Harran on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Harran (), historically known as Carrhae ( el, KÎŹĎĎιΚ, KĂĄrrhai), is a rural town and district of the
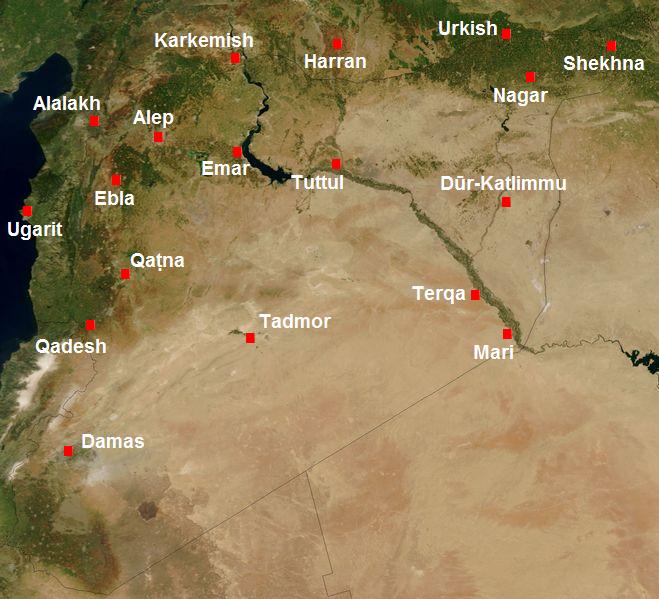 Harran is situated at an important geograp
Harran is situated at an important geograp
ĹanlÄąurfa Province
ĹanlÄąurfa Province ( tr, ĹanlÄąurfa ili; ku, ParĂŞzgeha RihayĂŞ) or simply Urfa Province is a province in southeastern Turkey. The city of ĹanlÄąurfa is the capital of the province which bears its name. The population is 1,845,667 (2014). The ...
in southeastern Turkey
Turkey ( tr, TĂźrkiye ), officially the Republic of TĂźrkiye ( tr, TĂźrkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, approximately 40 kilometres (25 miles) southeast of Urfa
Urfa, officially known as ĹanlÄąurfa () and in ancient times as Edessa, is a city in southeastern Turkey and the capital of ĹanlÄąurfa Province. Urfa is situated on a plain about 80 km east of the Euphrates River. Its climate features e ...
and 20 kilometers from the border crossing with Syria at Akçakale
Akçakale ( ar, ŘŁŮŘŹŘŠ ŮŮؚ؊) is an ethnic Arab town and a district of ĹanlÄąurfa Province, in southeastern Turkey.
Akçakale forms a divided city with Tell Abyad in Syria, maintaining a border crossing. The Mayor is Mehmet YalçĹnkay ...
.
Harran was founded at some point between the 25th and 20th centuries BC as a merchant colony by Sumerian traders from Ur. Over the course of its early history, Harran rapidly grew into a major Mesopotamian
Mesopotamia ''MesopotamĂÄ''; ar, بŮŮŮاد ŮąŮŘąŮŮاŮŮŘŻŮŮŮŮ or ; syc, ÜÜŞÜĄ ܢÜÜŞĚÜܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the TigrisâEuphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
cultural, commercial and religious center. It was made a religiously and politically influential city through its association with the moon-god Sin
In a religious context, sin is a transgression against divine law. Each culture has its own interpretation of what it means to commit a sin. While sins are generally considered actions, any thought, word, or act considered immoral, selfish, ...
; many prominent Mesopotamian rulers consulted with and renovated the moon-temple of Ekhulkhul in Harran. Harran came under Assyrian
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
rule under Adad-nirari I
Adad-nÄrÄrÄŤ I, rendered in all but two inscriptions ideographically as md''adad-''ZAB+DAḪ, meaning âAdad (is) my helper,â (1305â1274 BC or 1295â1263 BC short chronology) was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian Empire. He is th ...
( BC) and became a provincial capital often second in importance only to the Assyrian capital of Assur
AĹĄĹĄur (; Sumerian: AN.Ĺ AR2KI, Assyrian cuneiform: ''AĹĄ-ĹĄurKI'', "City of God AĹĄĹĄur"; syr, ÜÜŤÜÜŞ ''ÄĹĄĹŤr''; Old Persian ''Aθur'', fa, آشŮŘą: ''ÄĹĄĹŤr''; he, ×֡׊֟××֟ר, ', ar, اشŮŘą), also known as Ashur and Qal'at ...
itself. During the collapse of the Assyrian Empire, Harran briefly served as the final capital of the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew ...
612â609 BC.
The city continued to be prominent after the fall of Assyria and experienced varying degrees of foreign cultural influence during its time under the Neo-Babylonian
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC and bein ...
(609â539 BC), Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, đ§đđ, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
(539â330 BC), Macedonian (330â312 BC) and Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, ÎÎąĎΚΝξίι Ď῜ν ΣξΝξĎ
κΚδ῜ν, ''BasileĂa tĹn SeleukidĹn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the M ...
(312â132 BC) empires. During classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations ...
Harran was often contested between the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
and Parthian (later Sasanian
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
) empires. In 53 BC Harran was the site of the Battle of Carrhae
The Battle of Carrhae () was fought in 53 BC between the Roman Republic and the Parthian Empire near the ancient town of Carrhae (present-day Harran, Turkey). An invading force of seven legions of Roman heavy infantry under Marcus Licinius Cr ...
, one of the worst military defeats in Roman history. The Harranian moon cult of Sin proved to be enduring and lasted long into the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, known to have existed as late as the 11th century AD. Harran was captured by the Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, اŮŮŮŘŽŮŮŮاŮŮŘŠŮ ŮąŮŘąŮŮاشŮŘŻŮŘŠŮ, al-KhilÄfah ar-RÄĹĄidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after hi ...
in 640 and remained an important city in the Islamic period. It flourished as a center of science and learning and was the site of both the first Islamic university (the Harran University
Harran University ( tr, Harran Ăniversitesi) is a state university in ĹanlÄąurfa, Turkey, founded in 1992.
History
ĹanlÄąurfa is the homecity of Harran University. It is one of the oldest settlements in the world, with its history going bac ...
) and the oldest mosque in Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu YarÄąmadasÄą), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
(the ). Harran twice served as a capital city in the Middle Ages, first briefly under the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661â750 CE; , ; ar, ŮąŮŮŘŽŮŮŮاŮŮŘŠ ŮąŮŮŘŁŮŮ
ŮŮŮŮŮŮŘŠ, al-KhilÄfah al-ĘžUmawÄŤyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
744â750 and later under the Numayrid Emirate 990â1081.
The city was conquered by the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe ...
in 1260 but was largely destroyed and left abandoned in 1271. Although Harran was kept as a military outpost under some later regimes, it has over the last five centuries mainly been used as a temporary settlement by local nomadic societies. Harran retransitioned into a semi-permanent village settlement in the 1840s but has only recently grown into a permanent town through advancements in local irrigation and agriculture. Harran was a Turkish district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipa ...
until 1946, after when it was downgraded to a sub-district of the Akçakale district. It regained its status as a district in 1987. Today, it is a major local tourist spot. The town is particularly famous for its unique beehive houses, which are reminiscent of buildings that were already present at Harran in ancient Mesopotamian times.
Toponomy
The name Harran is recorded for the city from the earliest documents mentioning it and has remained in continuous use and largely unchanged since ancient times. Harran is mentioned in early cuneiform records of theSumerians
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of ...
and Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750â1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-cent ...
as đˇđŽđ (), sometimes shortened to đ (), transliterated as ''ḪarrÄnu''(''m''). ''ḪarrÄnu'' literally means "journey", "caravan" or "crossroad". It is often interpreted as "caravan path" or "intersection of routes and travel". Harran is rendered as Üܳܪܳܢ (''hrn'') in Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ÜÜŞÜĄÜÜ, ArÄmÄyÄ; oar, đ¤đ¤đ¤đ¤đ¤; arc, đĄđĄđĄđĄđĄ; tmr, ×ֲרָ×Ö´×ת), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated i ...
, ŘŮŘąŮŮا٠(''Ḥarrân'') in Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
, Řعا٠(''HarrÄn'') in Ottoman Turkish
Ottoman Turkish ( ota, ŮŮساŮŮ ŘšŮŘŤŮ
اŮŮ, Lisân-Äą OsmânĂŽ, ; tr, OsmanlÄą TĂźrkçesi) was the standardized register of the Turkish language used by the citizens of the Ottoman Empire (14th to 20th centuries CE). It borrowed exten ...
, and ''Harran'' in modern Turkish.
The ancient Assyrians
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
called the city ''Huzirina''. ''ḪarrÄnu'' was Hellenised
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in the ...
to ''KĂĄrrhai'' (KÎŹĎĎιΚ) in the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
. The Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
later Latinised the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
name into ''Carrhae''. Due to the prominence of both Harran and Carrhae in historical literary sources, some scholars use the compound name "Carrhae-Harran" for the ancient city. Under the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
, the city continued to be called Carrhae (KÎŹĎĎιΚ) but was also sometimes referred to as ''Hellenopolis'' (EΝΝΡνóĎoΝΚĎ), "city of the agan
The Agan (russian: Đган) is a river in Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug in Russia. It is long, and its basin covers .
Course
The Agan is a left tributary of the Tromyogan, of the Ob basin. To the south of its course lies the basin of the Va ...
Greeks", in reference to the strong pagan traditions there.
History
Ancient Near East (2500â539 BC)
Early history