) was an Italian people, Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so well known as a writer that he was sometimes simply known as "the Certaldese" and one of the most important figures in the European literary panorama of the 14th century, fourteenth century. Some scholars (including Vittore Branca) define him as the greatest European prose writer of his time, a versatile writer who amalgamated different literary trends and genres, making them converge in original works, thanks to a creative activity exercised under the banner of experimentalism. His most notable works are ''The Decameron'', a collection of short stories, and ''De Mulieribus Claris, On Famous Women''. ''The Decameron'' became a determining element for the Italian literary tradition, especially after Pietro Bembo elevated the Boccaccian styl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilisk
In European bestiary, bestiaries and legends, a basilisk ( or ) is a legendary reptile reputed to be a Serpent symbolism, serpent king, who causes death to those who look into its eyes. According to the ''Natural History (Pliny), Naturalis Historia'' of Pliny the Elder, the basilisk of Cyrene, Libya, Cyrene is a small snake, "being not more than twelve inches in length", that is so venomous, it leaves a wide trail of deadly venom in its path, and its gaze is likewise lethal. According to Pliny, the basilisk's weakness is the odor of a weasel. The weasel was thrown into the basilisk's hole, recognizable because some of the surrounding shrubs and grass had been scorched by its presence. It is possible that the legend of the basilisk and its association with the weasel in Europe was inspired by accounts of certain species of Asiatic and African snakes (such as Naja, cobras) and their natural predator, the mongoose. Etymology The word originates from the Greek form ''basilískos'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Il Filostrato
"Il Filostrato" is a poem by the Italian writer Giovanni Boccaccio, and the inspiration for Geoffrey Chaucer's ''Troilus and Criseyde'' and, through Chaucer, the Shakespeare play '' Troilus and Cressida''. It is itself loosely based on '' Le Roman de Troie'', by 12th-century poet Benoît de Sainte-Maure. ''Il Filostrato'' is a narrative poem on a classical topic written in "royal octaves" ('' ottava rima'') and divided into eight cantos. The title, a combination of Greek and Latin words, can be translated approximately as "laid prostrate by love". The poem has a mythological plot: it narrates the love of Troilo ( Troilus), a younger son of Priam of Troy, for Criseida ( Cressida or Criseyde), daughter of Calcas ( Calchas). Although its setting is Trojan, Boccaccio's story is not taken from Greek myth, but from the '' Roman de Troie'', a twelfth-century French medieval re-elaboration of the Trojan legend by Benoît de Sainte-Maure known to Boccaccio in the Latin prose version by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
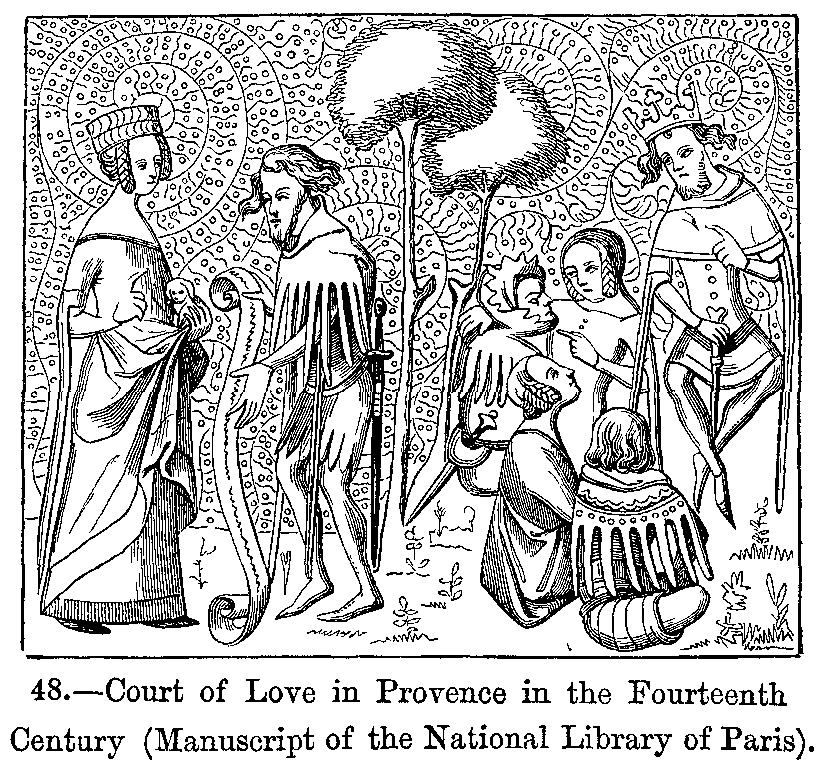
Courtly Love
Courtly love ( ; ) was a medieval European literary conception of love that emphasized nobility and chivalry. Medieval literature is filled with examples of knights setting out on adventures and performing various deeds or services for ladies because of their "courtly love". This kind of love was originally a literary fiction created for the entertainment of the nobility, but as time passed, these ideas about love spread to popular culture and attracted a larger literate audience. In the High Middle Ages, a "game of love" developed around these ideas as a set of social practices. "Loving nobly" was considered to be an enriching and improving practice. Courtly love began in the ducal and princely courts of Aquitaine, Provence, Champagne, ducal Burgundy and the Norman Kingdom of Sicily at the end of the eleventh century. In essence, courtly love was an experience between erotic desire and spiritual attainment, "a love at once illicit and morally elevating, passionate and disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troubadour
A troubadour (, ; ) was a composer and performer of Old Occitan lyric poetry during the High Middle Ages (1100–1350). Since the word ''troubadour'' is etymologically masculine, a female equivalent is usually called a ''trobairitz''. The troubadour school or tradition began in the late 11th century in Occitania, but it subsequently spread to the Italian and Iberian Peninsulas. Under the influence of the troubadours, related movements sprang up throughout Europe: the Minnesang in Germany, '' trovadorismo'' in Galicia and Portugal, and that of the trouvères in northern France. Dante Alighieri in his '' De vulgari eloquentia'' defined the troubadour lyric as ''fictio rethorica musicaque poita'': rhetorical, musical, and poetical fiction. After the "classical" period around the turn of the 13th century and a mid-century resurgence, the art of the troubadours declined in the 14th century and around the time of the Black Death (1348) and since died out. The texts of troubado ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provence
Provence is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which stretches from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border to the east; it is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the south. It largely corresponds with the modern administrative Regions of France, region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur and includes the Departments of France, departments of Var (department), Var, Bouches-du-Rhône, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence, as well as parts of Alpes-Maritimes and Vaucluse.''Le Petit Robert, Dictionnaire Universel des Noms Propres'' (1988). The largest city of the region and its modern-day capital is Marseille. The Ancient Rome, Romans made the region the first Roman province beyond the Alps and called it ''Provincia Romana'', which evolved into the present name. Until 1481 it was ruled by the List of rulers of Provence, counts of Provence from their capital in Aquae Sextiae (today Aix-en-Provence), then became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |