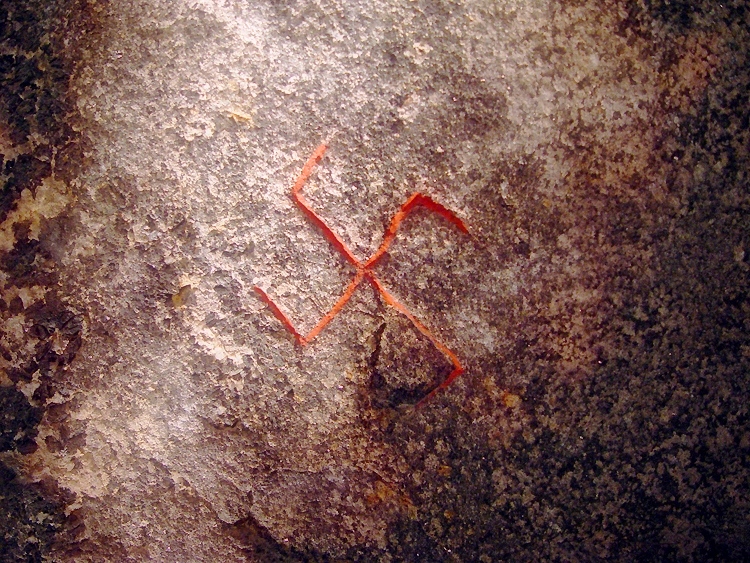|
Jain Flag
The official flag of Jainism has five colours: White, Red, Yellow, Green and Blue. These five colours represent the '' Pañca-Parameṣṭhi'' (five supreme beings). It also represents the five main vows of Jainism. Colours These five colours represent the " Pañca-Parameṣṭhi" and the five vows, small as well as great: *White – represents the arihants, souls who have conquered all passions (anger, attachments, aversion) and have attained omniscience and eternal bliss through self-realization. It also denotes peace or ''ahimsa'' (non-violence). *Red – represents the siddha, souls that have attained salvation and truth. It also denotes truthfulness (''satya''). *Yellow – represents the acharya the Masters of Adepts. The colour also stands for non-stealing (''achaurya''). *Green – represents the upadhyaya (adepts), those who teach scriptures to monks. It also signifies chastity (''brahmacharya''). *Black – represents the sadhus and sadhvis or monks and nuns. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four , supreme preachers of ''dharma''. The first in the current time cycle is Rishabhadeva, who tradition holds lived millions of years ago; the 23rd is Parshvanatha, traditionally dated to the 9th century Common Era, BCE; and the 24th is Mahāvīra, Mahavira, who lived . Jainism is considered an eternal ''dharma'' with the guiding every time cycle of the Jain cosmology, cosmology. Central to understanding Jain philosophy is the concept of ''bhedavijñāna'', or the clear distinction in the nature of the soul and non-soul entities. This principle underscores the innate purity and potential for liberation within every Jīva (Jainism), soul, distinct from the physical and menta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neminatha
Neminātha (Devanagari: नेमिनाथ) (Sanskrit: नेमिनाथः), also known as Nemi and Ariṣṭanemi (Devanagari: अरिष्टनेमि), is the twenty-second tirthankara of Jainism in the present age (). Neminath lived 84,000 years before the 23rd ''Tirthankar'' Parshvanath. According to traditional accounts, he was born to King Samudravijaya and Queen Shivadevi of the Yadu dynasty in the north Indian city of Sauripura. His birth date was the fifth day of ''Shravan Shukla'' of the Jain calendar. Balarama and Krishna, who were the 9th and last Baladeva and Vasudeva respectively, were his first cousins. Neminatha, when heard the cries of animals being killed for his marriage feast, freed the animals and renounced his worldly life and became a Jain ascetic. The representatives of this event are popular in Jain art. He had attained ''moksha'' on Girnar Hills near Junagadh, and became a siddha, a liberated soul which has destroyed all of its ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Villupuram District
Viluppuram, Villupuram or Vizhuppuram is one of the 38 districts that make up the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It was founded on 30 September 1993, prior to which it was part of the Cuddalore district. Vizhuppuram district lies in the way of the national highway connecting Tiruchirappalli and Chennai, and contains historical landmarks like the 500 year-old Gingee Fort. __TOC__ History Vizhuppuram district was once a part of the South Arcot district along with the Cuddalore district. Later, the Cuddalore district was bifurcated and Vizhuppuram district came into existence on 30 September 1993. As a result, the Vizhuppuram district's history closely resembles that of Cuddalore's. The Cholas were among the earliest rulers. Karikala Chola was the most influential. Simhavishnu Pallava overthrew the Cholas, and the region came under the Pallava rule. Vijayalaya Chola restored the rule of Chola, marking the beginning of the Chola Empire. The entire district became a war zone durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gingee
Gingee, also known as Senji or Jinji and originally called Singapuri, is a panchayat town in Viluppuram district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Gingee is located between three hills covering a perimeter of 3 km, and lies west of the Sankaraparani River. History The founding of the Kon dynasty established Gingee Fort as a fortified royal center. The Gingee country then came under the rule of the Hoysalas in the later part of the 13th and in the first half of the 14th century. From the Hoysalas, it passed to the first rulers of the Vijayanagara empire. The imperial Vijayanagara dominion gradually expanded over Southern India and divided the administration of the tamil country into three important provinces, which were assigned to the Nayaks. These were the Nayaks of Madurai, Nayaks of Tanjore, and Nayaks of Gingee. Information about the Gingee Nayaks and their rule is very scant. It is said that Tupakula Krishnappa Nayaka (1490 to 1521) of a Chandragiri family w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
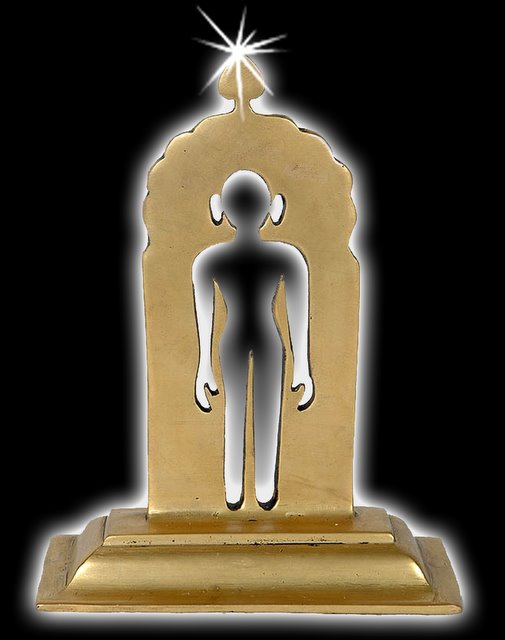
Siddhashila
Siddhashila is an area in Jain cosmology at the apex of the universe, which is where the Jains believe people who have become '' arihants'' and ''tirthankaras'' go after they die and attain ''moksha ''Moksha'' (; , '), also called ''vimoksha'', ''vimukti'', and ''mukti'', is a term in Jainism, Buddhism, Hinduism, and Sikhism for various forms of emancipation, liberation, '' nirvana'', or release. In its soteriological and eschatologic ...''. Such people are called '' siddhas'' after they discard their mortal body, hence the origin of the term. See also * Kevala jnana * Jainism and non-creationism * Timeline of Jainism References Moksha Jain cosmology {{Jainism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saṃsāra (Jainism)
''Saṃsāra'' (transmigration)(Sanskrit: संसार, IAST: saṃsāra) in Jain philosophy, refers to the worldly life characterized by continuous rebirths and reincarnations in various realms of existence. is described as mundane existence, a life full of suffering and misery, and hence it is considered undesirable and worth renunciation. The ''Saṃsāra'' is without any beginning, and the soul finds itself in bondage with its karma since the beginning-less time. ''Moksha'' is the only way to be liberated from ''saṃsāra''. Influx of karmas (''asrava'') According to the Jain text ''Tattvartha Sutra ''Tattvārthasūtra'', meaning "On the Nature 'artha''of Reality 'tattva'' (also known as ''Tattvarth-adhigama-sutra'' or ''Moksha-shastra'') is an ancient Jain text written by ''Acharya (Jainism), Acharya'' Umaswami in Sanskrit betwee ...'': Activities that lead to the influx of karmas (''asrava'') which extends transmigration are: *Five senses *Four passions (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Karma In Jainism
Karma is the basic principle within an overarching psycho-cosmology in Jainism. Human moral actions form the basis of the transmigration of the soul ('). The soul is constrained to a cycle of rebirth, trapped within the Temporality, temporal world ('), until it finally achieves liberation ('). Liberation is achieved by following a path of purification. Jains believe that karma is a physical substance that is everywhere in the universe. Karma particles are attracted to the soul by the actions of that soul. Karma particles are attracted when we do, think, or say things, when we kill something, when we lie, when we steal and so on. Karma not only encompasses the causality of transmigration, but is also conceived of as an extremely subtle matter, which infiltrates the soul—obscuring its natural, transparent and pure qualities. Karma is thought of as a kind of pollution, that taints the soul with various colours (''Lesya, leśyā''). Based on its karma, a soul undergoes transmigr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jiva
''Jiva'' (, IAST: ), also referred as ''Jivātman,'' is a living being or any entity imbued with a life force in Hinduism and Jīva (Jainism), Jainism. The word itself originates from the Sanskrit verb-root ''jīv'', which translates as 'to breathe' or 'to live'. The ''jiva'', as a metaphysical entity, has been described in various scriptures such as the Bhagavad Gita and the Upanishads. Each subschool of Vedanta describes the role of the ''jiva'' with the other metaphysical entities in varying capacities. The closest translation into English and Abrahamic philosophies would be the ''soul.'' Described in the scriptures A common metaphysical entity discussed in the scriptures (such as the Bhagavad Gita, Upanishad and Vachanamrut) in the seven schools of Vedanta is the ''jiva'' or Ātman (Hinduism), ''atman'': the soul or self. Bhagavad Gita Chapter 2 of the Bhagavad Gita contains verses describing the ''jiva''. For example, the ''jiva'' is described as eternal and indestruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ratnatraya
Jainism emphasises that ratnatraya (triple gems of Jainism) — the right faith (''Samyak Darshana''), right knowledge (''Samyak Gyana'') and right conduct (''Samyak Charitra'') — constitutes the path to liberation. These are known as the triple gems (or jewels) of Jainism and hence also known as ''Ratnatraya'' The Path to liberation According to Jainism, purification of soul and liberation can be achieved through the path of three jewels: ''Samyak darśana'' (Correct View), meaning faith, acceptance of the truth of soul (''jīva''); ''Samyak jnana'' (Correct Knowledge), meaning undoubting knowledge of the ''tattvas''; and ''Samyak charitra'' (Correct Conduct), meaning behavior consistent with the Five vows. Jain texts often add ''samyak tap'' (Correct Asceticism) as a fourth jewel, emphasizing belief in ascetic practices as the means to liberation (moksha). The four jewels are called ''moksha marg''. According to Jain texts, the liberated pure soul (''Siddha'') goes up to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siddha
''Siddha'' (Sanskrit: '; "perfected one") is a term that is used widely in Indian religions and culture. It means "one who is accomplished." It refers to perfected masters who have achieved a high degree of perfection of the intellect as well as moksha, liberation or Enlightenment in Buddhism, enlightenment. In Jainism, the term is used to refer to the liberated souls. ''Siddha'' may also refer to one who has attained a siddhi, paranormal capabilities. Siddhas may broadly refer to siddhars, naths, asceticism, ascetics, sadhus, or yogis because they all practice sādhanā. Jainism In Jainism, the term ''siddha'' is used to refer the liberated souls who have destroyed all Karma in Jainism, karmas and have obtained Moksha (Jainism), moksha.They are free from the transmigratory cycle of birth and death (''Saṃsāra (Jainism), saṃsāra'') and are above ''Arihant (Jainism), Arihantas'' (omniscient beings). Siddhas do not have a body; they are soul in its purest form. They r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Swastika
The swastika (卐 or 卍, ) is a symbol used in various Eurasian religions and cultures, as well as a few Indigenous peoples of Africa, African and Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American cultures. In the Western world, it is widely recognized as a symbol of the German Nazi Party who Cultural appropriation, appropriated it for their party insignia starting in the early 20th century. The appropriation continues with its use by Neo-Nazism, neo-Nazis around the world. The swastika was and continues to be used as a symbol of divinity and spirituality in Indian religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. It generally takes the form of a cross, the arms of which are of equal length and perpendicular to the adjacent arms, each bent midway at a right angle. The word ''swastika'' comes from , meaning 'conducive to well-being'. In Hinduism, the right-facing symbol (clockwise) () is called , symbolizing ('sun'), prosperity and good luck, while the left-facing symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |