|
Jílové
Jílové (until 1945 Jílové u Podmokel; ) is a town in Děčín District in the Ústí nad Labem Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 4,900 inhabitants. Administrative division Jílové consists of six municipal parts (in brackets population according to the 2021 census): *Jílové (1,171) *Kamenec (217) *Kamenná (2,175) *Martiněves (900) *Modrá (370) *Sněžník (102) Etymology The adjective is derived from ''jíl'', i.e. 'clay'. The name was probably transferred to the settlement from the local stream. Geography Jílové is located about west of Děčín and north of Ústí nad Labem. It lies in the Elbe Sandstone Mountains and in the eponymous protected landscape area. The built-up area is situated in the valley of the stream Jílovský potok, a left tributary of the Elbe River. The town is located at the foot of the Děčínský Sněžník mountain, which is the highest peak of the municipal territory at above sea level. History Jílové was probably founde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thun Und Hohenstein
The House of Thun und Hohenstein, also known as Thun-Hohenstein, belonged to the historical Austrian nobility, Austrian and Bohemian nobility. There is one princely and several count, comital branches of the family. The princely branch of the family lived at Děčín () in Bohemia for more than 200 years. The family maintained an expansive library, including two important albums depicting artistically and technologically innovative armour made for the Habsburg court during the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries. History A feudalism, feudal family originally from Ton, Trentino, formerly an Italian-speaking part of Tyrol (state), Tyrol (today part of the Trentino province of Italy), the male line traces back to Manfreinus of Tunno in 1187.Almanach de Gotha, ''Thun und Hohenstein''. Justus Perthes, 1944, p. 539 (in French). In 1469, they became hereditary cup-bearers of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Trento, Prince-bishopric of Trent and in 1558 of the Roman Catholic Diocese of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Děčín District
Děčín District () is a district in the Ústí nad Labem Region of the Czech Republic. Its capital is the city of Děčín. Administrative division Děčín District is divided into three administrative districts of municipalities with extended competence: Děčín, Rumburk and Varnsdorf. List of municipalities Cities and towns are marked in bold: Arnoltice - Benešov nad Ploučnicí - Bynovec - Česká Kamenice - Děčín - Dobkovice - Dobrná - Dolní Habartice - Dolní Podluží - Dolní Poustevna - Doubice - Františkov nad Ploučnicí - Heřmanov - Horní Habartice - Horní Podluží - Hřensko - Huntířov - Chřibská - Janov - Janská - Jetřichovice - Jílové - Jiřetín pod Jedlovou - Jiříkov - Kámen - Krásná Lípa - Kunratice - Kytlice - Labská Stráň - Lipová - Lobendava - Ludvíkovice - Malá Veleň - Malšovice - Markvartice - Merboltice - Mikulášovice - Rumburk - Růžová - Rybniště - Srbská Kamenice - Star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Děčínský Sněžník
The Děčínský Sněžník () is a mountain in the Czech Republic. At above sea level, it is the highest peak of the Elbe Sandstone Mountains. Geography Děčínský Sněžník is located in the Elbe Sandstone Mountains in the Ústí nad Labem Region. It is located mostly in the Jílové municipality, only the eastern slopes are located in the territory of Děčín. The mountain is the highest mesa in the Czech Republic. Tourism History One of the first historical figures to visit Děčínský Sněžník was Emperor Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, Joseph II of Habsburg, who climbed the peak in September 1779. The Sněžník was considered an important geodesy, geodetic point for triangulation and cartographers asked the owner of the principality of Děčín, Prince Franz, Prince of Thun and Hohenstein, Franz of Thun and Hohenstein, for permission to establish the peak as a triangulation point. Prince Franz contracted the Dresden architect, Karl Moritz Haenel, to design a stone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of Bohemian Succession (1125–1140)
The War of Bohemian Succession (1125–1140) was a war between the Imperial Forces of the Holy Roman Empire and the Duchy of Bohemia about the succession in the Duchy of Bohemia. Background Since Duke Bretislaus I of Bohemia had implemented the inheritance principle of agnatic seniority in the 11th century, the order of succession in Bohemia, many rivalling scions of the ramified Přemyslid dynasty waged war against each other. The claimants to the Prague throne sought for formal recognition by the Holy Roman Emperor, when in actuality, the accession required the active support by the Bohemian nobility. The Přemyslid duke Vladislaus I of Bohemia, ruling since 1109, likewise had to struggle to consolidate his authority, defying the claims raised by his brother Bořivoj II who had reached his enfeoffment by Emperor Henry IV in 1101. When Vladislaus died in 1125 his succession was disputed among his surviving brother Soběslav I and his Moravian cousin Otto II, duke in Olomou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obec
(, ; plural ) is the Czech and Slovak word for a municipality (in the Czech Republic, in Slovakia and abroad). The literal meaning of the word is " commune" or " community". It is the smallest administrative unit that is governed by elected representatives. Cities and towns are also municipalities. Definition The legal definition (according to the Czech code of law with similar definition in the Slovak code of law) is: ''"The municipality is a basic territorial self-governing community of citizens; it forms a territorial unit, which is defined by the boundary of the municipality."'' Every municipality is composed of one or more cadastral areas. Every municipality is also composed of one or more municipal parts (), which are usually town quarters or villages. A municipality can have its own flag and coat of arms. Czech Republic Almost the entire area of the Czech Republic is divided into municipalities, with the only exception being military training areas. The smaller mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lothair II, Holy Roman Emperor
Lothair III, sometimes numbered Lothair II and also known as Lothair of Supplinburg ( June 1075 – 4 December 1137), was Holy Roman Emperor from 1133 until his death. He was appointed Duke of Saxony in 1106 and elected King of Germany in 1125 before being crowned emperor in Rome. The son of the Saxon count Gebhard of Supplinburg, his reign was troubled by the constant intriguing of the Hohenstaufens, Duke Frederick II of Swabia and Duke Conrad of Franconia. He died while returning from a successful campaign against the Norman Kingdom of Sicily. Rise to power In 1013, a certain Saxon nobleman named ''Liutger'' was mentioned as a count in or of the Harzgau subdivision of Eastphalia. His grandson Count Gebhard, father of Emperor Lothair, possibly acquired the castle of Süpplingenburg about 1060 via his marriage with Hedwig, a daughter of the Bavarian count Frederick of Formbach and his wife Gertrud, herself a descendant of the Saxon margrave Dietrich of Haldensleben who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles IV (; ; ; 14 May 1316 – 29 November 1378''Karl IV''. In: (1960): ''Geschichte in Gestalten'' (''History in figures''), vol. 2: ''F–K''. 38, Frankfurt 1963, p. 294), also known as Charles of Luxembourg, born Wenceslaus (, ), was Holy Roman Emperor from 1355 until his death in 1378. He was elected King of Germany (King of the Romans) in 1346 and became King of Bohemia (as Charles I) that same year. He was a member of the House of Luxembourg from his father's side and the Bohemian House of Přemyslid from his mother's side; he emphasized the latter due to his lifelong affinity for the Bohemian side of his inheritance, and also because his direct ancestors in the Přemyslid line included two saints. He was the eldest son and heir of John of Bohemia, King of Bohemia and Count of Luxembourg, who died at the Battle of Crécy on 26 August 1346. His mother, Elizabeth of Bohemia (1292–1330), Elizabeth, Queen of Bohemia, was the sister of Wenceslaus III of Bohemia, W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
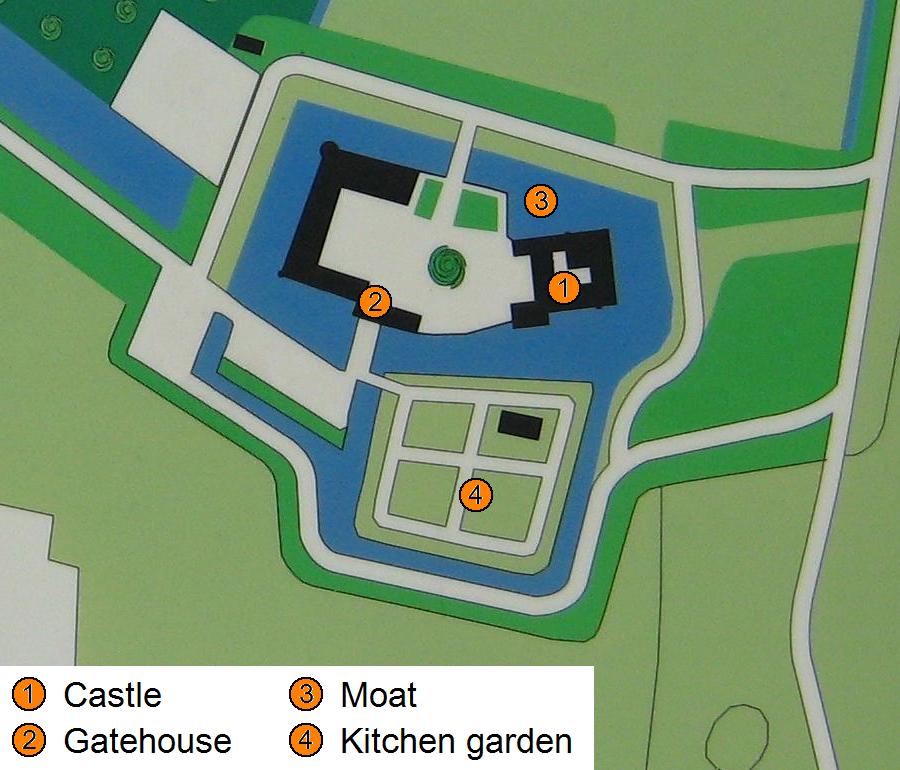
Water Castle
A water castle, sometimes water-castle, is a castle which incorporates a natural or artificial body of water into its defences.Forde-Johnston (1979), p. 163. It can be entirely surrounded by water-filled moats (moated castle) or natural waterbodies such as island castles in a river or offshore. The term comes from European castle studies, mainly German ''Burgenkunde''. Some interpretations of the category emphasise that the use of water extends beyond a defensive purpose.Plowman (2005), p. 44. When stately homes were built in such a location, or a Wasserburg was later rebuilt as a residential manor, the German term becomes Wasserschloss, lit. "water palace/manor". Description Forde-Johnston describes such a site as "a castle in which water plays a prominent part in the defences." Apart from hindering attackers, an abundant supply of water was also an advantage during a siege. Topographically, such structures are a type of low-lying castle. Such a castle usually had only one e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
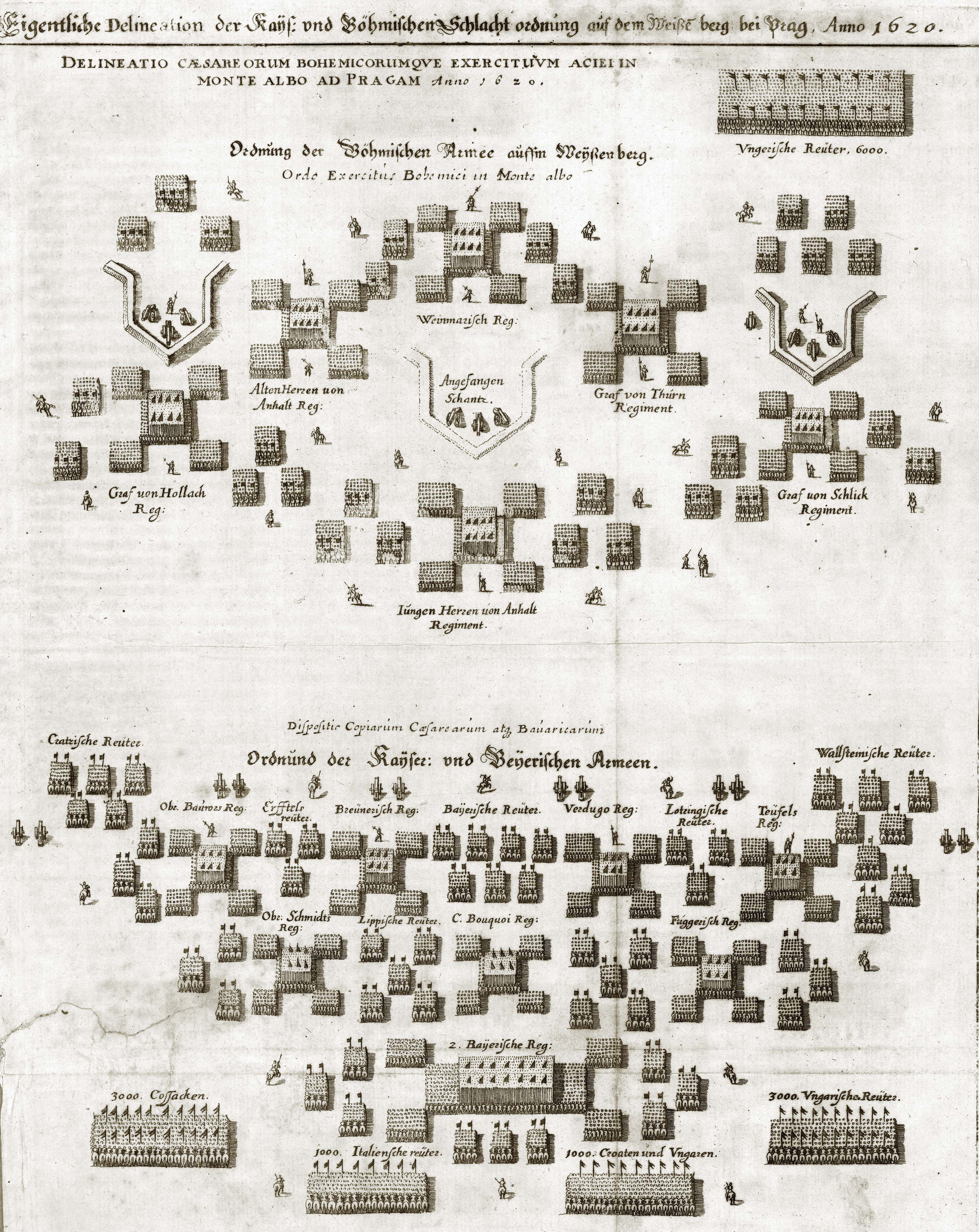
Battle Of White Mountain
The Battle of White Mountain (; ) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian Revolt and ensured Habsburg control for the next three hundred years. It was fought on 8 November 1620. An army of 21,000 Bohemians and mercenaries under Christian of Anhalt was defeated by 23,000 men of the combined armies of Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor, led by Charles Bonaventure de Longueval, Count of Bucquoy, and the German Catholic League led by Johann Tserclaes, later Count of Tilly, at Bílá Hora ("White Mountain") near Prague. Bohemian casualties were not severe but their morale collapsed and Imperial forces occupied Prague the next day. Prelude In the early 17th century most of the Bohemian estates, although under the dominion of the predominantly Catholic Holy Roman Empire, had large Protestant populations, and had been granted rights and protections allowing them varying degrees of religious and political freedom. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand II (9 July 1578 – 15 February 1637) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia, King of Hungary, Hungary, and List of Croatian monarchs, Croatia from 1619 until his death in 1637. He was the son of Archduke Charles II, Archduke of Austria, Charles II of Inner Austria and Maria Anna of Bavaria (born 1551), Maria of Bavaria, who were devout Catholic Church, Catholics. In 1590, when Ferdinand was 11 years old, they sent him to study at the University of Ingolstadt, Jesuits' college in Ingolstadt because they wanted to isolate him from the Lutheranism, Lutheran nobles. A few months later, his father died, and he inherited Inner Austria–Duchy of Styria, Styria, Duchy of Carinthia, Carinthia, Duchy of Carniola, Carniola and smaller provinces. His cousin, Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, who was the head of the Habsburg family, appointed regents to administer these lands. Ferdinand was installed as the actual ruler of the Inner Austrian provinces in 1596 and 1597. Rudolf II al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudeten Germans
German Bohemians ( ; ), later known as Sudeten Germans ( ; ), were ethnic Germans living in the Czech lands of the Bohemian Crown, which later became an integral part of Czechoslovakia. Before 1945, over three million German Bohemians constituted about 23% of the population of the whole country and about 29.5% of the population of Bohemia and Moravia. Ethnic Germans migrated into the Kingdom of Bohemia, an prince-electors, electoral territory of the Holy Roman Empire, from the 11th century, mostly in the border regions of what was later called the "Sudetenland", which was named after the Sudeten Mountains. The process of German expansion was known as ("Settling of the East"). The name "Sudeten Germans" was adopted during rising nationalism after the fall of Austria-Hungary in the aftermath of First World War. After the Munich Agreement (1938), the so-called Sudetenland became part of Nazi Germany, Germany. After the Second World War, most of the German-speaking population (most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |