|
Kleiber's Law
Kleiber's law, named after Max Kleiber for his biology work in the early 1930s, states, after many observations that, for a vast number of animals, an animal's Basal Metabolic Rate scales to the power of the animal's mass. More precisely : posing w = mass of the animal in kilograms, then BMR = 70w^ kilocalories per day, or BMR = 3.4w^ watts. Thus, over the same time span, a cat having a mass 100 times that of a mouse will consume only about 32 times the energy the mouse uses. It is presently unclear if the value of the exponent in Kleiber's law is correct, in part because the law currently lacks a single theoretical explanation that is entirely satisfactory. More recently, Kleiber's law has also been shown to apply in plants, suggesting that Kleiber's observation is much more general. Proposed explanations for the law Kleiber's law, like many other biological allometric laws, is a consequence of the physics and/or geometry of circulatory systems in biology. Max Kleiber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allometry
Allometry (Ancient Greek "other", "measurement") is the study of the relationship of body size to shape, anatomy, physiology and behaviour, first outlined by Otto Snell in 1892, by D'Arcy Thompson in 1917 in ''On Growth and Form'' and by Julian Huxley in 1932. Overview Allometry is a well-known study, particularly in statistical shape analysis for its theoretical developments, as well as in biology for practical applications to the differential growth rates of the parts of a living organism's body. One application is in the study of various insect species (e.g., Hercules beetles), where a small change in overall body size can lead to an enormous and disproportionate increase in the dimensions of appendages such as legs, antennae, or horns. The relationship between the two measured quantities is often expressed as a power law equation (allometric equation) which expresses a remarkable scale symmetry: : y = k x^a, or in a logarithmic form, : \log y = a \log x + \log k, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipocytes
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through adipogenesis. In cell culture, adipocyte progenitors can also form osteoblasts, myocytes and other cell types. There are two types of adipose tissue, white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT), which are also known as white and brown fat, respectively, and comprise two types of fat cells. Structure White fat cells White fat cells contain a single large lipid droplet surrounded by a layer of cytoplasm, and are known as unilocular. The nucleus is flattened and pushed to the periphery. A typical fat cell is 0.1 mm in diameter with some being twice that size, and others half that size. However, these numerical estimates of fat cell size depend largely on the measurement method and the location of the adipose tissue. The fat stored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analysis Of Variance
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a family of statistical methods used to compare the Mean, means of two or more groups by analyzing variance. Specifically, ANOVA compares the amount of variation ''between'' the group means to the amount of variation ''within'' each group. If the between-group variation is substantially larger than the within-group variation, it suggests that the group means are likely different. This comparison is done using an F-test. The underlying principle of ANOVA is based on the law of total variance, which states that the total variance in a dataset can be broken down into components attributable to different sources. In the case of ANOVA, these sources are the variation between groups and the variation within groups. ANOVA was developed by the statistician Ronald Fisher. In its simplest form, it provides a statistical test of whether two or more population means are equal, and therefore generalizes the Student's t-test#Independent two-sample t-test, ''t''- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, it is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" for intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in a Metabolism, metabolic process, ATP converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. It is also a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. An average adult human processes around 50 kilograms (about 100 mole (unit), moles) daily. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of three parts: a sugar, an amine base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose Oxidation Reaction
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes. The wide occurrence of glycolysis in other species indicates that it is an ancient metabolic pathway. Indeed, the reactions that make up glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, can occur in the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes, catalyzed by metal ions, meaning this is a plausible prebiotic pathway for abiogenesis. The most common type of glycolysis is the ''Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP) pathway'', which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
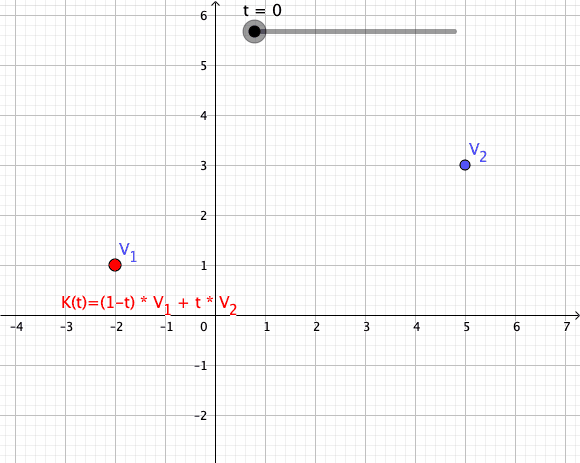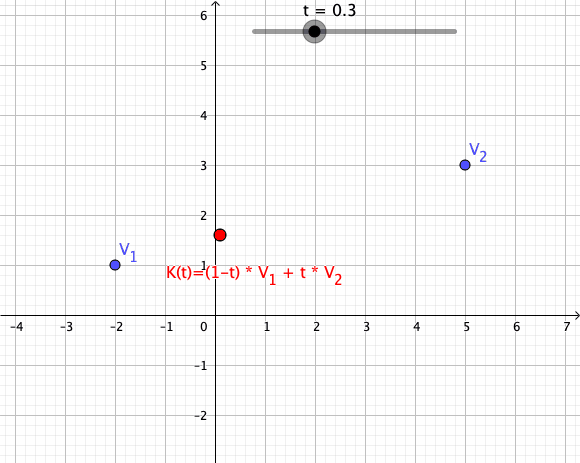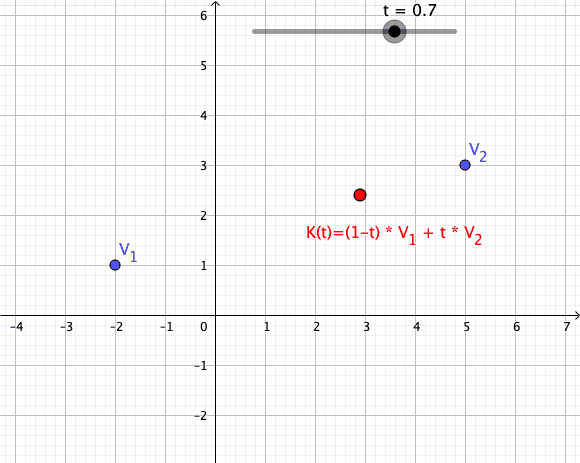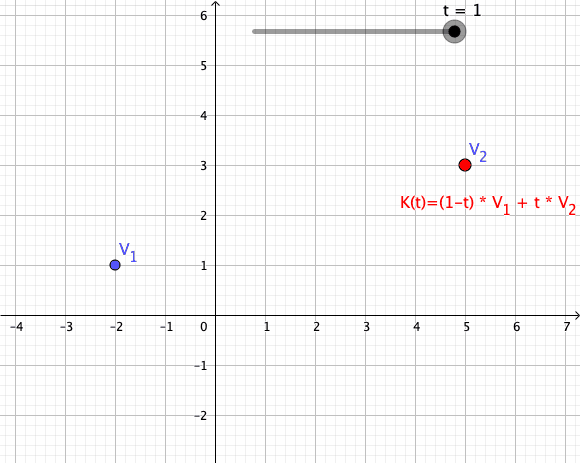
Convex Combination
In convex geometry and Vector space, vector algebra, a convex combination is a linear combination of point (geometry), points (which can be vector (geometric), vectors, scalar (mathematics), scalars, or more generally points in an affine space) where all coefficients are non-negative and sum to 1. In other words, the operation is equivalent to a standard weighted average, but whose weights are expressed as a percent of the total weight, instead of as a fraction of the ''count'' of the weights as in a standard weighted average. Formal definition More formally, given a finite number of points x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n in a real vector space, a convex combination of these points is a point of the form : \alpha_1x_1+\alpha_2x_2+\cdots+\alpha_nx_n where the real numbers \alpha_i satisfy \alpha_i\ge 0 and \alpha_1+\alpha_2+\cdots+\alpha_n=1. As a particular example, every convex combination of two points lies on the line segment between the points. A set is convex set, convex if it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stabilizing Selection
Stabilizing selection (not to be confused with negative or purifying selection) is a type of natural selection in which the population mean stabilizes on a particular non-extreme trait value. This is thought to be the most common mechanism of action for natural selection because most traits do not appear to change drastically over time. Stabilizing selection commonly uses negative selection (a.k.a. purifying selection) to select against extreme values of the character. Stabilizing selection is the opposite of disruptive selection. Instead of favoring individuals with extreme phenotypes, it favors the intermediate variants. Stabilizing selection tends to remove the more severe phenotypes, resulting in the reproductive success of the norm or average phenotypes. This means that most common phenotype in the population is selected for and continues to dominate in future generations. History The Ukrainian and later Soviet evolutionary biologist Ivan Schmalhausen founded the theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal
In mathematics, a fractal is a Shape, geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illustrated in successive magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. This exhibition of similar patterns at increasingly smaller scales is called self-similarity, also known as expanding symmetry or unfolding symmetry; if this replication is exactly the same at every scale, as in the Menger sponge, the shape is called affine geometry, affine self-similar. Fractal geometry lies within the mathematical branch of measure theory. One way that fractals are different from finite geometric figures is how they Scaling (geometry), scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a filled polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the conventional dimension of the filled polygon). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murray's Law
In Biophysics, biophysical fluid dynamics, Murray's law is a potential relationship between Radius, radii at Junction (traffic), junctions in a network of fluid-carrying Cylinder, tubular Pipeline transport, pipes. Its simplest version proposes that whenever a branch of radius r splits into two branches of radii r_1 and r_2, then the three radii should obey the equation r^3 = r_1^3 + r_2^3\textIf network flow is Laminar flow, smooth and leak-free, then systems that obey Murray's law minimize the resistance to flow through the network. For Turbulence, turbulent networks, the law takes the same form but with a different Scaling law, characteristic exponent . Murray's law is observed in the Blood vessel, vascular and respiratory systems of animals, xylem in plants, and the respiratory system of insects. In principle, Murray's law also applies to biomimetics, biomimetic engineering, but human designs rarely exploit the law. Murray's law is named after Cecil D. Murray, a physiologist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |