|
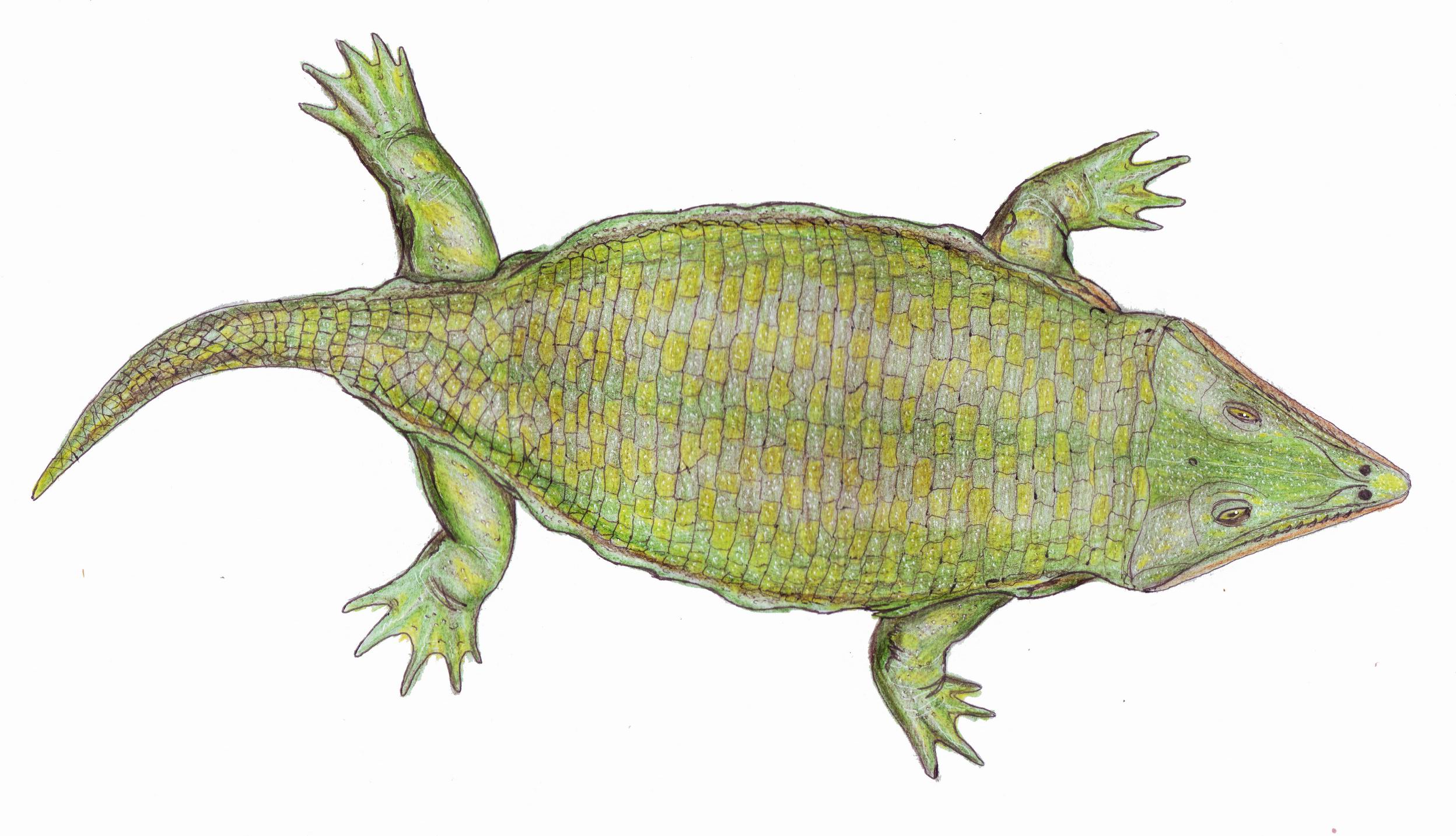
Llistrofus
''Llistrofus'' is an extinct genus of early Permian microsaur within the family Hapsidopareiidae that is known from Oklahoma. Discovery ''Llistrofus'' was described by Canadian paleontologists Robert Carroll and Pamela Gaskill in 1978. The genus name is an anagram of Fort Sill, the historic name of the Richards Spur locality from which material of ''Llistrofus'' was collected. The species name, ''L. pricei'', is given for the Brazilian paleontologist Llewellyn Price. The holotype of this taxon is currently reposited at the Field Museum of Natural History. The skull of the holotype was reappraised by Bolt & Rieppel in 2009. New material from Richards Spur was described by Gee et al. (2019). Description ''Llistrofus'' is readily identified by the presence of a large temporal emargination, a feature shared with '' Hapsidopareion lepton'' that unites the Hapsidopareiidae. Carroll & Gaskill (1978) differentiated ''Llistrofus'' from ''Hapsidopareion'' by four features: (1) posto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hapsidopareion
''Hapsidopareion'' is an extinct genus of microsaur belonging to the family Hapsidopareiidae. Fossils have been found in the early Permian of Oklahoma. History of study ''Hapsidopareion'' was named in 1973 by American paleontologist Eleanor Daly based on material collected from the early Permian South Grandfield locality in southwestern Oklahoma. The genus name is given for the Greek ''hapsido''- ('arch') and -''pareion'' ('cheek'). The species name, ''H. lepton'', is given for the slightness of the animal. The taxon is known from several partial to complete skulls and possibly by some isolated postcranial material. Anatomy ''Hapsidopareion'' was originally differentiated from other microsaurs by the large temporal emargination, which produced other variable morphology of the circum-emargination bones (e.g., postorbital). It is similar to the more recently described '' Llistrofus pricei'' in this regard, but can be differentiated from ''L. pricei'' by features such as the abse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hapsidopareiidae
Hapsidopareiontidae is an extinct family of tuditanomorph microsaurs. Hapsidopareiontids are known from the Early Permian of the United States and possibly Germany and the Czech Republic. Hapsidopareiontids are characterized by a large temporal embayment near the cheek region in which the quadratojugal is greatly reduced or absent. Members of Ostodolepidae, another microsaur family, also possess temporal embayments, but they not as extensive as those of hapsidopareiontids, which extend into the skull roof. In hapsidopareiontids, the embayment may have provided space for an enlarged jaw adductor musculature, although certain characteristics of the skull do not support this idea. '' Hapsidopareion'' and ''Llistrofus'' both possess this embayment, but in ''Saxonerpeton ''Saxonerpeton'' is an extinct genus of microsaur of the family Hapsidopareiontidae. Fossils have been found from Early Permian strata near Dresden, Germany. See also * List of prehistoric amphibians Referenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richards Spur
Richards Spur is a Permian fossil locality located at the Dolese Brothers Limestone Quarry north of Lawton, Oklahoma. The locality preserves clay and mudstone fissure fills of a karst system eroded out of Ordovician limestone and dolomite, with the infilling dating to the Artinskian stage of the early Permian (Cisuralian), around 289 to 286 million years ago. Fossils of terrestrial animals are abundant and well-preserved, representing one of the most diverse Paleozoic tetrapod communities known. A common historical name for the site is Fort Sill, in reference to the nearby military base. Fossils were first reported at the quarry by workers in 1932, spurring a wave of collecting by local and international geologists. Early taxa of interest included the abundant reptile '' Captorhinus'' and microsaurs such as '' Cardiocephalus'' and '' Euryodus''. Later notable discoveries include '' Doleserpeton'' (one of the most lissamphibian-like Paleozoic tetrapods), the most diverse assortmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsaur
Microsauria ("small lizards") is an extinct, possibly polyphyletic order of tetrapods from the late Carboniferous and early Permian periods. It is the most diverse and species-rich group of lepospondyls. Recently, Microsauria has been considered paraphyletic, as several other non-microsaur lepospondyl groups such as Lysorophia seem to be nested in it. Microsauria is now commonly used as a collective term for the grade of lepospondyls that were originally classified as members of Microsauria. The microsaurs all had short tails and small legs, but were otherwise quite varied in form. The group included lizard-like animals that were relatively well-adapted to living on dry land, burrowing forms, and others that, like the modern axolotl, retained their gills into adult life, and so presumably never left the water. Distribution Microsaur remains have been found from Europe and North America in Late Carboniferous and Early Permian localities. Most North American microsaurs have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuditanomorpha
Tuditanomorpha is a suborder of microsaur lepospondyls. Tuditanomorphs lived from the Late Carboniferous to the Early Permian and are known from North America and Europe. Tuditanomorphs have a similar pattern of bones in the skull roof. Tuditanomorphs display considerable variability, especially in body size, proportions, dentition, and presacral vertebral count. Currently there are seven families of tuditanomorphs, with two being monotypic. Tuditanids, gymnarthrids, and pantylids first appear in the Lower Pennsylvanian. Goniorhynchidae, Hapsidopareiontidae, Ostodolepidae, and Trihecatontidae appear in the Late Pennsylvanian and Early Permian. Classification Suborder Tuditanomorpha *Family Goniorhynchidae **'' Rhynchonkos'' *Family Gymnarthridae **'' Cardiocephalus'' **'' Elfridia'' **'' Euryodus'' **'' Leiocephalikon'' **'' Pariotichus'' **'' Sparodus'' *Family Hapsidopareiontidae **'' Hapsidopareion'' **'' Llistrofus'' **'' Ricnodon'' **'' Saxonerpeton'' *Family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Amphibian
This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomina dubia''), or were not formally published ('' nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered amphibians. Modern forms are excluded from this list. The list currently includes 454 names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type specimens are later assigned to the same genus, the first to be published (in chronological order) is the senior synon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenial
The splenial is a small bone in the lower jaw of reptiles, amphibians and birds, usually located on the lingual side (closest to the tongue) between the angular and surangular The suprangular or surangular is a jaw bone found in most land vertebrates, except mammals. Usually in the back of the jaw, on the upper edge, it is connected to all other jaw bones: dentary, angular, splenial and articular The articular bone ....Watson, D. M. S. (1912). LXVII.—On some reptilian lower jaws. Journal of Natural History, 10(60), 573-587. References Vertebrate anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomer
The vomer (; lat, vomer, lit=ploughshare) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms the inferior part of the nasal septum in humans, with the superior part formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. The name is derived from the Latin word for a ploughshare and the shape of the bone. In humans The vomer is situated in the median plane, but its anterior portion is frequently bent to one side. It is thin, somewhat quadrilateral in shape, and forms the hinder and lower part of the nasal septum; it has two surfaces and four borders. The surfaces are marked by small furrows for blood vessels, and on each is the nasopalatine groove, which runs obliquely downward and forward, and lodges the nasopalatine nerve and vessels. Borders The ''superior border'', the thickest, presents a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or ''os premaxillare'', intermaxillary bone or ''os intermaxillare'', and Goethe's bone. Human anatomy In human anatomy, the premaxilla is referred to as the incisive bone (') and is the part of the maxilla which bears the incisor teeth, and encompasses the anterior nasal spine and alar region. In the nasal cavity, the premaxillary element projects higher than the maxillary element behind. The palatal portion of the premaxilla is a bony plate with a generally transverse orientation. The incisive foramen is bound anteriorly and laterally by the premaxilla and posteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla. It is formed from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabular Bone
The tabular bones are a pair of triangular flat bones along the rear edge of the skull which form pointed structures known as tabular horns in primitive Teleostomi Teleostomi is an obsolete clade of jawed vertebrates that supposedly includes the tetrapods, bony fish, and the wholly extinct acanthodian fish. Key characters of this group include an operculum and a single pair of respiratory openings, feat .... References Fish anatomy Amphibian anatomy {{vertebrate-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |