|
List Of AMD FX Processors
AMD FX is a discontinued series of AMD microprocessors for personal computers. The following is a list of AMD FX brand microprocessors. Some APUs also carry an FX model name, but the term "FX" normally only refers to CPUs which are not just APUs with the iGPU disabled. Features overview CPUs VS RF APU features table Desktop CPUs Athlon 64 Family (90–130 nm) These processors were the first AMD CPUs to use the "FX" designation and identified the chip as being higher-performance. The frequency multiplier was unlocked in these chips. SledgeHammer Core (130 nm) * Socket 940 * L1 cache: 64 kb + 64 kb (data + instruction) * L2 cache: 1024 kb (full speed) * Instruction sets: MMX, SSE, SSE2, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit, AMD64 FX-51 (2.2 GHz) and FX-53 (2.4 GHz) ClawHammer Core (130 nm) * Socket 939 * L1 cache: 64 kb + 64 kb (data + instruction) * L2 cache: 1024 kb (full speed) * Instruction sets: MMX, SSE, SSE2, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit, AMD64 FX-53 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of AMD Processors
This article gives a list of AMD microprocessors, sorted by generation and release year. If applicable and openly known, the designation(s) of each processor's core (versions) is (are) listed in parentheses. For an overview over concrete product, you then need to consult further articles, like e.g. list of AMD accelerated processing units. Features overview AMD IP x86 CPUs APUs APU features table AMD-originated architectures Am2900 series (1975) * Am2901 4- bit-slice ALU (1975) * Am2902 Look-Ahead Carry Generator * Am2903 4-bit-slice ALU, with hardware multiply * Am2904 Status and Shift Control Unit * Am2905 Bus Transceiver * Am2906 Bus Transceiver with Parity * Am2907 Bus Transceiver with Parity * Am2908 Bus Transceiver with Parity * Am2909 4-bit-slice address sequencer * Am2910 12-bit address sequencer * Am2911 4-bit-slice address sequencer * Am2912 Bus Transceiver * Am2913 Priority Interrupt Expander * Am2914 Priority Interrupt Controller 29000 (2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
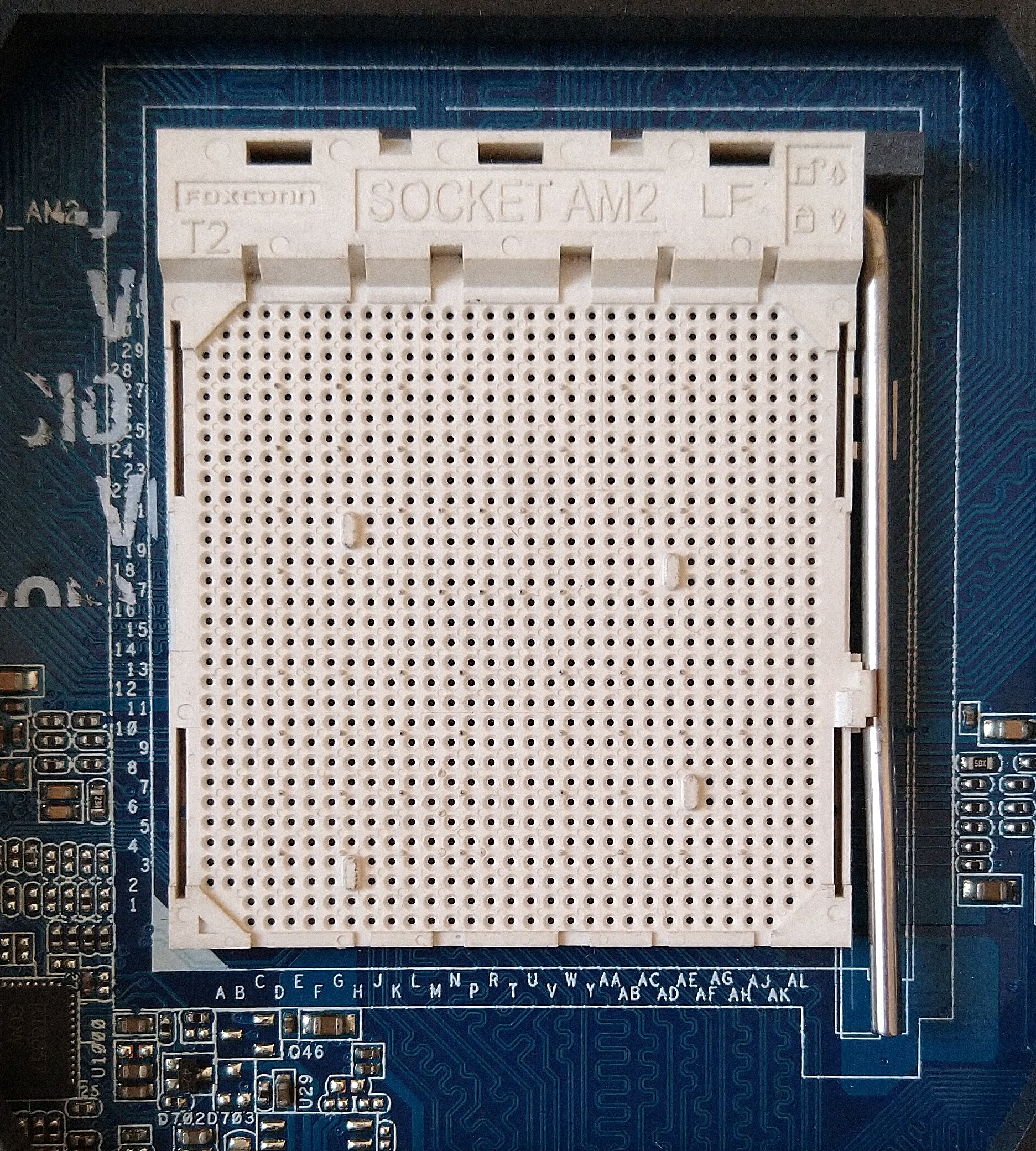
Socket AM2
The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 (to prevent using the same name as Cyrix MII processors), is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments. It was released on May 23, 2006, as a replacement for Socket 939. Technical specifications AM2 processors are incompatible with 939 motherboards and vice versa, and although it has 940 pins, it is incompatible with Socket 940. Socket AM2 supports DDR2 SDRAM memory but not DDR memory, which the previous Socket 939 supported. ''AnandTech'' reported that Socket AM2 system performance was only about 7% faster than Socket 939 equivalents, with most applications about 2% faster, despite having over 30% greater memory bandwidth due to DDR2 support. The first processor cores to support socket AM2 were the single-core Orleans (Athlon 64) and Manila (Sempron), and the dual-core Windsor ( Athlon 64 X2 and Athlon 64 FX). Most processors on Socket AM2 include SSE3 instructions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Input–output Memory Management Unit
In computing, an input–output memory management unit (IOMMU) is a memory management unit (MMU) connecting a direct-memory-access–capable (DMA-capable) I/O bus to the main memory. Like a traditional MMU, which translates CPU-visible virtual addresses to physical addresses, the IOMMU maps device-visible virtual addresses (also called ''device addresses'' or ''memory mapped'' ''I/O addresses'' in this context) to physical addresses. Some units also provide memory protection from faulty or malicious devices. An example IOMMU is the graphics address remapping table (GART) used by AGP and PCI Express graphics cards on Intel Architecture and AMD computers. On the x86 architecture, prior to splitting the functionality of northbridge and southbridge between the CPU and Platform Controller Hub (PCH), I/O virtualization was not performed by the CPU but instead by the chipset. Advantages The advantages of having an IOMMU, compared to direct physical addressing of the memory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X86 Virtualization
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU. In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities while attaining reasonable performance. In 2005 and 2006, both Intel ( VT-x) and AMD ( AMD-V) introduced limited hardware virtualization support that allowed simpler virtualization software but offered very few speed benefits. Greater hardware support, which allowed substantial speed improvements, came with later processor models. Software-based virtualization The following discussion focuses only on virtualization of the x86 architecture protected mode. In protected mode the operating system kernel runs at a higher privilege such as ring 0, and applications at a lower privilege such as ring 3. In software-based virtualization, a host OS has direct access to hardware while the guest OSs have limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSE4
SSE4 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 4) is a SIMD CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 (K8L). It was announced on September 27, 2006, at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper;Intel Streaming SIMD Extensions 4 (SSE4) Instruction Set Innovation , Intel. more precise details of 47 instructions became available at the Spring 2007 Intel Developer Forum in , in the presentation. SSE4 extended the SSE3 instruction set which was released in early 2004. All software using previous Intel SIMD instructio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSSE3
Supplemental Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSSE3 or SSE3S) is a SIMD instruction set created by Intel and is the fourth iteration of the SSE technology. History SSSE3 was first introduced with Intel processors based on the Core microarchitecture on June 26, 2006 with the "Woodcrest" Xeons. SSSE3 has been referred to by the codenames Tejas New Instructions (TNI) or Merom New Instructions (MNI) for the first processor designs intended to support it. SSSE3 has enhanced for HD audio/video decoding/encoding, for example AAC. Functionality SSSE3 contains 16 new discrete instructions. Each instruction can act on 64-bit MMX or 128-bit XMM registers. Therefore, Intel's materials refer to 32 new instructions. They include: * Twelve instructions that perform horizontal addition or subtraction operations. * Six instructions that evaluate absolute values. * Two instructions that perform multiply-and-add operations and speed up the evaluation of dot products. * Two instructions tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die (integrated Circuit)
A die, in the context of integrated circuits, is a small block of semiconducting material on which a given functional circuit is Semiconductor fabrication, fabricated. Typically, integrated circuits are produced in large batches on a single wafer (electronics), wafer of electronic-grade Monocrystalline silicon, silicon (EGS) or other semiconductor (such as Gallium arsenide, GaAs) through processes such as photolithography. The wafer is cut (wafer dicing, diced) into many pieces, each containing one copy of the circuit. Each of these pieces is called a die. There are three commonly used plural forms: ''dice'', ''dies,'' and ''die''. To simplify handling and integration onto a printed circuit board, most dies are integrated circuit packaging, packaged in List of electronic component packaging types, various forms. Manufacturing process Most dies are composed of silicon and used for integrated circuits. The process begins with the production of Single crystal, monocrystalline sili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDR3 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth (" double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-speed successor to DDR and DDR2 and predecessor to DDR4 synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) chips. DDR3 SDRAM is neither forward nor backward compatible with any earlier type of random-access memory (RAM) because of different signaling voltages, timings, and other factors. DDR3 is a DRAM interface specification. The actual DRAM arrays that store the data are similar to earlier types, with similar performance. The primary benefit of DDR3 SDRAM over its immediate predecessor DDR2 SDRAM, is its ability to transfer data at twice the rate (eight times the speed of its internal memory arrays), enabling higher bandwidth or peak data rates. The DDR3 standard permits DRAM chip capacities of up to 8 gigabits (Gbit) (so 1 gigabyte by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIMM
A DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) is a popular type of memory module used in computers. It is a printed circuit board with one or both sides (front and back) holding DRAM chips and pins. The vast majority of DIMMs are manufactured in compliance with JEDEC memory standards, although there are proprietary DIMMs. DIMMs come in a variety of speeds and capacities, and are generally one of two lengths: PC, which are , and laptop (SO-DIMM), which are about half the length at . History DIMMs (Dual In-line Memory Module) were a 1990s upgrade for SIMMs (Single In-line Memory Modules) as Intel P5-based Pentium processors began to gain market share. The Pentium had a 64-bit bus width, which would require SIMMs installed in matched pairs in order to populate the data bus. The processor would then access the two SIMMs in parallel. DIMMs were introduced to eliminate this disadvantage. The contacts on SIMMs on both sides are redundant, while DIMMs have separate electrical contacts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
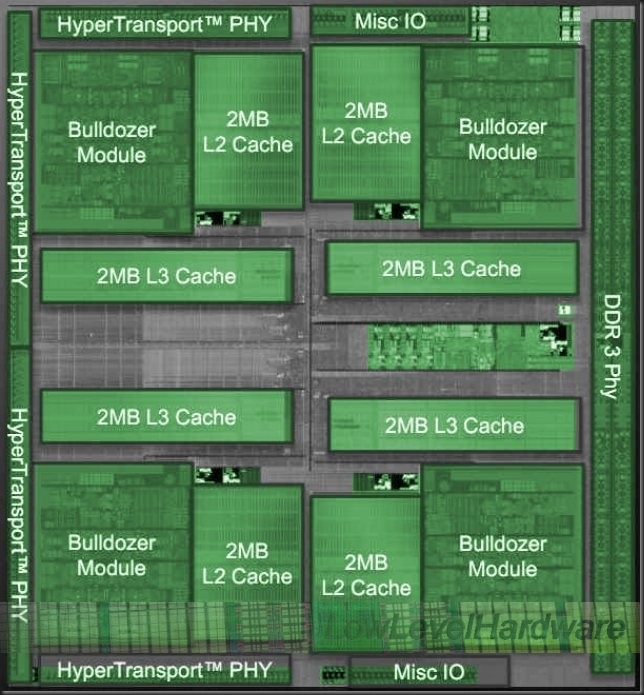
Bulldozer (microarchitecture)
The AMD Bulldozer Family 15h is a microprocessor microarchitecture for the FX and Opteron line of processors, developed by AMD for the desktop and server markets. Bulldozer is the codename for this family of microarchitectures. It was released on October 12, 2011, as the successor to the K10 microarchitecture. Bulldozer is designed from scratch, not a development of earlier processors. The core is specifically aimed at computing products with TDPs of 10 to 125 watts. AMD claims dramatic performance-per-watt efficiency improvements in high-performance computing (HPC) applications with Bulldozer cores. The ''Bulldozer'' cores support most of the instruction sets implemented by Intel processors ( Sandy Bridge) available at its introduction (including SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, AES, CLMUL, and AVX) as well as new instruction sets proposed by AMD; ABM, XOP, FMA4 and F16C. Only Bulldozer GEN4 (Excavator) supports AVX2 instruction sets. Overview According to AMD, Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPU Socket
In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the central processing unit (CPU) without soldering. Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with many pins, zero insertion force (ZIF) sockets are preferred. Common sockets include pin grid array (PGA) or land grid array (LGA). These designs apply a compression force once either a handle (PGA type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending pins when inserting the chip into the socket. Certain devices use Ball Grid Array (BGA) sockets, although these require soldering and are generally not considered user replaceable. CPU sockets are used on the motherboard in desktop and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket AM3+
Socket AM3+ is a modification of Socket AM3, which was released on February 9, 2009. AM3+ was released in mid-2011 designed for CPUs which use the AMD Bulldozer (processor), Bulldozer microarchitecture and retains compatibility with processors made for AM3. The Piledriver (microarchitecture), Vishera line of AMD CPUs also all use Socket AM3+. It is the last AMD socket for which Windows XP support officially exists. Technical specifications The AM3+ Socket specification contains a few noteworthy design changes over its AM3 predecessor. The 942 pin count for the AM3+ is an increase of one compared to the AM3 Socket layout. The AM3+ Socket has larger pin socket diameter of 0.51 millimeter, mm compared to 0.45 mm with the AM3 Socket. There is a faster serial link of 3400 kHz from the CPU to the power controller, compared to 400 kHz. The AM3+ Socket offers improved power regulation and power quality specifications, including an increased maximum current support of 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |