|
Kaidu
Kaidu (; Middle Mongol: , Modern Mongol: , ''Khaidu'' ; c. 1235 – 1301) was a grandson of the Mongol khagan Ögedei (1185–1241) and thus leader of the House of Ögedei and the '' de facto'' khan of the Chagatai Khanate, a division of the Mongol Empire. He ruled parts of modern-day Xinjiang and Central Asia during the 13th century, and actively opposed his cousin, Kublai, who established the Yuan dynasty. Medieval chroniclers often mistranslated Kadan as Kaidu, mistakenly placing Kaidu at the Battle of Legnica. Kadan was the brother of Güyük, and Kaidu's uncle. Chambers, James. ''The Devil's Horsemen: The Mongol Invasion of Europe''. Atheneum. New York. 1979. Early life Kaidu was born in c. 1235 during the reign of his grandfather, the Great Khan Ögedei. Kaidu was the posthumous son of the Mongol Prince Kashin, who was himself the 4th son of Ögedei and his chief consort, the Great Khatun Töregene, and thus a vital part of the House of Ögedei even in his earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaidu–Kublai War
Kaidu, the leader of the Mongol House of Ögedei, fought a war against Kublai Khan and his successor Temür from 1268 to 1301. Kaidu was the de facto khan of the Chagatai Khanate, while Kublai was the founder of the Yuan dynasty. The Kaidu–Kublai war followed the Toluid Civil War (1260–1264) and resulted in the permanent division of the Mongol Empire. By the time of Kublai's death in 1294, the Mongol Empire had fractured into four separate polities: the Golden Horde khanate in the northwest, the Chagatai Khanate in the middle, the Ilkhanate in the southwest, and the Yuan dynasty in the east based in modern-day Beijing. Although Temür later made peace with the three western khanates in 1304 after Kaidu's death, the four successor states of the Mongol Empire continued their own separate development and fell at different times. History Chagatai–Ilkhanid war After the Toluid Civil War, Kublai Khan summoned Kaidu at his court, but Kaidu avoided appearing at his court, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
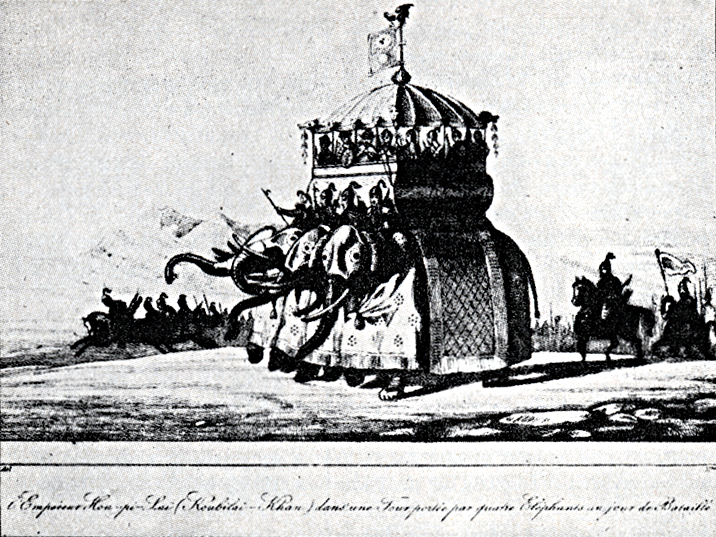
Kublai Khan
Kublai Khan (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder and first emperor of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China. He proclaimed the dynastic name "Great Yuan" in 1271, and ruled Yuan China until his death in 1294. Kublai was the second son of Tolui by his chief wife Sorghaghtani Beki, and a grandson of Genghis Khan. He was almost 12 when Genghis Khan died in 1227. He had succeeded his older brother Möngke as Khagan in 1260, but had to defeat his younger brother Ariq Böke in the Toluid Civil War lasting until 1264. This episode marked the beginning of the division of the Mongol Empire. Kublai's real power was limited to the Yuan Empire, even though as Khagan he still influenced the Ilkhanate and, to a significantly lesser degree, the Golden Horde. In 1271, Kublai established the Yuan dynasty and formally claimed orthodox succession from prior Chinese dynasties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
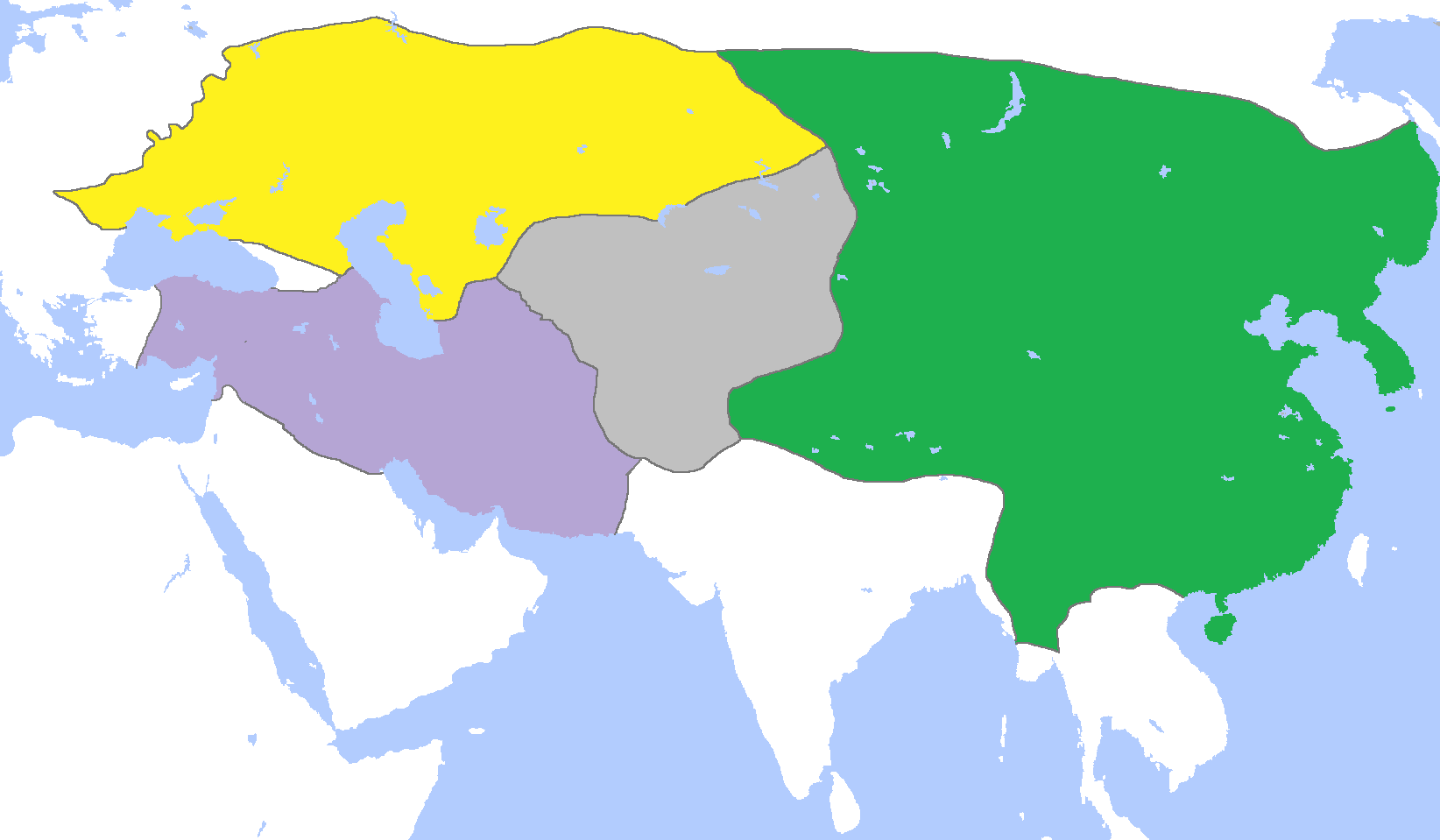
Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, also known as the Chagatai Ulus, was a Mongol and later Turkification, Turkicized khanate that comprised the lands ruled by Chagatai Khan, second son of Genghis Khan, and his descendants and successors. At its height in the late 13th century the khanate extended from the Amu Darya south of the Aral Sea to the Altai Mountains in the border of modern-day Mongolia and China, roughly corresponding to the area once ruled by the Qara Khitai (Western Liao dynasty). Initially, the rulers of the Chagatai Khanate recognized the supremacy of the Great Khan, but by the reign of Kublai Khan, Ghiyas-ud-din Baraq no longer obeyed the emperor's orders. From 1363, the Chagatais progressively lost Transoxiana to the Timurids. The reduced realm came to be known as Moghulistan, which lasted until the late 15th century, when it broke off into the Yarkent Khanate and Turpan Khanate. In 1680, the remaining Chagatai domains lost their independence to the Dzungar Khanate. Finally, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khutulun
Khutulun ({{circa, 1260 – {{circa, 1306), also known as Aigiarne,{{Cite book, title = Il Milione, last = Polo, first = Marco, publisher = L'Unità – Editori Riuniti, year = 1982, chapter = De la Grande Turchia Aiyurug, Khotol Tsagaan or Ay Yaruq ({{lit, Moonlight) was a Mongol noblewoman, the most famous daughter of Kaidu, a cousin of Kublai Khan. Both Marco Polo and Rashid al-Din Hamadani wrote accounts of their encounters with her. Life Khutulun was born about 1260.{{Cite web , last=Weatherford , first=Jack , date=2010-09-27 , title=The Wrestler Princess , url=https://www.laphamsquarterly.org/roundtable/wrestler-princess , url-status=live , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240701032820/https://www.laphamsquarterly.org/roundtable/wrestler-princess , archive-date=July 1, 2024 , access-date=2024-12-01 , website=Roundtable , language=en By 1280, her father Kaidu became the most powerful ruler of Central Asia, reigning in the realms from western Mongolia to Oxus, and fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, extending northward into parts of the Arctic; eastward and southward into parts of the Indian subcontinent, mounting invasions of Southeast Asia, and conquering the Iranian plateau; and reaching westward as far as the Levant and the Carpathian Mountains. The Mongol Empire emerged from the unification of several nomad, nomadic tribes in the Mongol heartland under the leadership of Temüjin, known by the title of Genghis Khan (–1227), whom a council proclaimed as the ruler of all Mongols in 1206. The empire grew rapidly under his rule and that of his descendants, who sent out Mongol invasions, invading armies in every direction. The vast transcontinental empire connected the Eastern world, East with the Western world, West, and the Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Ögedei
The House of Ögedei, sometimes called the Ögedeids, was an influential Mongol family and a branch of the Borjigin clan from the 12th to 14th centuries. They were descended from Ögedei (c. 1186–1241), a son of Genghis Khan who succeeded his father to become the second khagan of the Mongol Empire. Ögedei continued the expansion of the Mongol Empire. When, after the Toluid Möngke Khan's death, the Mongol Empire disintegrated into civil war, the members of the House of Ögedei were influential players in the politics of the region. Among the lines of Genghis Khan's sons — Ögedei, Jochi, Chagatai, and Tolui, the House of Ögedei tended to ally with the Chagataids (descendants of Chagatai) against the House of Jochi, while seeking control for themselves within the Chagatai Khanate at first. The Ögedeids also allied with the Golden Horde against the Yuan founding emperor Kublai (son of Tolui), who was allied with his brother Hulagu, leader of the Ilkhanate in Persia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakorum
Karakorum (Khalkha Mongolian: Хархорум, ''Kharkhorum''; Mongolian script:, ''Qaraqorum'') was the capital city, capital of the Mongol Empire between 1235 and 1260 and of the Northern Yuan, Northern Yuan dynasty in the late 14th and 15th centuries. Its ruins lie in the northwestern corner of the Övörkhangai Province of modern-day Mongolia, near the present town of Kharkhorin and adjacent to the Erdene Zuu Monastery, which is likely the oldest surviving Buddhist monastery in Mongolia. They are located in the upper part of the World Heritage Site Orkhon Valley. History Founding The Orkhon valley was a center of the Xiongnu, Göktürks, Göktürk, and Uyghur Empire, Uyghur empires. To the Göktürks, the nearby Khangai Mountains had been the location of the Ötüken (the locus of power), and the Uyghur capital Karabalgasun was located close to where later Karakorum would be erected (downstream the Orkhon River 27 km north–west from Karakorum). This area is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Legnica
The Battle of Legnica (), also known as the Battle of Liegnitz () or Battle of Wahlstatt (), was fought between the Mongol Empire and combined European forces at the village of Legnickie Pole (''Wahlstatt''), approximately southeast of the city of Legnica in the Duchy of Silesia on 9 April 1241. A combined force of Poles and Moravians under the command of Duke Henry II the Pious of Silesia, supported by feudal nobility and a few knights from military orders sent by Pope Gregory IX, attempted to halt the Mongol invasion of Poland. The battle took place two days before the Mongol victory over the Hungarians at the much larger Battle of Mohi. Historical disputations As with many historical battles, the exact details of force composition, tactics, and the actual course of the battle are lacking and sometimes contradictory. The general historical view is that it was a crushing defeat for the Polish and Moravian forces where they suffered heavy casualties. One of the Mong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the Northwest China, northwest of the country at the crossroads of Central Asia and East Asia. Being the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, largest province-level division of China by area and the List of the largest country subdivisions by area, 8th-largest country subdivision in the world, Xinjiang spans over and has about 25 million inhabitants. Xinjiang Borders of China, borders the countries of Afghanistan, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Pakistan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The rugged Karakoram, Kunlun Mountains, Kunlun and Tian Shan mountain ranges occupy much of Xinjiang's borders, as well as its western and southern regions. The Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the Mongol Empire, its division. It was established by Kublai (Emperor Shizu or Setsen Khan), the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In Chinese history, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan's enthronement as Khagan in 1206 was described in Chinese language, Chinese as the Han Chinese, Han-style title of Emperor of China, Emperor and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danishmendji
Dānishmandchī ( Chagatai and Persian: دانشمندچی; died 1348) was Khan of the Chagatai Khanate from 1346 to 1348. He was the second Khan of the Western Chagatai ''ulus'' to be descended from Ögedei, the third son of Genghis Khan. In 1346 he was raised to the Khanship by Amir Qazaghan, who was the leader of the Qara'unas and who recently had taken effective control of the ''ulus''. Two years later Qazaghan had him executed and replaced him with Bayan Quli, who was a member of the house of Chagatai Khan Chagatai Khan (; – 1242) was a son of Genghis Khan and a prominent figure in the early Mongol Empire. The second son of Genghis's wife Börte, Chagatai was renowned for his masterful knowledge of Mongol custom and law, which he scrupulously .... References 1348 deaths Chagatai khans 14th-century monarchs in Asia Year of birth unknown {{Mongol-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Möngke Khan
Möngke Khan (also Möngke Khagan or Möngke; 11 January 120911 August 1259) was the fourth khagan of the Mongol Empire, ruling from 1 July 1251 to 11 August 1259. He was the first Khagan from the Toluid line, and made significant reforms to improve the administration of the Empire during his reign. Under Möngke, the Mongols conquered Iraq and Syria as well as the kingdom of Dali (modern Yunnan). Early life Möngke was born on 11 January 1209, as the eldest son of Genghis Khan's teenaged son Tolui and Sorghaghtani Beki. Teb Tengri Khokhcuu, a shaman, claimed to have seen in the stars a great future for the child and bestowed on him the name Möngke, meaning 'eternal' in Mongolian. His uncle Ögedei Khan's childless queen Angqui raised him at her orda (nomadic palace). Ögedei instructed Persian scholar Idi-dan Muhammed to teach writing to Möngke. On his way back home after the Mongol conquest of Khwarezmia, Genghis Khan performed a ceremony on his grandsons Möngke and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |