|
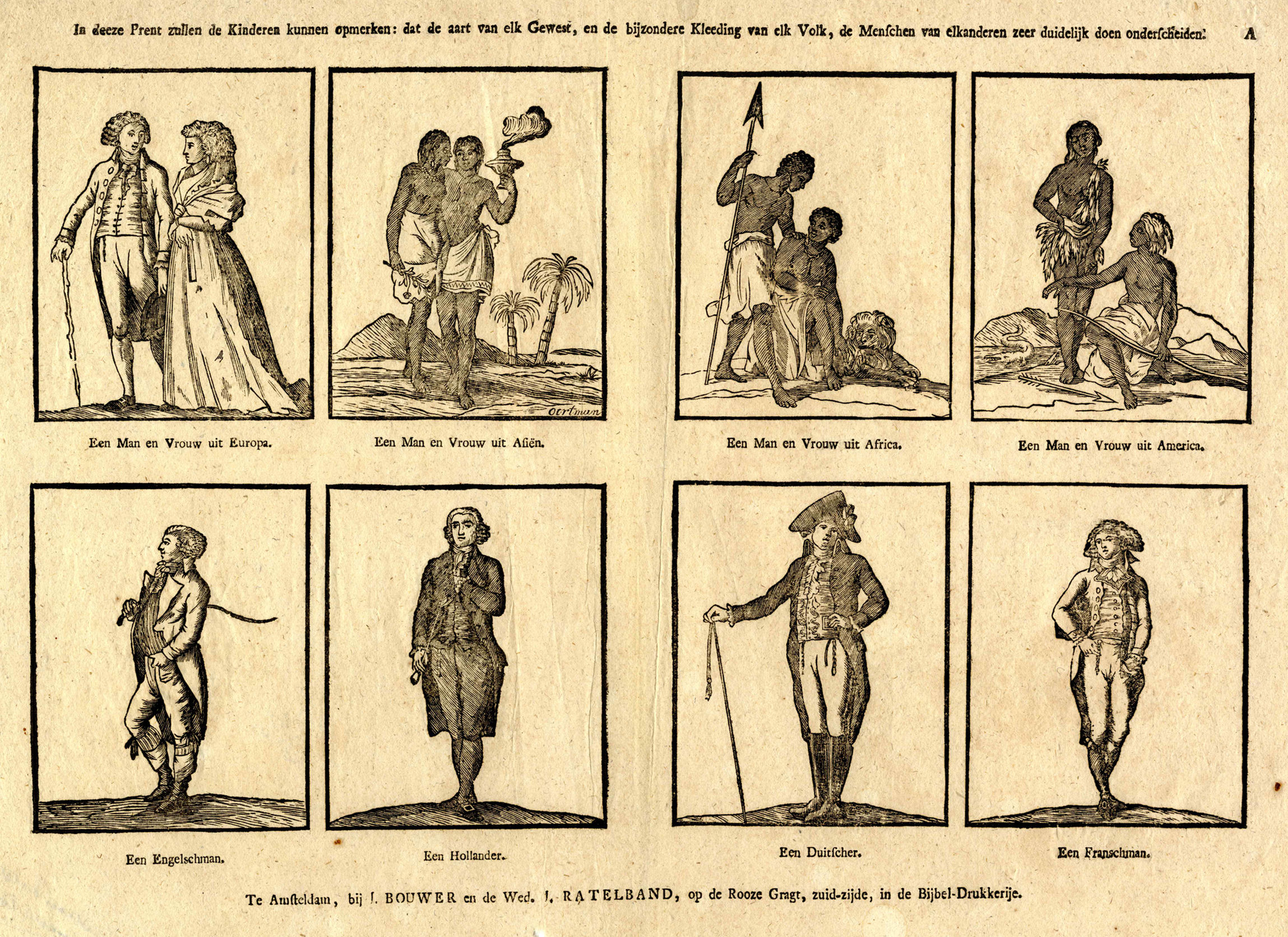
Institutional Racism
Institutional racism, also known as systemic racism, is a form of institutional discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race or ethnic group and can include policies and practices that exist throughout a whole society or organization that result in and support a continued unfair advantage to some people and unfair or harmful treatment of others. It manifests as racial discrimination, discrimination in areas such as criminal justice, employment, housing, healthcare, education and Representation (politics), political representation. The term ''institutional racism'' was first coined in 1967 by Stokely Carmichael and Charles V. Hamilton in ''Black Power: The Politics of Liberation''. Carmichael and Hamilton wrote in 1967 that, while individual racism is often identifiable because of its overt nature, institutional racism is less perceptible because of its "less overt, far more subtle" nature. Institutional racism "originates in the operation of established and respecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institutional Discrimination
Institutional discrimination is discriminatory treatment of an individual or group of individuals by institutions, through unequal consideration of members of subordinate groups. Societal discrimination is discrimination by society. These unfair and indirect methods of discrimination are often embedded in an institution's policies, procedures, laws, and objectives. The discrimination can be on grounds of gender, caste, race, ethnicity, religion, disability, or socio-economic status. State religions are a form of societal discrimination. Institutional racism Institutional racism (also known as systemic racism) is a form of institutional discrimination applied to Race (human categorization), race and considered a form of racism that is embedded as normal practice within an institution. It can lead to such issues as discrimination in criminal justice, employment, housing, health care, political power, and education, among other issues. The term "institutional racism" was first coi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-esteem
Self-esteem is confidence in one's own worth, abilities, or morals. Self-esteem encompasses beliefs about oneself (for example, "I am loved", "I am worthy") as well as emotional states, such as triumph, despair, pride, and shame. Smith and Mackie define it by saying "The self-concept is what we think about the self; self-esteem, is the positive or negative evaluations of the self, as in how we feel about it (see self)." The construct of self-esteem has been shown to be a desirable one in psychology, as it is associated with a variety of positive outcomes, such as academic achievement, relationship satisfaction, happiness, and lower rates of criminal behavior. The benefits of high self-esteem are thought to include improved mental and physical health, and less anti-social behavior while drawbacks of low self-esteem have been found to be anxiety, loneliness, and increased vulnerability to substance abuse. Self-esteem can apply to a specific attribute or globally. Psychologists usu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stigmatized
Stigma, originally referring to the visible marking of people considered inferior, has evolved to mean a negative perception or sense of disapproval that a society places on a group or individual based on certain characteristics such as their socioeconomic status, gender, race, religion, appearance, upbringing, origin, or health status. Social stigma can take different forms and depends on the specific time and place in which it arises. Once a person is stigmatized, they are often associated with stereotypes that lead to discrimination, marginalization, and psychological problems. This process of stigmatization not only affects the social status and behavior of stigmatized persons, but also shapes their own self-perception, which can lead to psychological problems such as depression and low self-esteem. Stigmatized people are often aware that they are perceived and treated differently, which can start at an early age. Research shows that children are aware of cultural stereotyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotyping
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example, an expectation about the group's personality, preferences, appearance or ability. Stereotypes make information processing easier by allowing the perceiver to rely on previously stored knowledge in place of incoming information. Stereotypes are often faulty, inaccurate, and resistant to new information. Although stereotypes generally have negative implications, they aren't necessarily negative. They may be positive, neutral, or negative. They can be broken down into two categories: explicit stereotypes, which are conscious, and implicit stereotypes, which are subconscious. Explicit stereotypes An explicit stereotype is a belief about a group that a person is consciously aware of and knowingly uses to judge others. If person ''A ''is mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigotry
Prejudice can be an affective feeling towards a person based on their perceived social group membership. The word is often used to refer to a preconceived (usually unfavourable) evaluation or classification of another person based on that person's perceived personal characteristics, such as political affiliation, sex, gender, gender identity, beliefs, values, social class, friendship, age, disability, religion, sexuality, race, ethnicity, language, nationality, culture, complexion, beauty, height, body weight, occupation, wealth, education, criminality, sport-team affiliation, music tastes or other perceived characteristics. The word "prejudice" can also refer to unfounded or pigeonholed beliefs and it may apply to "any unreasonable attitude that is unusually resistant to rational influence". Gordon Allport defined prejudice as a "feeling, favorable or unfavorable, toward a person or thing, prior to, or not based on, actual experience". Auestad (2015) defines pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McGraw-Hill
McGraw Hill is an American education science company that provides educational content, software, and services for students and educators across various levels—from K-12 to higher education and professional settings. They produce textbooks, digital learning tools, and adaptive technology to enhance learning experiences and outcomes. It is one of the "big three" educational publishers along with Houghton Mifflin Harcourt and Pearson Education. McGraw Hill also publishes reference and trade publications for the medical, business, and engineering professions. Formerly a division of The McGraw Hill Companies (later renamed McGraw Hill Financial, now S&P Global), McGraw Hill Education was divested and acquired by Apollo Global Management in March 2013 for $2.4 billion in cash. McGraw Hill was sold in 2021 to Platinum Equity for $4.5 billion. History McGraw Hill was founded in 1888, when James H. McGraw, co-founder of McGraw Hill, purchased the ''American Journal of Railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internalized Racism
In social justice studies, internalized racism is a form of internalized oppression, defined by sociologist Karen D. Pyke as the " internalization of racial oppression by the racially subordinated." In her study ''The Psychology of Racism, '' Robin Nicole Johnson emphasizes that internalized racism involves both "conscious and unconsious acceptance of a racial hierarchy in which a presumed superior race are consistently ranked above other races. These definitions encompass a wide range of instances, including, but not limited to, belief in negative stereotypes, adaptations to cultural standards, and thinking that supports the status quo (i.e. denying that racism exists). Internalized racism as a phenomenon is a direct product of a racial classification system, and is found across different racial groups and regions around the world where race exists as a social construct. In these places, internalized racism can have adverse effects on those who experience it. For example, high in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Jones (psychologist)
James McCoy Jones is an African-American social psychologist and cultural diversity scholar. He is Trustees' Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Psychological and Brain Sciences and Black American Studies and Director of the Center for the Study of Diversity at the University of Delaware. He is a past president of both the Society of Experimental Social Psychology and the Society for the Psychological Study of Social Issues. He previously taught at Harvard University and Howard University before joining the University of Delaware. In 2011, he received the Outstanding Lifetime Contributions to Psychology Award from the American Psychological Association The American Psychological Association (APA) is the main professional organization of psychologists in the United States, and the largest psychological association in the world. It has over 170,000 members, including scientists, educators, clin .... He retired from the University of Delaware in 2018, and gave a retirement lectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessment to form Cambridge University Press and Assessment under Queen Elizabeth II's approval in August 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 countries, it published over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publications include more than 420 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also published Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Sports and Social Centre. It also served as the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press, as part of the University of Cambridge, was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stand Up To Racism (42540231585)
Unite Against Fascism (UAF) is a British anti-fascist group. Its joint secretaries are Weyman Bennett and Sabby Dhalu, formerly of the National Assembly Against Racism (NAAR). Its chair is Steve Hart of Unite the Union and its assistant secretary was the late Jude Woodward of Socialist Action. Since 2013, UAF has mainly operated in partnership with its sister organisation Stand Up To Racism, which has many of the same officers as UAF: Bennett and Dhalu as joint secretaries, Diane Abbott as president and co-chairs Dave Ward of the Communication Workers' Union and Talha Ahmad of the Muslim Council of Britain. History Unite Against Fascism (UAF) was formed in Great Britain in late 2003 in response to electoral successes by the BNP. Its main elements were the Anti-Nazi League and the National Assembly Against Racism, with the support of the Trades Union Congress (TUC) and leading British unions such as the Transport and General Workers' Union (T&G) (now Unite) and UNISO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diversity, Equity, And Inclusion
In the United States, diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) are organizational frameworks that seek to promote the fair treatment and full participation of all people, particularly groups who have historically been underrepresented or subject to discrimination based on identity or disability. These three notions (diversity, equity, and inclusion) together represent "three closely linked values" which organizations seek to institutionalize through DEI frameworks. The concepts predate this terminology and other variations sometimes include terms such as belonging, justice, and accessibility. As such, frameworks such as inclusion and diversity (I&D), diversity, equity, inclusion and belonging (DEIB), justice, equity, diversity and inclusion (JEDI or EDIJ), or diversity, equity, inclusion and accessibility (IDEA, DEIA or DEAI) exist. In the United Kingdom, the term equality, diversity, and inclusion (EDI) is used in a similar way. ''Diversity'' refers to the presence of variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |