|
Käthe Braun
Käthe Braun (11 November 1913 – 9 September 1994) was a German stage and film actress. She was married to director Falk Harnack and acted in several of his films. Career Katharina Braun was born in Wasserburg am Inn. After studying acting privately with Magda Lena in Munich, she had her first theater engagement at the Bavarian state theater, Cuvilliés-Theater. In 1938, she began working at the Düsseldorf Schauspielhaus and in 1941, at the city theater in Strasbourg, staying there until Goebbels closed all the theaters in August 1944. After World War II, she returned to Munich and, from 1947 to 1951, worked periodically at the Deutsches Theater in Berlin. She also played major roles in East German DEFA productions, such as Stine Teetjen, the wife in '' Das Beil von Wandsbek'', adapted from the book by Arnold Zweig and directed by her husband.Falk Harnack was a former member of the German Resistance who had been involved with the White Rose and the Red Orche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wasserburg Am Inn
Wasserburg am Inn ( Central Bavarian: ''Wassabuag am Inn'') is a town in Rosenheim district in Upper Bavaria, Germany. The historic centre is a peninsula formed by the meandering river Inn. Many Medieval structures remain intact, giving the city a unique view. History The town was first mentioned in a document (now considered to be a fake) in 1137, when Hallgraf Engelbert moved his residence from the nearby castle Limburg to his "Wasserburg" (Water Castle). It is one of the most historic towns of Old Bavaria – somewhat older than Munich, continually fought over by the Bavarian nobility and, up to the 16th century, on an equal footing with larger cities. The privileges afforded by this enabled the salt trade to flourish right into the 19th century. At the junction of the main overland route with the main water route, Wasserburg became the most important trade centre with the Balkans, Austria and Italy, a means of attaining power and wealth for the shipping owners and merchants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Resistance To Nazism
Many individuals and groups in Germany that were opposed to the Nazi regime engaged in active resistance, including attempts to remove Adolf Hitler from power by assassination or by overthrowing his established regime. German resistance was not recognized as a collective united resistance movement during the height of Nazi Germany, unlike the more coordinated efforts in other countries, such as Italy, Denmark, the Soviet Union, Poland, Greece, Yugoslavia, France, the Netherlands, Czechoslovakia and Norway. The German resistance consisted of small, isolated groups that were unable to mobilize widespread political opposition. Individual attacks on Nazi authority, sabotage, and the successful disclosure of information regarding Nazi armaments factories to the Allies, as by the Austrian resistance group led by Heinrich Maier prevailed alongside this as well. One strategy was to persuade leaders of the Wehrmacht to stage a coup against the regime; the 1944 assassination attemp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goethe's Faust
''Faust'' is a tragic play in two parts by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, usually known in English as '' Faust, Part One'' and '' Faust, Part Two''. Nearly all of Part One and the majority of Part Two are written in rhymed verse. Although rarely staged in its entirety, it is the play with the largest audience numbers on German-language stages. ''Faust'' is considered by many to be Goethe's ''magnum opus'' and the greatest work of German literature. The earliest forms of the work, known as the ''Urfaust'', were developed between 1772 and 1775; however, the details of that development are not entirely clear. ''Urfaust'' has twenty-two scenes, one in prose, two largely prose and the remaining 1,441 lines in rhymed verse. The manuscript is lost, but a copy was discovered in 1886. The first appearance of the work in print was ''Faust, a Fragment'', published in 1790. Goethe completed a preliminary version of what is now known as ''Part One'' in 1806. Its publication in 1808 was follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mourning Becomes Electra
''Mourning Becomes Electra'' is a play cycle written by American playwright Eugene O'Neill. The play premiered on Broadway at the Guild Theatre on 26 October 1931 where it ran for 150 performances before closing in March 1932, starring Lee Baker (Ezra), Earle Larimore (Orin), Alice Brady (Lavinia) and Alla Nazimova (Christine). In May 1932, it was unsuccessfully revived at the Alvin Theatre (now the Neil Simon Theatre) with Thurston Hall (Ezra), Walter Abel (Orin), Judith Anderson (Lavinia) and Florence Reed (Christine), and, in 1972, at the Circle in the Square Theatre, with Donald Davis (Ezra), Stephen McHattie (Orin), Pamela Payton-Wright (Lavinia), and Colleen Dewhurst (Christine). Characters and background Main characters * Brigadier General Ezra Mannon * Christine Mannon, ''his wife'' * Lavinia Mannon – ''their daughter'' * Orin Mannon – ''their son, First Lieutenant of Infantry'' * Captain Adam Brant – ''of the clipper "Flying Trades"'' * Captain Peter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene O’Neill
Eugene Gladstone O'Neill (October 16, 1888 – November 27, 1953) was an American playwright and Nobel laureate in Nobel Prize in Literature, literature. His poetically titled plays were among the first to introduce into the U.S. the drama techniques of Realism (theatre), realism, earlier associated with Russian playwright Anton Chekhov, Norwegian playwright Henrik Ibsen, and Swedish playwright August Strindberg. The tragedy ''Long Day's Journey into Night'' is often included on lists of the finest U.S. plays in the 20th century, alongside Tennessee Williams's ''A Streetcar Named Desire (play), A Streetcar Named Desire'' and Arthur Miller's ''Death of a Salesman''. O'Neill's plays were among the first to include speeches in American English vernacular and involve characters on the fringes of society. They struggle to maintain their hopes and aspirations, but ultimately slide into disillusion and despair. Of his very few comedies, only one is well-known (''Ah, Wilderness!'').The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerhart Hauptmann
Gerhart Johann Robert Hauptmann (; 15 November 1862 – 6 June 1946) was a German dramatist and novelist. He is counted among the most important promoters of literary naturalism, though he integrated other styles into his work as well. He received the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1912. Life Childhood and youth Gerhart Hauptmann was born in 1862 in Obersalzbrunn, now known as Szczawno-Zdrój, in Lower Silesia (then a part of the Kingdom of Prussia, now a part of Poland). His parents were Robert and Marie Hauptmann, who ran a hotel in the area. As a youth, Hauptmann had a reputation of being loose with the truth. His elder brother was Carl Hauptmann. Beginning in 1868, he attended the village school and then, in 1874, the Realschule in Breslau for which he had only barely passed the qualifying exam. Hauptmann had difficulties adjusting himself to his new surroundings in the city. He lived, along with his brother Carl, in a somewhat run-down student boarding house before fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Halbe
Max Halbe (4 October 1865 – 30 November 1944) was a German dramatist and main exponent of Naturalism. Biography Halbe was born at the manor of Güttland (Koźliny) near Danzig (Gdańsk), where he grew up. He was a member of an old family of peasants who had immigrated two centuries earlier from Westphalia. He attended the ''gymnasium'' (secondary school) at Marienburg. In 1883 he began his study of law at the University of Heidelberg. He studied history and Germanic philology at the University of Berlin, 1885–1887. He obtained his doctorate at the University of Munich in 1888. He then moved to Berlin. In both Berlin and Munich, Halbe became acquainted with the leaders of the new naturalistic movement in German literature, and became associated with the Free Stage (german: Freie Bühne) movement in 1889. He was strongly influenced by the association with, and the works of, Johannes Schlaf and Arno Holt. In the spring of 1890, he wrote the play ''Free Love'' (german: Freie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Das Käthchen Von Heilbronn
' (''Katie of Heilbronn or The Trial by Fire'') (1807–1808) is a "great historical knightly play" (German: ') in five acts by the German playwright Heinrich von Kleist. The action of the drama takes place in Swabia during the Middle Ages. Performances The play was first performed at the Theater an der Wien on 17 March 1810 and then published in the same year. Originally, the first two acts appeared separately with the play ''Phöbus'', also by Kleist. Although the play has gained respect among modern audiences, it was originally largely rejected. Goethe, who was director of the theatre at Weimar when it was written, refused at first to present it, calling it "a jumble of sense and nonsense." It was also passed over by the Dresdener Hoftheater and the Berliner Schauspielhaus, and in Germany the play was initially only seen in Bamberg's less famous theatre. List of characters * The Emperor * Gebhardt, ''Archbishop of Worms'' * Friedrich Wetter Count von Strahl * Countess Hele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 October 1990. During the Cold War, the western portion of Germany and the associated territory of West Berlin were parts of the Western Bloc. West Germany was formed as a political entity during the Allied occupation of Germany after World War II, established from eleven states formed in the three Allied zones of occupation held by the United States, the United Kingdom, and France. The FRG's provisional capital was the city of Bonn, and the Cold War era country is retrospectively designated as the Bonn Republic. At the onset of the Cold War, Europe was divided between the Western and Eastern blocs. Germany was divided into the two countries. Initially, West Germany claimed an exclusive mandate for all of Germany, representing itself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Berlin
West Berlin (german: Berlin (West) or , ) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although West Berlin was de jure not part of West Germany, lacked any sovereignty, and was under military occupation until German reunification in 1990, the territory was claimed by the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) which was heavily disputed by the Soviet Union and other Eastern Bloc countries. However, West Berlin de facto aligned itself politically with the FRG on 23 May 1949, was directly or indirectly represented in its federal institutions, and most of its residents were citizens of the FRG. West Berlin was formally controlled by the Western Allies and entirely surrounded by the Soviet-controlled East Berlin and East Germany. West Berlin had great symbolic significance during the Cold War, as it was widely considered by westerners an "island of freedom" and America's most loyal counterpart in Europe. It was heavily subsidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
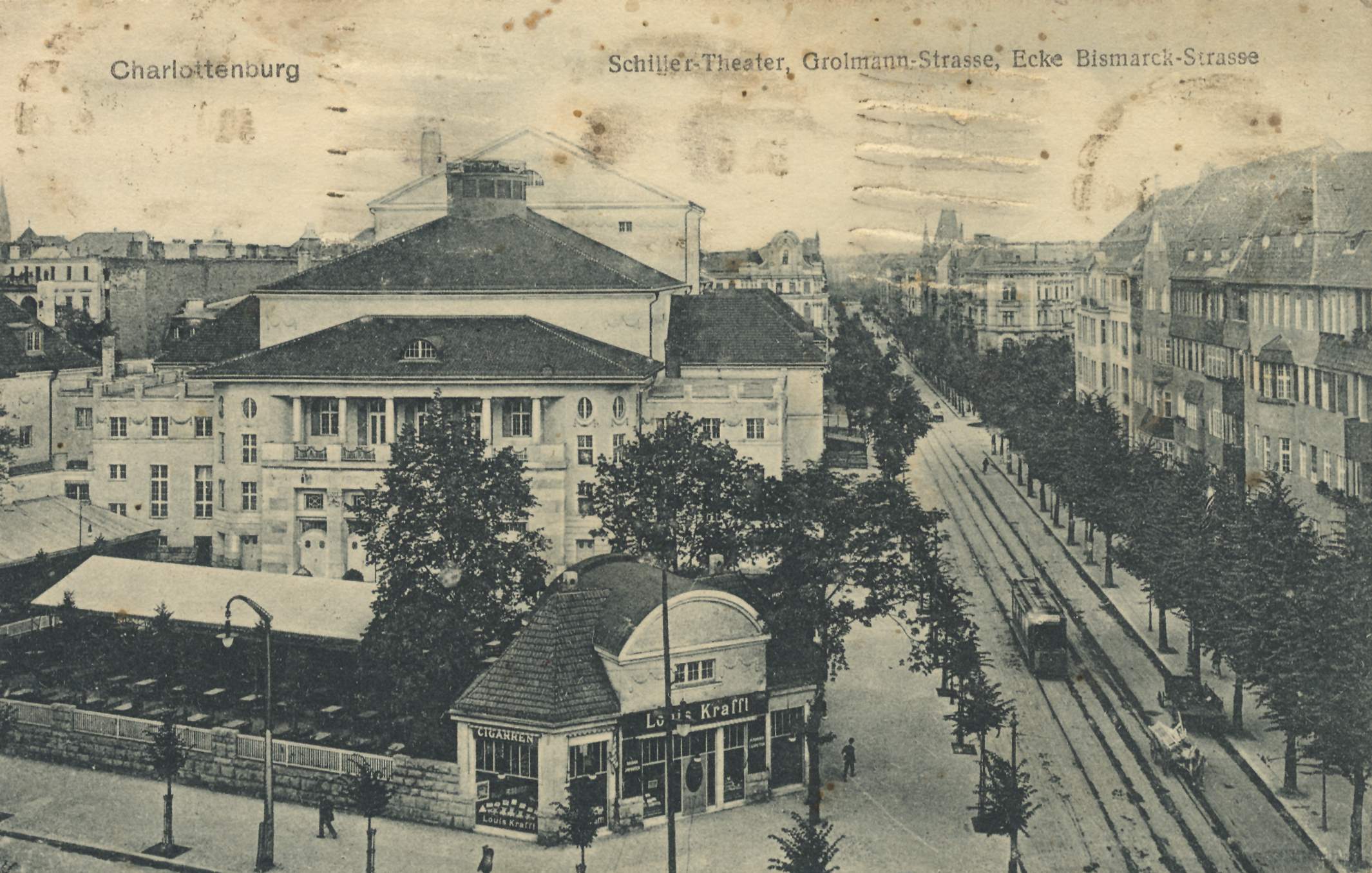
Schiller Theater
The Schiller Theater is a theatre building in Berlin, Germany. It is located in the central Charlottenburg district at Bismarckstraße 110, near Ernst-Reuter-Platz. Opened in 1907, the building served as a second venue for the Prussian State Theatre company in the 1920s and 1930s. After post-war rebuilding, it was the main stage of the Berlin State Theatres from 1951, until in 1993, the City Senate decided to close it for financial reasons. Since then, it has been rented out for theatre performances and other events, and was used by the Berlin State Opera as an interim venue during extensive renovation work from 2010 to 2017. History The Schiller Theater was built from 1905 to 1906 according to plans by the Munich architect Max Littmann on behalf of Schiller-Theater company and the then-independent city of Charlottenburg. Littmann, founder of the Heilmann & Littmann contracting business, had considerable experience in theatre architecture, having designed and built the Munic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialist Unity Party Of Germany
The Socialist Unity Party of Germany (german: Sozialistische Einheitspartei Deutschlands, ; SED, ), often known in English as the East German Communist Party, was the founding and ruling party of the German Democratic Republic (GDR; East Germany) from the country's foundation in October 1949 until its dissolution after the Peaceful Revolution in 1989. It was a Marxist–Leninist communist party, established in April 1946 as a merger between the East German branches of the Communist Party of Germany and Social Democratic Party of Germany. Although the GDR was a one-party state, some other institutional popular front parties were permitted to exist in alliance with the SED; these parties included the Christian Democratic Union, the Liberal Democratic Party, the Democratic Farmers' Party, and the National Democratic Party. In the 1980s, the SED rejected the liberalisation policies of Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev, such as '' perestroika'' and '' glasnost'', which wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)

