|
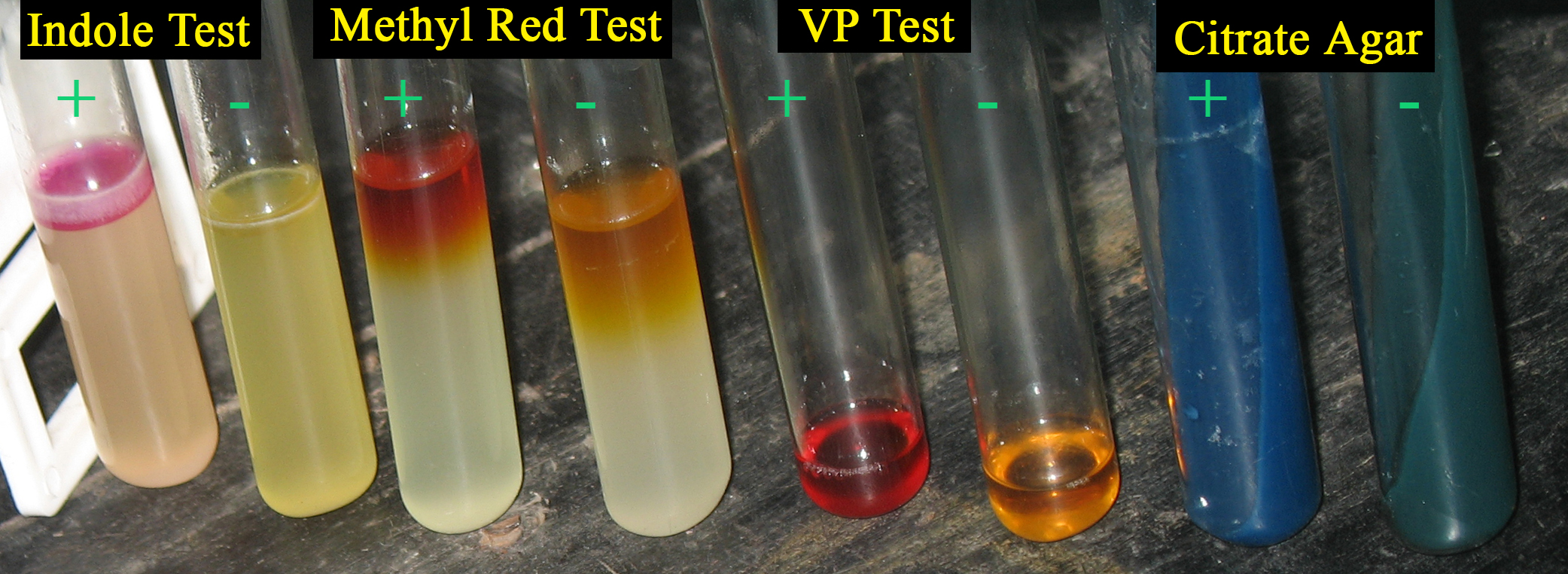
IMViC Results
The IMViC tests are a group of individual tests used in microbiology lab testing to identify an organism in the coliform group. A coliform is a gram negative, aerobic, or facultative anaerobic rod, which produces gas from lactose within 48 hours. The presence of some coliforms indicate fecal contamination. The term "IMViC" is an acronym for each of these tests. "I" is for indole test; "M" is for methyl red test; "V" is for Voges-Proskauer test, and "C" is for citrate test. The lower case "i" is merely for "in" as the Citrate test requires coliform samples to be placed "in Citrate". These tests are useful in distinguishing members of Enterobacteriaceae. Indole test In this test, the organism under consideration is grown in peptone water broth. It contains tryptophan, which under the action of enzyme tryptophanase is converted to an Indole molecule, pyruvate and ammonium. The indole is then extracted from the broth by means of xylene. The broth is sterilized for 15 minut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coliform Bacteria
Coliform bacteria are defined as either motile or non-motile Gram-negative non- spore forming Bacilli that possess β-galactosidase to produce acids and gases under their optimal growth temperature of 35-37°C. They can be aerobes or facultative aerobes, and are a commonly used indicator of low sanitary quality of foods, milk, and water. Coliforms can be found in the aquatic environment, in soil and on vegetation; they are universally present in large numbers in the feces of warm-blooded animals as they are known to inhabit the gastrointestinal system. While coliform bacteria are not normally causes of serious illness, they are easy to culture, and their presence is used to infer that other pathogenic organisms of fecal origin may be present in a sample, or that said sample is not safe to consume. Such pathogens include disease-causing bacteria, viruses, or protozoa and many multicellular parasites. Genera Typical genera include: * ''Citrobacter ''are peritrichous f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butanediol Fermentation
2,3-Butanediol fermentation is anaerobic fermentation of glucose with 2,3-butanediol as one of the end products. The overall stoichiometry of the reaction is :2 pyruvate + NADH --> 2 CO2 + 2,3-butanediol. Butanediol fermentation is typical for the facultative anaerobes ''Klebsiella'' and '' Enterobacter'' and is tested for using the Voges–Proskauer (VP) test. There are other alternative strains that can be used, talked about in details in the Alternative Bacteria Strains section below. The metabolic function of 2,3-butanediol is not known, although some have speculated that it was an evolutionary advantage for these microorganisms to produce a neutral product that's less inhibitory than other partial oxidation products and doesn't reduce the pH as much as mixed acids. There are many important industrial applications that butanediol can be used for, including antifreeze, food additives, antiseptic, and pharmaceuticals. It also is produced naturally in various places of the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of rod-shaped (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and '' Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' is the type species and is further divided into six subspecies that include over 2,600 serotypes. ''Salmonella'' was named after Daniel Elmer Salmon (1850–1914), an American veterinary surgeon. ''Salmonella'' species are non-spore-forming, predominantly motile enterobacteria with cell diameters between about 0.7 and 1.5 μm, lengths from 2 to 5 μm, and peritrichous flagella (all around the cell body, allowing them to move). They are chemotrophs, obtaining their energy from oxidation and reduction reactions, using organic sources. They are also facultative anaerobes, capable of generating ATP with oxygen ("aerobically") when it is available, or using other electron acceptors or fermentation ("anaerobically") when oxygen is not available. ''Salmonella'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shigella
''Shigella'' is a genus of bacteria that is Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, non-spore-forming, nonmotile, rod-shaped, and genetically closely related to '' E. coli''. The genus is named after Kiyoshi Shiga, who first discovered it in 1897. The causative agent of human shigellosis, ''Shigella'' causes disease in primates, but not in other mammals. It is only naturally found in humans and gorillas. During infection, it typically causes dysentery. ''Shigella'' is one of the leading bacterial causes of diarrhea worldwide, causing an estimated 80–165 million cases. The number of deaths it causes each year is estimated at between 74,000 and 600,000. It is one of the top four pathogens that cause moderate-to-severe diarrhea in African and South Asian children. Classification ''Shigella'' species are classified by three serogroups and one serotype: * Serogroup ''A'': '' S. dysenteriae'' (15 serotypes) * Serogroup ''B'': '' S. flexneri'' (9 serotypes) * Serogroup ''C'': '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of the Bay of Bengal. According to the 2011 Indian census, Chennai is the sixth-most populous city in the country and forms the fourth-most populous urban agglomeration. The Greater Chennai Corporation is the civic body responsible for the city; it is the oldest city corporation of India, established in 1688—the second oldest in the world after London. The city of Chennai is coterminous with Chennai district, which together with the adjoining suburbs constitutes the Chennai Metropolitan Area, the 36th-largest urban area in the world by population and one of the largest metropolitan economies of India. The traditional and de facto gateway of South India, Chennai is among the most-visited Indian cities by foreign tourists. It was rank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orient Longman
Orient Blackswan Pvt. Ltd. (formerly Orient Longman India, commonly referred to as Orient Longman), is an Indian publishing house headquartered in Hyderabad, Telangana. The company publishes academic, professional and general works as well as school textbooks, of which the "Gulmohar" series of English-language schools books grew popular. It also publishes low cost reprints of foreign titles. History Established in 1948 as Longman Green by the UK publishing company Longman, it was taken over by J. Rameshwar Rao, who bought the majority shareholding and became the company chairman in 1968. Rao retained the majority holding till 1984. The company's board included Khushwant Singh and the Patwardhans of Pune. The "Indianisation" of Orient Longman's management during this period was also reflected in its product, where Indian writers found an increasingly prominent place. Also during this period various subsidiaries came about such as Orion Books, and Gyan Publishings which sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urease Test
Rapid urease test, also known as the CLO test (Campylobacter-like organism test), is a rapid diagnostic test for diagnosis of '' Helicobacter pylori''. The basis of the test is the ability of ''H. pylori'' to secrete the urease enzyme, which catalyzes the conversion of urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide. Process The test is performed at the time of gastroscopy. A biopsy of mucosa is taken from the antrum of the stomach, and is placed into a medium containing urea and an indicator such as phenol red. The urease produced by ''H. pylori'' hydrolyzes urea to ammonia, which raises the pH of the medium, and changes the color of the specimen from yellow (NEGATIVE) to red (POSITIVE). Among different kinds of rapid urease tests (liquid-based, gel-based, dry cool) there is a design type with single-layer sensitive element — a layer impregnated simultaneously with urea and an indicator composition. Such a design bears the risk of false-positive result due to the pH value of the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromothymol Blue
Bromothymol blue (also known as bromothymol sulfone phthalein and BTB) is a pH indicator. It is mostly used in applications that require measuring substances that would have a relatively neutral pH (near 7). A common use is for measuring the presence of carbonic acid in a liquid. It is typically sold in solid form as the sodium salt of the acid indicator. Structure and properties Bromothymol blue acts as a weak acid in a solution. It can thus be in protonated or deprotonated form, appearing yellow or blue, respectively. It is bright aquamarine by itself, and greenish-blue in a neutral solution. The deprotonation of the neutral form results in a highly conjugated structure, accounting for the difference in color. An intermediate of the deprotonation mechanism is responsible for the greenish color in neutral solution. The protonated form of bromothymol blue has its peak absorption at 427 nm thus transmitting yellow light in acidic solutions, and the deprotonated form has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simmon's Citrate Agar
Principle Simmons' citrate agar is used for differentiating gram-negative bacteria on the basis of citrate utilization. It is useful for selecting for organisms that use citrate as its main carbon and energy source. It is a defined, selective and differential medium that tests for an organism's ability to use citrate as a sole carbon source and ammonium ions as the sole nitrogen source. The medium contains sodium chloride Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35 ..., sodium citrate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, dipotassium phosphate, and magnesium sulphate. It also contains bromothymol blue, a pH indicator. Bromothymol blue is green at pH below 6.9, and then turns blue at a pH of 7.6 or greater. Physical Format Although it could be used in other formats (e.g., Petri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)




