|
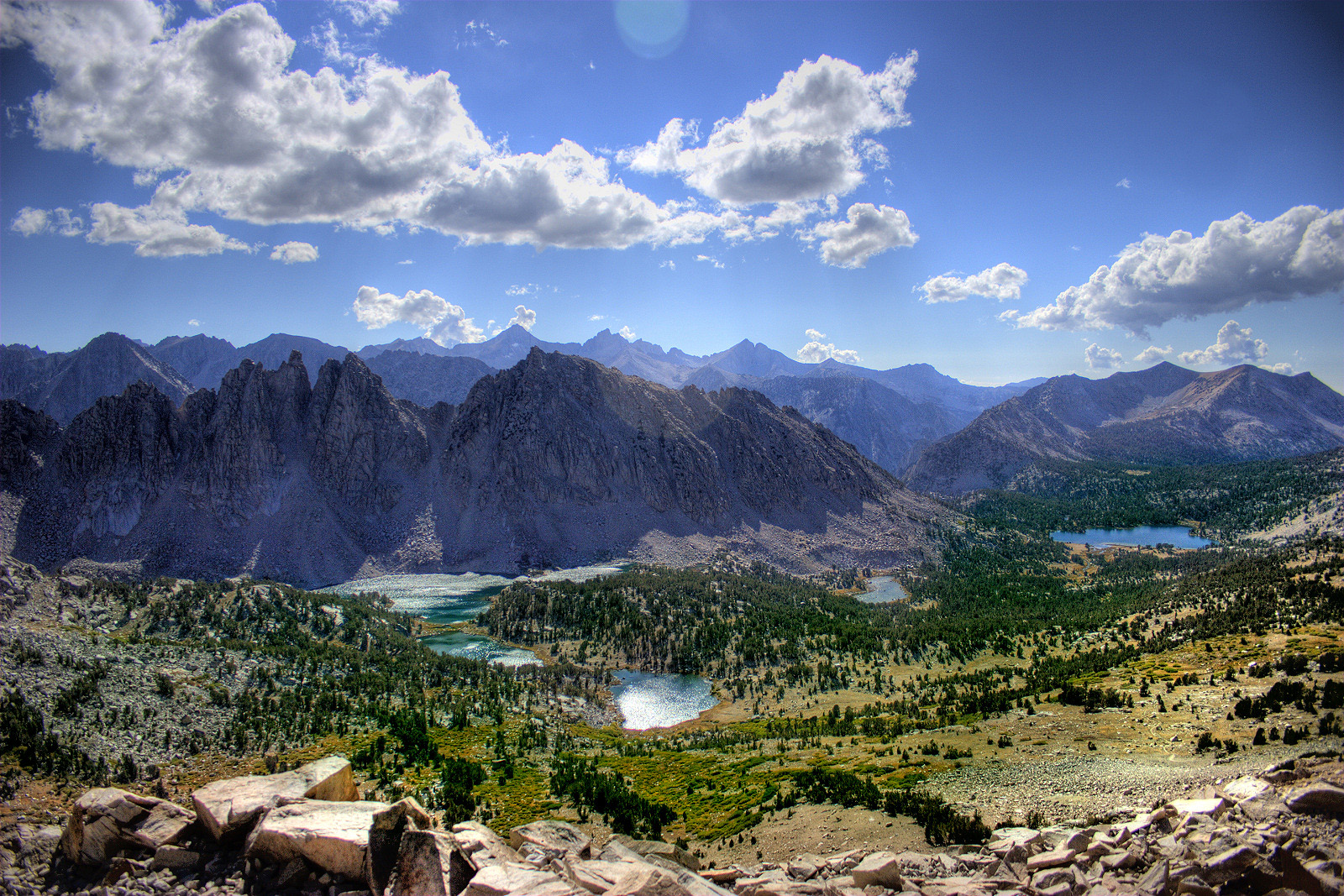
Lake Tahoe, Nevada
Lake Tahoe (; Washo: ''dáʔaw'') is a freshwater lake in the Sierra Nevada of the Western United States, straddling the border between California and Nevada. Lying at above sea level, Lake Tahoe is the largest alpine lake in North America, and at it trails only the five Great Lakes as the largest by volume in the United States. Its depth is , making it the second deepest in the United States after Crater Lake in Oregon (). The lake was formed about two million years ago as part of the Lake Tahoe Basin, and its modern extent was shaped during the ice ages. It is known for the clarity of its water and the panorama of surrounding mountains on all sides. The area surrounding the lake is also referred to as Lake Tahoe, or simply Tahoe; its English name is derived from its Washo name, . More than 75% of the lake's watershed is national forest land, covered by the Lake Tahoe Basin Management Unit of the United States Forest Service. Lake Tahoe is a major tourist attractio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Lake
An ancient lake is a lake that has consistently carried water for more than one million years. Twelve of the 20 ancient lakes have existed for more than 2.6 million years, the full Quaternary period. Ancient lakes continue to persist due to plate tectonics in an active rift zone. This active rift zone creates lakes that are extremely deep and difficult to naturally fill with sediment. Due to the prolonged life of ancient lakes, they serve as models for isolated evolutionary traits and speciation. Most of the world's bodies of water are less than 18,000 years old. There are only 20 ancient lakes over 1 million years old. Lake Baikal is often considered the oldest, as clear evidence shows that it is 25–30 million years old. Lake Zaysan may be even older, of Cretaceous origin and at least 66 million years old (most likely around 70 million years), but its exact age is controversial and labeled with some uncertainty. Another contender for oldest is Lake Maracaibo, estimated to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truckee
Truckee is an incorporated town in Nevada County, California, United States. As of the 2010 United States Census, the population was 16,180, reflecting an increase of 2,316 from the 13,864 counted in the 2000 Census. History Name Truckee's existence began in 1863 as Gray's Station, named for Joseph Gray's Roadhouse on the trans-Sierra wagon road.Union Pacific Railroad Historical Society Archives A blacksmith named Samuel S. Coburn was there almost from the beginning, and by 1866 the area was known as Coburn's Station. The Central Pacific Railroad selected Truckee as the name of its railroad station by August 1867, even though the tracks would not reach the station until a year later in 1868. It was renamed Truckee after a Paiute chief, whose assumed Paiute name was Tru-ki-zo. He was the father of Chief Winnemucca and grandfather of Sarah Winnemucca. The first Europeans who came to cross the Sierra Nevada encountered his tribe. The friendly chief rode toward them yelling, " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. The 42nd parallel north, 42° north parallel delineates the southern boundary with California and Nevada. The western boundary is formed by the Pacific Ocean. Oregon has been home to many Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous nations for thousands of years. The first European traders, explorers, and settlers began exploring what is now Oregon's Pacific coast in the early to mid-16th century. As early as 1564, the Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest, Spanish began sending vessels northeast from the Philippines, riding the Kuroshio Current in a sweeping circular route across the northern part of the Pacific. In 1592, Juan de Fuca undertook detailed mapping a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crater Lake
Crater Lake ( Klamath: ) is a volcanic crater lake in south-central Oregon in the Western United States. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and is a tourist attraction for its deep blue color and water clarity. The lake partly fills a caldera that was formed around 7,700 (± 150) years ago by the collapse of the volcano Mount Mazama. No rivers flow into or out of the lake; the evaporation is compensated for by rain and snowfall at a rate such that the total amount of water is replaced every 150 years. With a depth of , the lake is the deepest in the United States. In the world, it ranks eleventh for maximum depth, as well as fifth for mean depth. Crater Lake features two small islands. Wizard Island, located near the western shore of the lake, is a cinder cone about in size. Phantom Ship, a natural rock pillar, is located near the southern shore. Since 2002, one of Oregon's regular-issue license-plate design has featured Crater Lake and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Lakes By Depth
These articles lists the world's deepest lakes. Lakes ranked by maximum depth ''This list contains all lakes whose maximum depth is reliably known to exceed '' Geologically, the Caspian Sea, like the Black and Mediterranean seas, is a remnant of the ancient Tethys Ocean. The deepest area is oceanic rather than continental crust. However, it is generally regarded by geographers as a large endorheic salt lake. Of these registered lakes; 10 have a deepest point above the sea level. These are: Issyk-Kul, Crater Lake, Quesnel, Sarez, Toba, Tahoe, Kivu, Nahuel Huapi, Van and Poso. Lakes ranked by mean depth Mean depth can be a more useful indicator than maximum depth for many ecological purposes. Unfortunately, accurate mean depth figures are only available for well-studied lakes, as they must be calculated by dividing the lake's volume by its surface area. A reliable volume figure requires a bathymetric survey. Therefore, mean depth figures are not available for many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Lakes By Volume
This article lists lakes with a water volume of more than 100 km3, ranked by volume. The volume of a lake is a difficult quantity to measure. Generally, the volume must be inferred from bathymetric data by integration. Lake volumes can also change dramatically over time and during the year, especially for salt lakes in arid climates. For these reasons, and because of changing research, information on lake volumes can vary considerably from source to source. The base data for this article are from ''The Water Encyclopedia'' (1990). Where volume data from more recent surveys or other authoritative sources have been used, that usage is referenced in the respective entry. The total volume of Earth's lakes is 199,000 km3. The list The volumes of the lakes below vary little by season. This list does not include reservoirs; if it did, six reservoirs would appear on the list: Lake Kariba at 26th, Bratsk Reservoir, Lake Volta, Lake Nasser, Manicouagan Reservoir, and Lake Gur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, Huron, Lake Erie, Erie, and Lake Ontario, Ontario (though hydrologically, Lake Michigan–Huron, Michigan and Huron are a single body of water, joined at the Straits of Mackinac). The Great Lakes Waterway enables modern travel and shipping by water among the lakes. The lakes connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River, and to the Mississippi River basin through the Illinois Waterway. The Great Lakes are the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total area and the second-largest by total volume. They contain 21% of the world's surface fresh water by volume. The total surface is , and the total volume (measured at the low water datum) is , slightly less than the volume of Lake Baikal (, 22–23% of the world's surface f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes Middle America (Americas), Middle America (comprising the Caribbean, Central America, and Mexico) and Northern America. North America covers an area of about , representing approximately 16.5% of Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in list of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Lake
An alpine lake is a high-altitude lake in a mountainous area, usually near or above the tree line, with extended periods of ice#On lakes, ice cover. These lakes are commonly glacial lakes formed from glacial activity (either current or in the past) but can also be formed from geological processes such as volcanic activity (volcanogenic lakes) or landslides (landslide dam, barrier lakes). Many alpine lakes that are fed from glacial meltwater have the characteristic bright turquoise green color as a result of glacial flour, suspended minerals derived from a glacier scouring the bedrock. When active glaciers are not supplying water to the lake, such as a majority of Rocky Mountains alpine lakes in the United States, the lakes may still be bright blue due to the lack of algal growth resulting from cold temperatures, lack of nutrient run-off from surrounding land, and lack of sediment input. The coloration and mountain locations of alpine lakes attract lots of recreational activity. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Western States, the Far West, the Western territories, and the West) is List of regions of the United States, census regions United States Census Bureau. As American settlement in the U.S. Manifest destiny, expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the West'' changed. Before around 1800, the crest of the Appalachian Mountains was seen as the American frontier, western frontier. The frontier moved westward and eventually the lands west of the Mississippi River were considered ''the West''. The U.S. Census Bureau's definition of the 13 westernmost states includes the Rocky Mountains and the Great Basin to the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast, and the mid-Pacific islands state, Hawaii. To the east of the Western United States is the Midwestern United States and the Southern United States, with Canada to the north and Mexico to the south. The West contains several major biomes, including arid and Sem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily in Nevada. The Sierra Nevada is part of the American Cordillera, an almost continuous chain of mountain ranges that forms the western "backbone" of the Americas. The Sierra runs north-south, and its width ranges from to across east–west. Notable features include the General Sherman Tree, the largest tree in the world by volume; Lake Tahoe, the largest alpine lake in North America; Mount Whitney at , the highest point in the contiguous United States; and Yosemite Valley sculpted by glaciers from one-hundred-million-year-old granite, containing high waterfalls. The Sierra is home to three national parks, twenty-six wilderness areas, ten national forests, and two national monuments. These areas include Yosemite, Sequoia, and Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers. Lakes, as with other bodies of water, are part of the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Most lakes are fresh water and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume of water. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which are also water-filled basins on land, although there are no official definitions or scientific criteria distinguishing the two. Lakes are also distinct from lagoons, which are generally shallow tidal pools dammed by sandbars or other material at coastal regions of ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |