|
Jabbok
The Zarqa River (, ''Nahr az-Zarqāʾ'', lit. "the River of the Blue ity) is the second largest tributary of the lower Jordan River, after the Yarmouk River. It is the third largest river in the region by annual discharge and its watershed encompasses the most densely populated areas east of the Jordan River. The Zarqa rises in springs near Amman, and flows through a deep and broad valley into the Jordan, at an elevation lower. At its spring lays 'Ain Ghazal (Arabic: ), a major archaeological site that dates back to the Neolithic. Archaeological finds along the course of the river indicate the area was rich in flora and fauna in the past. The river is heavily polluted and its restoration is one of the top priorities for the Jordanian Ministry of the Environment. Geologically, the Zarqa River is about 30 million years old. It is well known for its amber deposits that date back to the Hauterivian era of the Early Cretaceous, 135 million years ago. A remarkable flora and fauna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
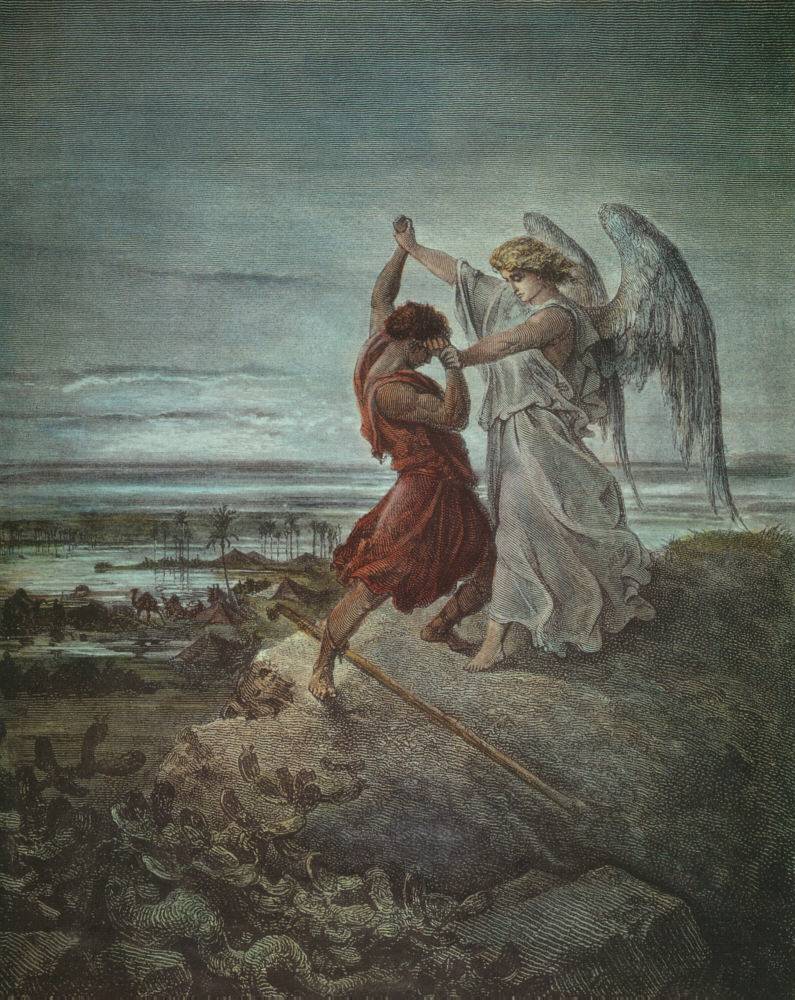
Jacob Wrestling With The Angel
Jacob wrestling with the angel is described in the Book of Genesis (Genesis 32, chapter 32:22–32; also referenced in the Book of Hosea, Hosea 12, chapter 12:3–5). The "Angels in Judaism, angel" in question is referred to as "man" (: ''Ish'') and "God in Judaism, God" (: ''El'') in Genesis, while Hosea references an "angel" (: ''Malakh''). The account includes the renaming of Jacob as ''Israel (name), Israel'' (etymologized as "contends-with-El (god), God"). In the Patriarchs (Bible), Genesis patriarchal narrative, Jacob spent the night alone on a riverside during his Jacob#Journey back to Canaan, journey back to Canaan. He encounters a "man" who proceeds to wrestle with him until dawn. In the end, Jacob is given the name ''Israel'' and Blessings in Judaism, blessed, while the "man" refuses to give his own name. Jacob then names the place where they wrestled ''Penuel'' (: "face of God" or "facing God"). Hebrew Bible The Masoretic Text reads as follows: The account contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammon
Ammon (; Ammonite language, Ammonite: 𐤏𐤌𐤍 ''ʻAmān''; '; ) was an ancient Semitic languages, Semitic-speaking kingdom occupying the east of the Jordan River, between the torrent valleys of Wadi Mujib, Arnon and Jabbok, in present-day Jordan. The chief city of the country was ''Rabbah'' or ''Rabbat Ammon'', site of the modern city of Amman, Jordan's capital. Milcom and Moloch, Molech are named in the Hebrew Bible as the gods of Ammon. The people of this kingdom are called Children of Ammon or Ammonites. History The Ammonites occupied the northern Central Trans-Jordanian Plateau from the latter part of the second millennium BC to at least the second century AD. Ammon maintained its independence from the Neo-Assyrian Empire (10th to 7th centuries BC) by paying tribute to the Assyrian kings at a time when that Empire raided or conquered nearby kingdoms. The Kurkh Monolith lists the Ammonite king Baasha ben Ruhubi's army as fighting alongside Ahab of Kingdom of Israe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob
Jacob, later known as Israel, is a Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions. He first appears in the Torah, where he is described in the Book of Genesis as a son of Isaac and Rebecca. Accordingly, alongside his older fraternal twin brother Esau, Jacob's paternal grandparents are Abraham and Sarah and his maternal grandfather is Bethuel, whose wife is not mentioned. He is said to have bought Esau's birthright and, with his mother's help, deceived his aging father to bless him instead of Esau. Then, following a severe drought in his homeland Canaan, Jacob and his descendants migrated to neighbouring Egypt through the efforts of his son Joseph, who had become a confidant of the pharaoh. After dying in Egypt at the age of 147, he is supposed to have been buried in the Cave of Machpelah in Hebron. Per the Hebrew Bible, Jacob's progeny were beget by four women: his wives (and maternal cousins) Leah and Rachel; and his concubines Bilhah and Zilpah. His sons were, in orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerash Governorate
Jerash Governorate () is one of 12 governorates in Jordan. It is located in the northwestern side of the country. The capital of the governorate is the city of Jerash. Jerash Governorate has the smallest area of the 12 governorates of Jordan, yet it has the second highest density in Jordan after Irbid Governorate. Jerash Governorate is ranked 7th by population. History In the first century of the Christian era this insignificant city (then Gerasa) experienced a fast ascent under Roman rule and the Pax Romana. It became part of the Decapolis and grew increasingly competitive with the older Petra as a commercial town. The inhabitants extracted iron ore from the nearby Ajlun mountains. Starting in the middle of the 1st century, this upswing led to active building and a rich abundance of architectural monuments, still impressive today. In the 2nd century, the Roman expansion wars in Asia led to further gains. Well-made roads were built to Pella, Philadelphia (now Amman), Dion an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaretan
Zaretan or Zarethan (), also known as Zeredathah, is a city mentioned in the Hebrew Bible as near the location where the Hebrews crossed the Jordan (). In the books of Joshua (, KJV "Zaretan") and 1 Kings ( KJV "Zartanah", "Zarthan"), it is called Zarethan, but in 2 Chronicles it is called Zeredathah (, KJV). Zaredathah stood in the Jordan Valley. Nelson Glueck looked for it on the east bank of the river, proposing , but some more recent authors place it on the west bank, one theory identifying it with Tell el-Mazar, also spelled Mezar, in Wadi Far'a. Tell el-Mezar is at the site called in Arabic Qerawa, known from antiquity by the name Korea(i) (κορεα � or Koreous (Kορεους) and located at the foot of Mount Sartabe. According to Hebrew Bible, the bronze castings for the Solomon's Temple were made in the clay grounds between Sukkot and Zaretan. The old identification of the site of the miracle of the Israelites' crossing of the Jordan with the waters stopping thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarmouk River
The Yarmuk River (, ; Greek: Ἱερομύκης, ; or ''Heromicas''; sometimes spelled Yarmouk) is the largest tributary of the Jordan River. It runs in Jordan, Syria and Israel, and drains much of the Hauran plateau. Its main tributaries are the wadis of 'Allan and Ruqqad from the north, Ehreir and Zeizun from the east. Although the Yarmuk is narrow and shallow throughout its course, at its mouth it is nearly as wide as the Jordan, measuring thirty feet in breadth and five in depth. History Yarmuk forms a natural border between the plains to the north - Hauran, Bashan and Golan Heights, Golan - and the Gilead mountains to the south. Thus it has often served as boundary line between political entities. Neolithic The Yarmukian Culture, Yarmukian is a Pottery Neolithic culture that inhabited parts of Israel and Jordan. Its type site is at Sha'ar HaGolan (archaeological site), Sha'ar HaGolan, on the river mouth. Bronze Age Early Bronze Age I is represented in the Golan only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
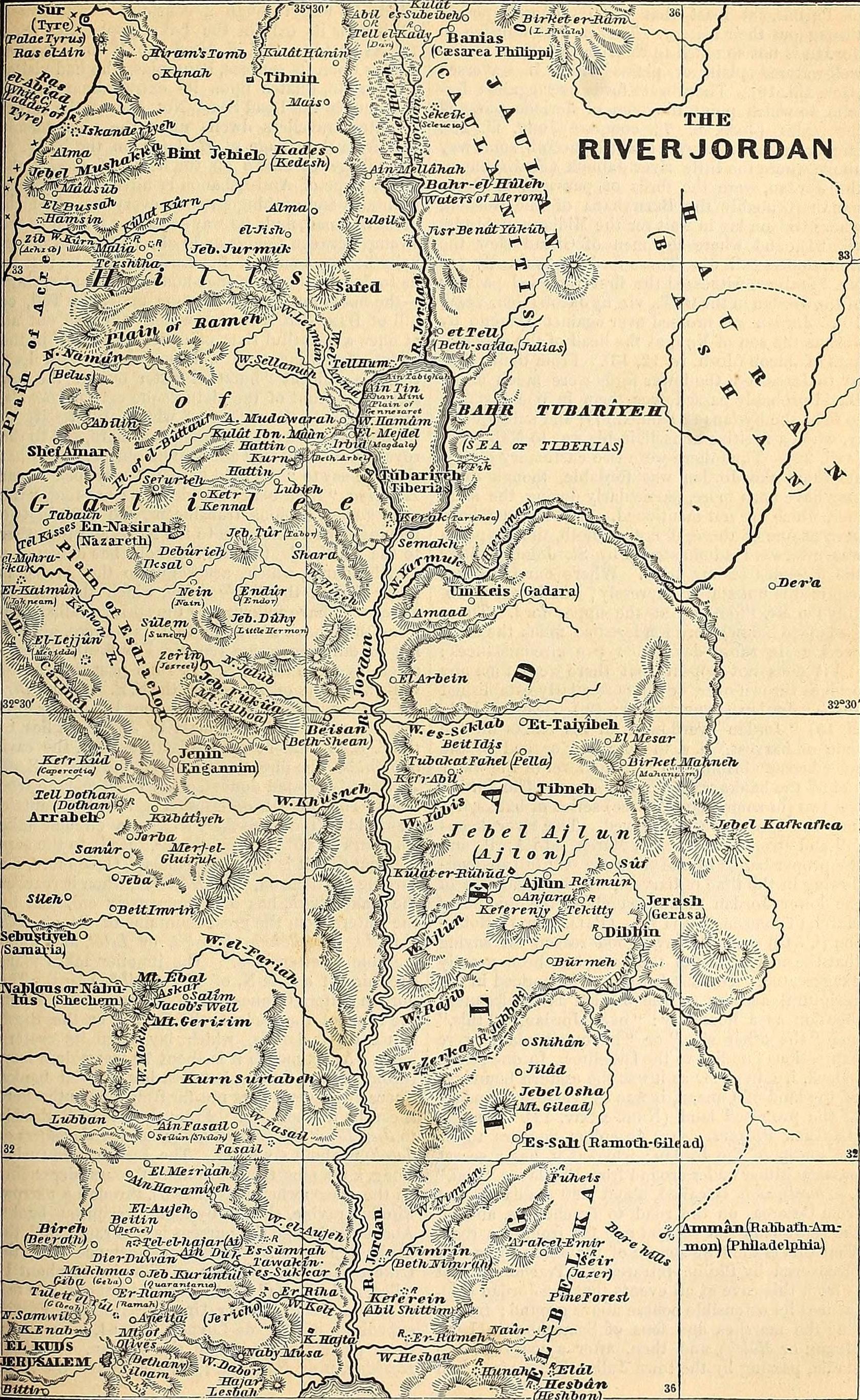
Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan (, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn''; , ''Nəhar hayYardēn''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Sharieat'' (), is a endorheic river in the Levant that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee and drains to the Dead Sea. The river passes by or through Jordan, Syria, Israel, and the Palestinian territories. Jordan and the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights border the river to the east, while Israel and the Israeli-occupied West Bank lie to its west. Both Jordan and the West Bank derive their names in relation to the river. The river holds major significance in Judaism and Christianity. According to the Bible, the Israelites crossed it into the Promised Land and Jesus of Nazareth was baptized by John the Baptist in it. Etymology Several hypotheses for the origin of most of the river's names in modern languages (e.g., Jordan, Yarden, Urdunn), one is that it comes from Semitic 'Yard, on' 'flow down' <√ירד reflecting the river's declivity, possibly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Reuben
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Reuben () was one of the twelve tribes of Israel. Unlike the majority of the tribes, the land of Reuben, along with that of Tribe of Gad, Gad and half of Manasseh (tribal patriarch), Manasseh, was on the eastern side of the Jordan and shared a border with Moab. According to the biblical narrative, the Tribe of Reuben descended from Reuben (son of Jacob), Reuben, the eldest son of the patriarch Jacob. Reuben, along with nine other tribes, is reckoned by the Bible as part of the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), northern kingdom of Israel, and disappears from history with the demise of that kingdom in c. 723 BC. Tribal territory The Book of Joshua records that the tribes of Reuben, Tribe of Gad, Gad and half of Tribe of Manasseh, Manasseh were allocated land by Moses on the Transjordan (Bible), eastern side of the Jordan River and the Dead Sea. The Tribe of Reuben was allocated the territory immediately east of the Dead Sea, reaching from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esau
Esau is the elder son of Isaac in the Hebrew Bible. He is mentioned in the Book of Genesis and by the minor prophet, prophets Obadiah and Malachi. The story of Jacob and Esau reflects the historical relationship between Israel and Edom, aiming to explain why Israel, despite being a younger kingdom, dominated Edom. The Christian New Testament alludes to him in the Epistle to the Romans and in the Epistle to the Hebrews. According to the Hebrew Bible, Esau is the progenitor of the Edomites and the elder brother of Jacob, the Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Israelites.Metzger & Coogan (1993). ''Oxford Companion to the Bible'', pp. 191–92. Jacob and Esau were the sons of Isaac and Rebecca, and the grandsons of Abraham and Sarah. Of the twins, Esau was the first to be born with Jacob following, holding his heel. Isaac was sixty years old when the boys were born. Esau, a "man of the field", became a hunter who had "rough" qualities that distinguished him from his twin brother. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genesis (Hebrew Bible)
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; ; ) is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( 'In the beginning'). Genesis purports to be an account of the creation of the world, the early history of humanity, and the origins of the Jewish people. In Judaism, the theological importance of Genesis centers on the covenants linking God to his chosen people and the people to the Promised Land. Genesis is part of the Torah or Pentateuch, the first five books of the Bible. Tradition credits Moses as the Torah's author. However, there is scholarly consensus that the Book of Genesis was composed several centuries later, after the Babylonian captivity, possibly in the fifth century BC. Based on the scientific interpretation of archaeological, genetic, and linguistic evidence, mainstream biblical scholars consider Genesis to be primarily mythological rather than historical. It is divisible into two parts, the primeval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" . '' Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; ; or ), also known in Hebrew as (; ), is the canonical collection of scriptures, comprising the Torah (the five Books of Moses), the Nevi'im (the Books of the Prophets), and the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |