|
List Of High-voltage Transmission Links In Lithuania
This is a list of high-voltage transmission links in Lithuania at voltages higher than 330 kV and/or the 400 kV-grid. The list does not include links at smaller voltages like 110 kV or less. International links Former International Links Local links Planned local links See also * Baltic states synchronization with CESA * List of power stations in Lithuania * List of high-voltage transmission links in Sweden References {{Lists of high-voltage transmission links Lithuania Lithuania Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ... High-voltage transmission Bilateral relations of Lithuania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Klaipėda
Klaipėda ( ; ) is a city in Lithuania on the Baltic Sea coast. It is the List of cities in Lithuania, third-largest city in Lithuania, the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, fifth-largest city in the Baltic States, and the capital of Klaipėda County, as well as the only major seaport in the country – the Port of Klaipėda, which is also the busiest port in the Baltic States. The city has a complex recorded history, partially due to the combined regional importance of the usually ice-free port at the mouth of the river . It was located in Lithuania Minor, and the State of the Teutonic Order and Duchy of Prussia under the suzerainty of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, then the Kingdom of Prussia and German Empire, within which it was the northernmost big city until it was placed under French occupation in 1919. From 1923, the city was part of Lithuania until its annexation by Nazi Germany in 1939, and after World War II it was part of the Lithuanian Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nybro
Nybro (, outdatedly ) is a city status in Sweden, city and the seat of Nybro Municipality, Kalmar County, Sweden with 13,583 inhabitants in 2020. Overview Nybro was founded as a rest area for travellers on the road between Växjö in the west and Kalmar in the east. In the 18th century a new bridge was built where the road crossed a stream and it was hence called ''Nybron'', The New Bridge. A small tavern called ''Lortkrogen'' (literally the Filth Tavern) opened there. The market town was founded in the 19th century, but it rapidly transformed into an industrial town. In 1865 the town became a municipality separately from Madesjö. It was granted city rights in 1932. Nybro is surrounded by forests and small agricultural enclaves. Kährs is a manufacturer of wooden floors and the largest employer in the city. But the two glassworks factories (Nybro glasbruk, Nybro and Pukeberg glasbruk, Pukeberg) are more known, because they also serve as tourist attraction. Nybro calls itself "The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electric Power Transmission Systems In Lithuania
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of either a positive or negative electric charge produces an electric field. The motion of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. In most applications, Coulomb's law determines the force acting on an electric charge. Electric potential is the work done to move an electric charge from one point to another within an electric field, typically measured in volts. Electricity plays a central role in many modern technologies, serving in electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment, and in electronics dealing with electrical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of High-voltage Transmission Links In Sweden
List of high-voltage transmission links in Sweden. International links In addition to the above named, submarine interconnectors Sweden has four AC submarine cables to Zealand, Denmark. These can import 1,700 MW and export 1,300 MW of power. National links See also *Electricity sector in Sweden *List of power stations in Sweden *Nordic energy market *List of high-voltage transmission links in Denmark *List of high-voltage transmission links in Lithuania References {{Lists of high-voltage transmission links Electric power transmission in Europe, Sweden HVDC transmission lines, Sweden Lists of buildings and structures in Sweden, High-voltage transmission Bilateral relations of Sweden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
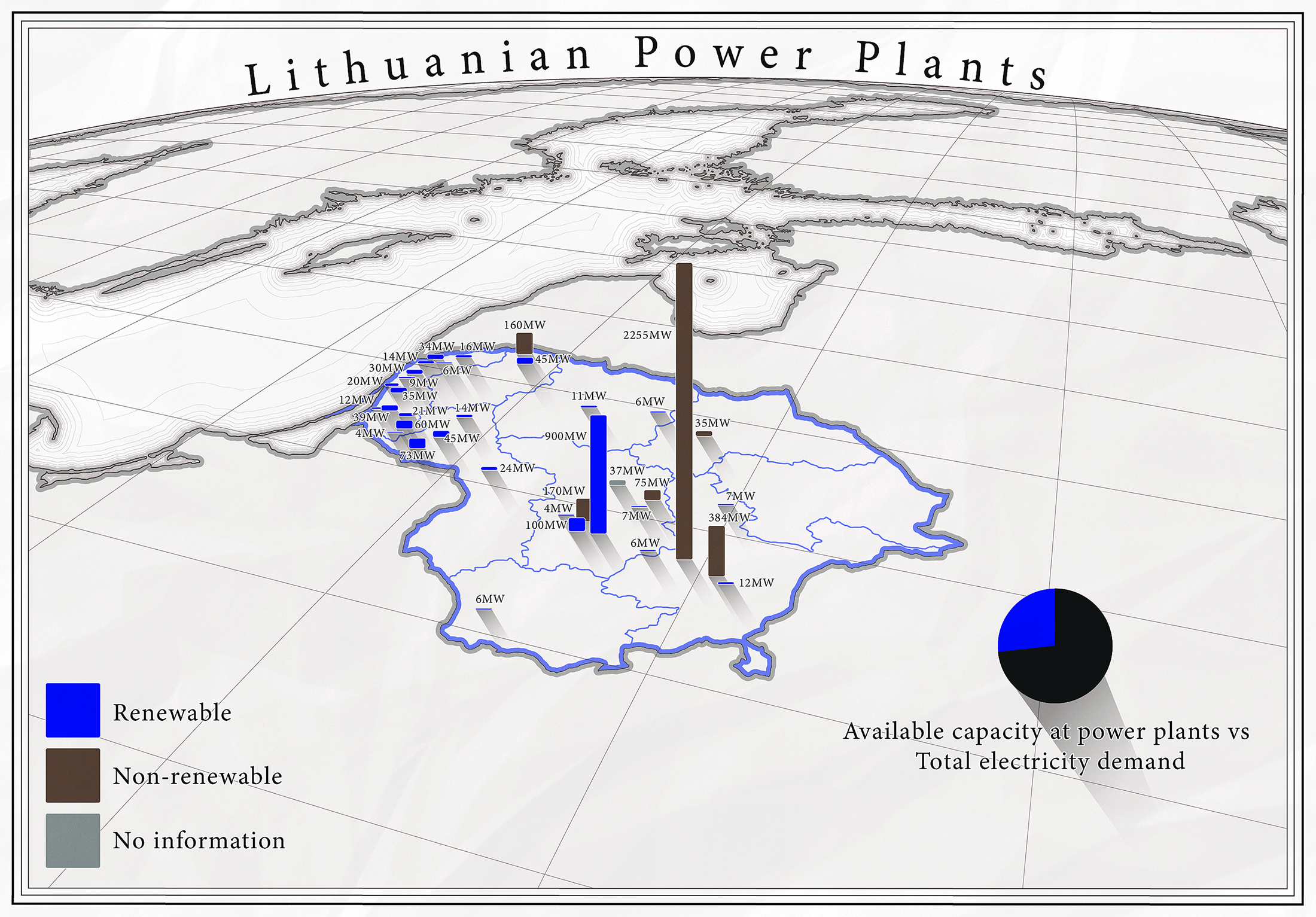
List Of Power Stations In Lithuania ...
The following page lists the largest power stations in Lithuania. See also * List of power stations in Europe * List of largest power stations in the world References {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Power Stations In Lithuania Lithuania Power stations A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the electricity generation, generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Baltic States Synchronization With CESA
The three Baltic states (Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia) undertook the synchronization of their electric power transmission infrastructure with the Continental Europe Synchronous Area (CESA), a project known as Baltic Synchro. Managed by ENTSO-E, this initiative aimed to disconnect from the IPS/UPS system, previously governed by the 2001 BRELL Agreement with Belarus and Russia. The project was successfully completed on 9 February 2025. History The electricity systems of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania were technologically integrated into the IPS/UPS grid in the early 1960s, during the Soviet occupation of the Baltic States. In 2001, the BRELL Agreement was signed between Belarus, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania on the technical management of the synchronization of their power grids as part of the IPS/UPS power distribution system. Nevertheless, IPS/UPS is largely managed centrally from Moscow. In 2007, the three Baltic states applied to join ENTSO-E (then UCTE) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mūša
The Mūša (; German: Muhsse) is a river in Northern Lithuania and Southern Latvia (Zemgale region). At its Confluence (geography), confluence with the river Nemunėlis () in Latvia, near the city of Bauska, the river Lielupe, Lielupė is formed. The river is 164 kilometers (146 km in Lithuania, 18 km in Latvia) long. References LIETUVOS RESPUBLIKOS UPIŲ IR TVENKINIŲ KLASIFIKATORIUS (Republic of Lithuania- River and Pond Classifications) Ministry of Environment (Lithuania). Accessed 2011-11-17. Rivers of Lithuania Rivers of Latvia International rivers of Europe Latvia–Lithuania border {{Latvia-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population was 607,667, and the Vilnius urban area (which extends beyond the city limits) has an estimated population of 747,864. Vilnius is notable for the architecture of its Vilnius Old Town, Old Town, considered one of Europe's largest and best-preserved old towns. The city was declared a World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994. The architectural style known as Vilnian Baroque is named after the city, which is farthest to the east among Baroque architecture, Baroque cities and the largest such city north of the Alps. The city was noted for its #Demographics, multicultural population during the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, with contemporary sources comparing it to Babylon. Before World War II and The Holocaust in Lithuania, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant
The Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant () is a Nuclear decommissioning, decommissioned two-unit RBMK-1500 nuclear power plant, nuclear power station in Visaginas Municipality, Lithuania. It was named after the nearby city of Ignalina. Due to the plant's similarities to the infamous Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in both reactor design and lack of a robust containment building, Lithuania agreed to close the plant as part of its agreement of 2004 enlargement of the European Union, accession to the European Union. Unit 1 was closed in December 2004; Unit 2 in December 2009. The plant accounted for 25% of Lithuania's electricity generating capacity and supplied about 70% of Lithuania's electrical demand. It was closed on 31 December 2009. Proposals have been made to construct a new nuclear power plant at the site, but such plans have yet to come to fruition. Reactors The Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant contained two Soviet Union, Soviet-designed RBMK-1500 water-cooled graphite-neutron mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Elektrėnai Power Plant
The Elektrėnai Power Plant or Elektrėnai Complex () is a gas- and fuel-oil-fired 1,055 MW electricity generating station near Elektrėnai, Lithuania, about west of the capital, Vilnius. It is operated by Ignitis gamyba AB, a subsidiary of Ignitis. History The plant was built in stages between 1960 and 1972. The Strėva River was dammed to supply it with cooling water, creating the Elektrėnai Reservoir. In 2008, the plant comprised eight units fired with natural gas. In the past, it used heavy fuel oil and, for a brief period in 1990s, a bitumen-based fuel known as Orimulsion imported from Venezuela. It was designed as a base load plant, and generated about 10 TWh per year until 1992. Its operations were then reduced to about 5% of its capacity, since it acted only as a reserve in the Lithuanian power system. After the shutdown of the Ignalina nuclear power plant in 2009, the plant became the primary source of Lithuania's electrical power. Since the plant did ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Elektrėnai
Elektrėnai () is a city of about 11,000 inhabitants in Vilnius County, Lithuania; since 2000 it has been the capital of the Elektrėnai Municipality. It is situated between the two largest cities in Lithuania – Vilnius and Kaunas. History Historically, two villages were located in the area; one of those was Perkūnas, Perkūnkiemis (Lithuanian: ''Perkūnas, Thunder's yard''). Elektrėnai is one of the newest towns of Lithuania, having been established during the Occupation of the Baltic states, Soviet occupation in the early 1960s as the living space for workers of the nearby power plant. It was expanded in the 1980s and early 1990s as a residence for builders and workers at the nearby Kruonis Pumped Storage Plant. The name of the new town was derived from word ''elektra'' (English: ''electricity'') – a borrowing to Lithuanian language from Greek language, Greek. ''Gintarėnai'' (''gintaras'' – Lithuanian word for amber) was another name considered, but was rejected before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kruonis Pumped Storage Plant
Kruonis Pumped Storage Plant (the KPSP) is a pumped storage hydroelectric power plant located near Kruonis, Lithuania, east of Kaunas. Its main purpose is to provide grid energy storage. It operates in conjunction with the Kaunas Hydroelectric Power Plant. During periods of low demand, usually at night, Kruonis PSHP raises water from the lower Kaunas reservoir to the upper one using cheap surplus energy. The station is designed to have an installed capacity of 1,600 MW but only four 225 MW generators are currently operational. With a fully filled upper reservoir the plant can generate 900 MW for about 12 hours. The KPSP uses hydro-resources of artificial water pools existing at different geographical levels. The electricity from this power plant is supplied to a 330 kV electricity line to Elektrėnai, where the largest fossil fuel plant in Lithuania is operating, and Kaunas. At times of surplus electricity generation, the KPSP uses the surplus electricity to pump water fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |