|
Jīva (nun)
Jīvaka (also referred to as Jiva) was a sister of a king of Kucha, and later a Buddhist nun. Jīvaka was a princess of Kucha (in Central Asia) in the early fourth century C.E. She was the sister of the King who introduced her to Kumārāyana, a noble Indian who came from Kashmir to China to study further. After two or three years they returned to Kashgar, renounced his fortune to become a Buddhist monk and thus stopped in Kucha on his journey. However, after meeting Jīvaka, Kumārāyana and she were married. Jīvaka is said to have possessed great talent and keen perception and understanding. According to the "Collection of Records concerning the Tripitaka", she "had only to glance over a written passage to master it, had only to hear something one time to be able to repeat it from memory." Daisaku Ikeda (1976), The Flower of Chinese Buddhism, Middleway Press, pp. 32-33. Combining their great talents, Jīvaka and Kumārāyana produced a son, Kumārajīva. When he was just ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
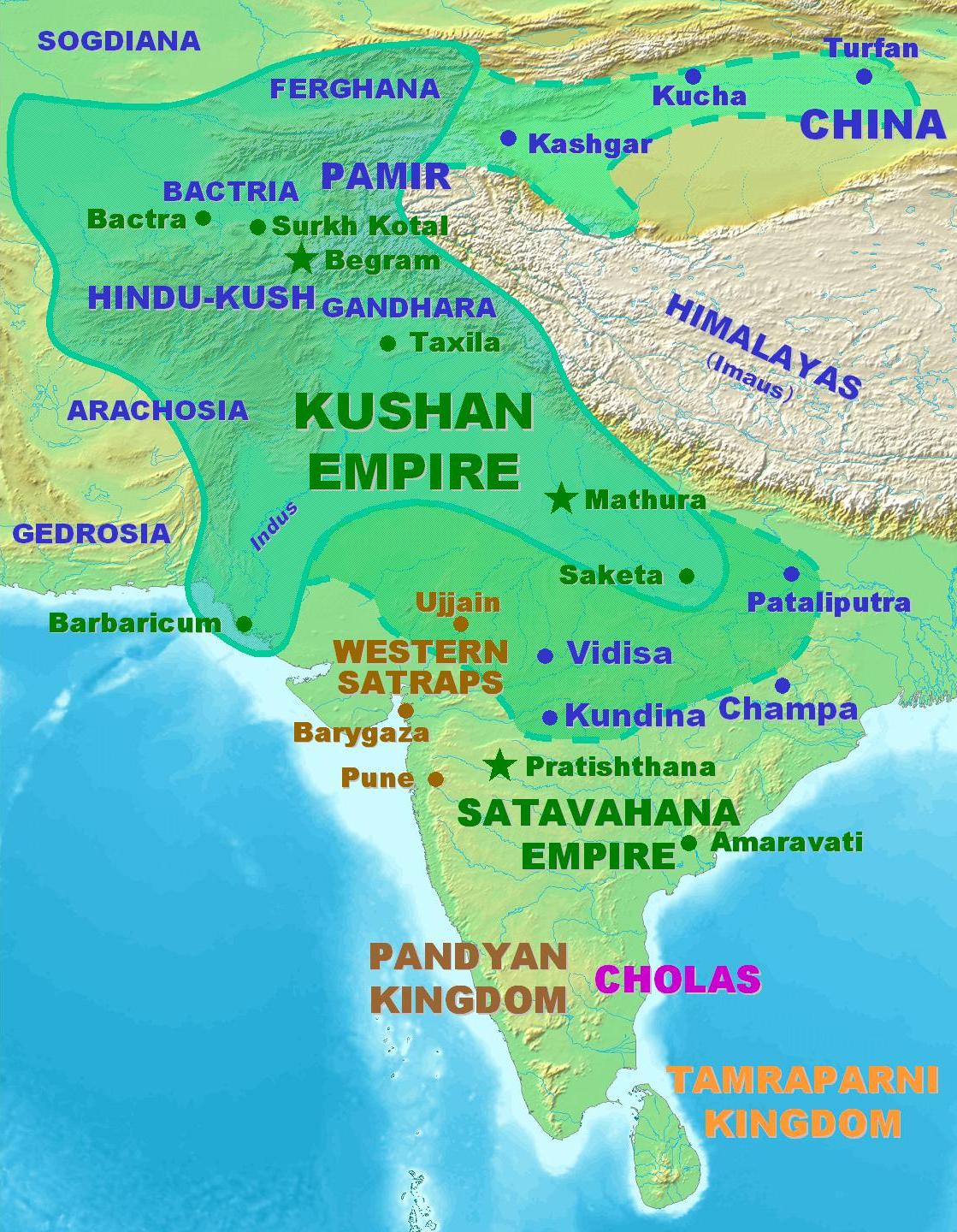
Kucha
Kucha or Kuche (also: ''Kuçar'', ''Kuchar''; , Кучар; zh, t= 龜茲, p=Qiūcí, zh, t= 庫車, p=Kùchē; ) was an ancient Buddhist kingdom located on the branch of the Silk Road that ran along the northern edge of what is now the Taklamakan Desert in the Tarim Basin and south of the Muzat River. The former area of Kucha now lies in present-day Aksu Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. Kuqa town is the county seat of Aksu Prefecture's Kuqa County. Its population was given as 74,632 in 1990. Etymology The history of toponyms for modern Kucha remains somewhat problematic; however, it is clear that Kucha (''Kuchar'', in Turkic languages) and ''Kuché'' (modern Chinese)Elias (1895): ''The Tarikh-i-Rashidi of Mirza Muhammad Haidar, Dughlát: A History of the Moghuls of Central Asia. An English Version Edited, with Commentary, Notes, and Map by N. Elias''. Translation by E. Denison Ross. London. Sampson, Low, Marston and Company Ltd.), p. 124, n. 1., ''et passim'' both co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumārāyana
Kumārāyana (also Kiu-mo-yen) was a Buddhist monk. Kumārāyana renounced his wealth to become a Buddhist monk. He left India, crossing to the Pamirs in order to spread the teachings of Buddhism to the countries east of Central Asia, namely China. Probably from Kashmir, Kumārāyana never made it to eastern China for on his journey he stopped in Kucha, where the king, respecting Kumārāyana's eminence and wisdom wanted him to discontinue his journey, and stay in Kucha to become a royal priest. In order to persuade Kumārāyana to stay in Kucha, the King introduced him to the wisest woman in Kucha, his sister Jīvaka. Jīvaka was coveted by many suitors for her great talents intellectual abilities. However, upon meeting Kumārāyana, Jīvaka was moved and they fell in love with each other. They married and combined their great talents. Though, they are mainly known in Buddhist history for the deeds of their son named Kumārajīva who, largely under Jīvaka's guidance, went on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. The term has since also come to encompass a larger area that includes the Indian-administered territories of Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, the Pakistani-administered territories of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan, and the Chinese-administered territories of Aksai Chin and the Trans-Karakoram Tract. Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang to the northeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east (both parts of China), by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south, by Pakistan to the west, and by Afghanistan to the northwest. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashgar
Kashgar () or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is a city in the Tarim Basin region of southern Xinjiang, China. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, located near the country's border with Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. For over 2,000 years, Kashgar was a strategically important oasis on the Silk Road between China, the Middle East, and Europe. It is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world and has a population of 711,300 people (). Kashgar's urban area covers , although its administrative area extends over . At the convergence point of widely varying cultures and empires, Kashgar has been under the rule of the Chinese, Turkic, Mongol and Tibetan empires. The city has also been the site of a number of battles between various groups of people on the steppes. Now administered as a county-level city, Kashgar is the administrative centre of Kashgar Prefecture, which has an area of and a population of approximately 4 million . Kashgar was declared a Special Economic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumārajīva
Kumārajīva (Sanskrit: कुमारजीव; , 344–413 CE) was a bhikkhu, Buddhist monk, scholar, missionary and translator from Kucha (present-day Aksu City, Aksu Prefecture, Xinjiang, China). Kumārajīva is seen as one of the greatest translators of Chinese Buddhism. According to Lu Cheng, Kumarajiva's translations are "unparalleled either in terms of translation technique or degree of fidelity". Kumārajīva first studied teachings of the Sarvastivada, Sarvastivadin schools, later studied under Buddhasvamin (monk), Buddhasvāmin, and finally became an adherent of Mahayana, Mahayana Buddhism, studying the Madhyamaka, Mādhyamaka doctrine of Nagarjuna, Nāgārjuna. After mastering the Chinese language, Kumārajīva settled as a translator and scholar in Chang'an (c. 401 CE) under the patronage of the Later Qin, Later Qin dynasty during the Sixteen Kingdoms period. He was the head of a team of translators which included his amanuensis Sengrui. This team was responsibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turpan
Turpan () or Turfan ( zh, s=吐鲁番) is a prefecture-level city located in the east of the Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of Xinjiang, China. It has an area of and a population of 693,988 (2020). The historical center of the prefectural area has shifted a number of times, from Jiaohe ruins, Yar-Khoto (Jiaohe, to the west of modern Turpan) to Qocho (Gaochang, to the southeast of Turpan) and to Turpan itself. Names Historically, many settlements in the Tarim Basin, being situated between Chinese, Turkic, Mongolian, and Persian language users, have a number of cognate names. Turpan or Turfan is one such example. The original name of the city is unknown. The form Turfan, while older than Turpan, was not used until the middle of the 2nd millennium CE and its use became widespread only in the post-Mongol period. History Turpan has long been the centre of a fertile oasis (with water provided by the ''Turpan water system, karez'' canal system) and an important tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Buddhist Nuns
Indian or Indians may refer to: Associated with India * of or related to India ** Indian people ** Indian diaspora ** Languages of India ** Indian English, a dialect of the English language ** Indian cuisine Associated with indigenous peoples of the Americas * Indigenous peoples of the Americas ** First Nations in Canada ** Native Americans in the United States ** Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean ** Indigenous languages of the Americas Places * Indian, West Virginia, U.S. * The Indians, an archipelago of islets in the British Virgin Islands Arts and entertainment Film * ''Indian'' (film series), a Tamil-language film series ** ''Indian'' (1996 film) * ''Indian'' (2001 film), a Hindi-language film Music * Indians (musician), Danish singer Søren Løkke Juul * "The Indian", an unreleased song by Basshunter * "Indian" (song), by Sturm und Drang, 2007 * "Indians" (song), by Anthrax, 1987 * Indians, a song by Gojira from the 2003 album '' The Link'' Other uses i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |