|
ICGV Ægir
ICGV ''Ægir'' is a former offshore patrol vessel of the Icelandic Coast Guard. Built by Aalborg Værft, in Denmark, she is the lead ship of the and has one sister ship of an improved design, . The ship entered service in 1968 and participated in the two last Cod Wars against the United Kingdom. ''Ægir'' primarily conducted patrols, search and rescue, fishery inspections, general law enforcement and counter-terrorism operations in the Icelandic exclusive economic zone. In 2020, the patrol vessel was taken out of service and sold two years later. Description ''Ægir'' has a standard displacement of and at full load. The ship measures long with a beam of and a draught of . The ship is powered by two MAN 8L 40/54 diesel engines turning two shafts with Kamewa controllable pitch propellers rated at . This gives the ship a maximum speed of with a range of at . The vessel has a 20-ton bollard-pulling winch and passive rolling tanks. The ''Ægir''-class ships were initially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aalborg Værft
Aalborg Shipyard ('' Danish: Aalborg Værft A/S'') was a shipyard located in Aalborg, Denmark. Founded in 1912 by brothers Immanuel Stuhr and Peter Philip Stuhr, the shipyard was founded under the name Stuhr Engine and Ship Construction, a development of their father's business. From 1937 until the yard closed in 1988, it was owned by J. Lauritzen A/S. Ships built at Aalborg Shipyard Closure In 1988, the company was split into five separate companies: *Danyard Aalborg, part of Royal Denship *Aalborg steelworks *Aalborg Industries ( Boilers) *Norks Industrial Services (NIS) *Danish Railway Club (Limfjord path). In 2005 the former yard area was cleared, the only building surviving demolition the 1912 machine shop, while the dry dock continues yacht production, leased by Danyard Aalborg. Today, the former yard is covered with new home and office developments. References Shipyard Danish companies established in 1912 Shipyard A shipyard, also called a dockyard or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
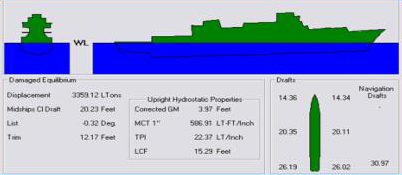
Displacement (ship)
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p. 5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks". A merchant vessel has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funnel (ship)
A funnel is the smokestack or chimney on a ship used to expel boiler steam and smoke or engine exhaust gas, exhaust. They are also commonly referred to as stacks. Purpose The primary purpose of a ship's funnel(s) is to lift the exhaust gases clear of the deck, in order not to foul the ship's structure or decks, and to avoid impairing the ability of the crew to carry out their duties. In steam ships the funnels also served to help induce a boiler draught, convection draught through the boilers. Design Since the introduction of steam-power to ships in the 19th century, the funnel has been a distinctive feature of the silhouette of a vessel, and used for recognition purposes. Funnel area The required funnel cross-sectional area is determined by the volume of exhaust gases produced by the propulsion plant. Often this area is too great for a single funnel. Early steam vessels needed multiple funnels ( had 5 when launched), but as efficiency increased new machinery needed fewe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, map weather formations, and terrain. The term ''RADAR'' was coined in 1940 by the United States Navy as an acronym for "radio detection and ranging". The term ''radar'' has since entered English and other languages as an anacronym, a common noun, losing all capitalization. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwave domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sperry Marine Northrop Grumman
Northrop Grumman Sperry Marine is a part of Northrop Grumman Mission Systems. Through various mergers, Northrop Grumman Sperry Marine was built out of companies including Decca Radars, Sperry Marine, and C. Plath and Litton Industries. The company is headquartered in New Malden, UK, with offices in Germany, Netherlands, Denmark, China, India, Singapore, South Korea, USA, and Canada. It is one of the few remaining namesakes of the Sperry Corporation still in business. Sperry Marine is one of the oldest manufacturers of gyrocompasses. Its founder, Elmer Ambrose Sperry, was working on the first prototype of the gyrocompass at the same time as Hermann Anschütz-Kaempfe was developing his. Eventually, the rivalry between these two inventors over the gyrocompass went to court, where Albert Einstein Albert Einstein (14 March 187918 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is best known for developing the theory of relativity. Einstein also made important contri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicopter Deck
A helicopter deck (or helo deck) is a helicopter pad on the deck of a ship, usually located on the stern and always clear of obstacles that would prove hazardous to a helicopter landing. In the United States Navy, it is commonly and properly referred to as the flight deck. In the UK's Fleet Air Arm, ''landing on'' is usually achieved by first lining up on the port quarter parallel to the ship's heading, then once the deck motion is deemed to be acceptable the pilot sidesteps the aircraft laterally using a white painted line (the bum line) as a reference. Shipboard landing for some helicopters is assisted though use of a haul-down device that involves attachment of a cable to a probe on the bottom of the aircraft prior to landing. Tension is maintained on the cable as the helicopter descends, assisting the pilot with accurate positioning of the aircraft on the deck; once on deck locking beams close on the probe, locking the aircraft to the flight deck. This device was pioneered b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net Cutter (fisheries Patrol)
Net cutters, or trawlwire cutters, are secret weaponsSæmundsson, Sveinn (1984) ''Guðmundur skipherra Kjærnested'', Örn og Örlygur. eykjavík p. 187-189. that were employed by the Icelandic Coast Guard during the latter two Cod Wars to cut the trawling wires of foreign fishing trawlers working within the then newly claimed Exclusive Fisheries zones. They were invented by Commander Pétur Sigurðsson, Director of the Coast Guard, with assistance from Friðrik Teitsson from the Icelandic lighthouse institution and Tómas Sigurðsson, who were both ironmongers. The invention was known as the trawlwire cutter, and was tested in 1958—but not used until 5 September 1972, after every Icelandic ship had been equipped with it. The first net cutting On September 5, 1972, at 10:25 ICGV ''Ægir'', under Cdr. Guðmundur Kjærnested's command, encountered an unmarked trawler fishing northeast of Hornbanki. The master of this black-hulled trawler refused to divulge the trawler's name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
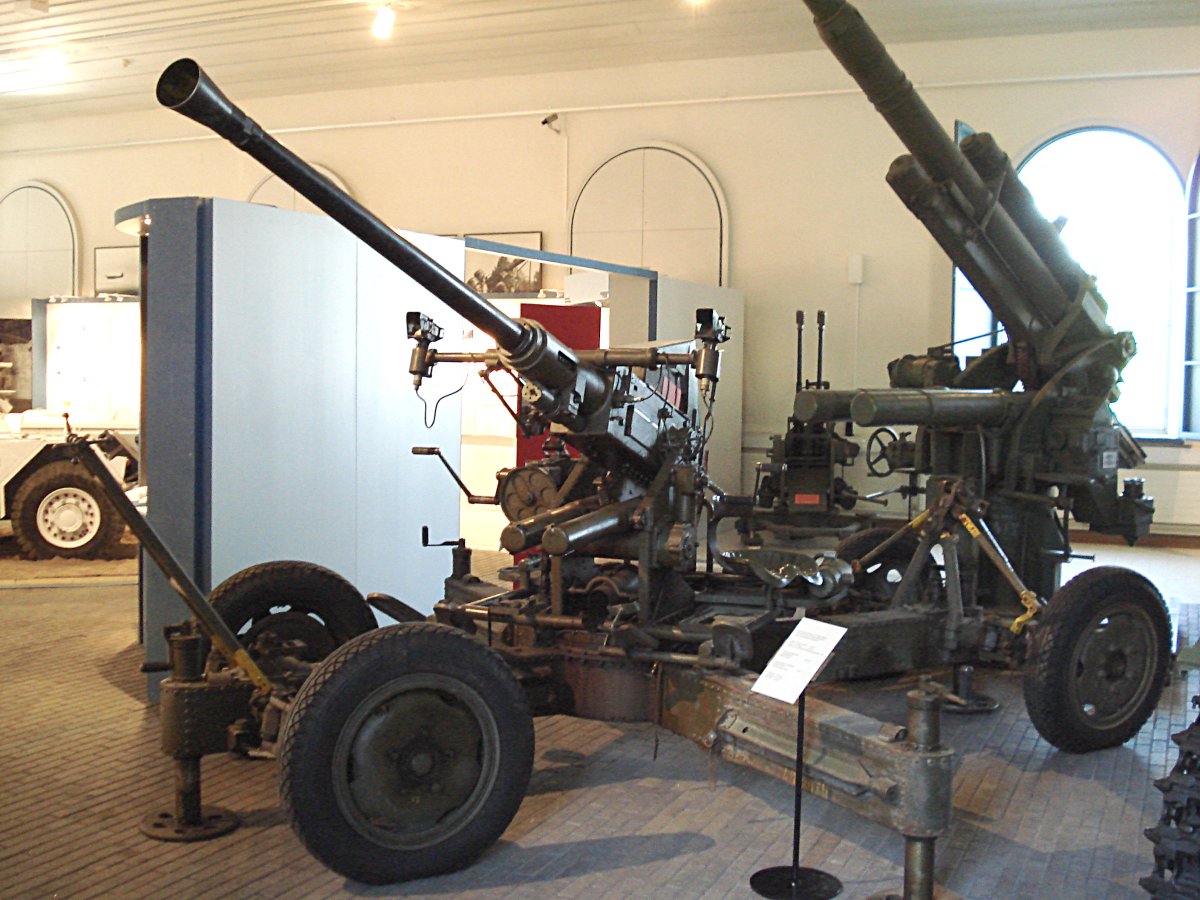
Bofors 40 Mm Automatic Gun L/60
The Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/60 (often referred to simply as the "Bofors 40 mm gun", the "Bofors gun" and the like, see #Name, name) is an Anti-aircraft warfare, anti-aircraft autocannon, designed in the 1930s by the Swedish arms manufacturer AB Bofors. The gun was designed as an intermediate anti-aircraft gun, filling the gap between fast firing close-range small calibre anti-aircraft guns and slower firing long-range high calibre anti-aircraft guns. For its time, the Bofors 40 mm L/60 was perfectly suited for this role and outperformed competing designs in the years leading up to World War II in both effectiveness and reliability. It entered the export market around 1932 and was in service with 18 countries by 1939. Throughout World War II it became one of the most popular and widespread medium-weight anti-aircraft guns. It was used by the majority of the western Allies of World War II, Allies and some Axis powers such as Nazi Germany and Hungary. In the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QF 6-pounder Hotchkiss
The Ordnance QF Hotchkiss 6 pounder gun Mk I and Mk II or QF 6 pounder 8 cwt were a family of long-lived light naval guns introduced in 1885 to defend against new, small and fast vessels such as torpedo boats and later submarines. Many variants were produced, often under license, which ranged in length from 40 to 58 calibres, with 40 calibre the most common. 6-pounders were widely used by the navies of a number of nations and often used by both sides in a conflict. Due to advances in torpedo delivery and performance, 6-pounder guns were rapidly made obsolete and were replaced with larger guns aboard most larger warships. This led to their being used ashore during World War I as coastal defence guns, the first tank guns and as anti-aircraft guns, whether on improvised or specialized HA/LA mounts. During World War II 6-pounder guns were put back in service to arm small warships and as coastal defence guns. The last ships to carry 6-pounders were the Aegir-class offshore pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
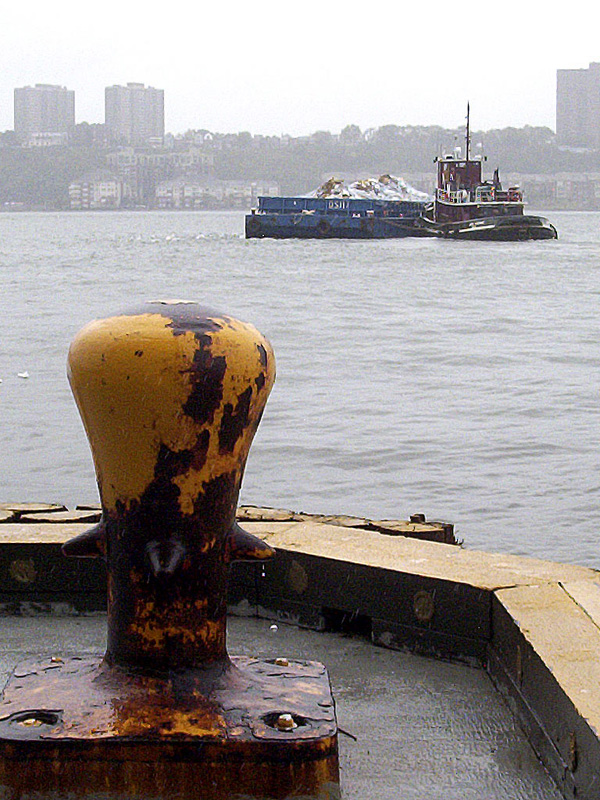
Bollard (mooring)
A bollard is a sturdy, short, vertical post on a ship or quay used principally for mooring boats. Etymology The term is probably related to '' bole'', meaning a tree trunk. The earliest citation given by the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (referring to a maritime bollard) dates from 1844, although a reference in the ''Caledonian Mercury'' in 1817 describes bollards as huge posts. Maritime use In maritime contexts, a bollard is either a wooden or iron post found as a deck-fitting on a ship or boat, and used to secure ropes for towing, mooring and other purposes; or its counterpart on land, a short wooden, iron, or stone post on a quayside to which craft can be moored. The ''Sailor's Word-Book'' of 1867 defines a bollard in a more specific context as "a thick piece of wood on the head of a whale-boat, round which the harpooner gives the line a turn, in order to veer it steadily, and check the animal's velocity". Bollards on ships, when arranged in pairs, may also be referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Controllable Pitch Propeller
Controllability is an important property of a control system and plays a crucial role in many regulation problems, such as the stabilization of unstable systems using feedback, tracking problems, obtaining optimal control strategies, or, simply prescribing an input that has a desired effect on the state. Controllability and observability are dual notions. Controllability pertains to regulating the state by a choice of a suitable input, while observability pertains to being able to know the state by observing the output (assuming that the input is also being observed). Broadly speaking, the concept of controllability relates to the ability to steer a system around in its configuration space using only certain admissible manipulations. The exact definition varies depending on the framework or the type of models dealt with. The following are examples of variants of notions of controllability that have been introduced in the systems and control literature: * State controllability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamewa
AB Karlstads Mekaniska Werkstad (''trans.'' Karlstad Mechanical Works Ltd), known as Kamewa, was a Swedish manufacturing company in the city of Kristinehamn. Kamewa started as a brand name of the controllable-pitch propellers manufactured by KMW. KMW was founded in the city of Karlstad in 1860. KMW also manufactured pulp and paper machines for paper mills and hydro power turbines. Kamewa was acquired by the British company Vickers plc in 1986. In 1999, Rolls-Royce acquired Vickers. In 2019 the Commercial Marine part of Rolls-Royce was acquired by the Kongsberg group and integrated into its maritime division Kongsberg Maritime. The Swedish part of the business is now called Kongsberg Maritime Sweden AB and is based in Kristinehamn. Water jets The Kamewa waterjets are still traded by Kongsberg Maritime under that name and are offered in five product lines in two product series. Previous products from Kamewa has been the A-series, a mix flow pump in aluminum, the SII and P62 p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |