|
I-name
I-names are one form of an Extensible Resource Identifier, XRI — an OASIS (organization), OASIS open standard for digital identifiers designed for sharing resources and data across domains and applications. OASIS (organization), OASIS XRI Technical Committee (14 November 2005) I-names are human readable XRIs intended to be as easy as possible for people to remember and use. For example, a personal i-name could be ''=Mary'' or ''=Mary.Jones''. An organizational i-name could be ''@Acme'' or ''@Acme.Corporation''. Persistence One problem XRIs are designed to solve is ''persistent addressing'' — how to maintain an address that does not need to change no matter how often the contact details of a person or organization change. XRIs accomplis ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I-number
i-numbers are a type of Internet identifier designed to solve the problem of how any web resource can have a persistent identity that never changes even when the web resource moves or changes its human-friendly name. For example, if a web page has an i-number, and links to that page use the i-number, then those links will not break even if the page is renamed, the website containing the page is completely reorganized, or the page is moved to another website. Conceptually, an i-number is similar to an IP address, except i-numbers operate at a much higher level of abstraction (computer science), abstraction in Internet addressing architecture. The other key difference is that i-numbers are persistent, i.e., once they are assigned to a resource, they are never reassigned. By contrast, IP addresses are constantly reassigned, e.g., your computer may have a different IP address every time it connects to the Internet. Technically, an i-number is one form of an extensible resource ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenID
OpenID is an open standard and decentralized authentication protocol promoted by the non-profit OpenID Foundation. It allows users to be authenticated by co-operating sites (known as relying parties, or RP) using a third-party identity provider (IDP) service, eliminating the need for webmasters to provide their own ''ad hoc'' login systems, and allowing users to log in to multiple unrelated websites without having to have a separate identity and password for each. Users create accounts by selecting an OpenID identity provider, and then use those accounts to sign on to any website that accepts OpenID authentication. Several large organizations either issue or accept OpenIDs on their websites. The OpenID standard provides a framework for the communication that must take place between the identity provider and the OpenID acceptor (the " relying party"). An extension to the standard (the OpenID Attribute Exchange) facilitates the transfer of user attributes, such as name and ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XRDS
The extensible resource descriptor sequence (XRDS) is an XML-based file format that provides a list of services. Background The XML format used by XRDS was originally developed in 2004 by the OASIS XRI ( extensible resource identifier) Technical Committee as the resolution format for XRIs. The acronym XRDS was coined during subsequent discussions between XRI TC members and OpenID developers at first Internet Identity Workshop held in Berkeley, CA in October 2005. The protocol for discovering an XRDS document from a URL was formalized as the Yadis specification published by Yadis.org in March 2006. Yadis became the service discovery format for OpenID 1.1. A common discovery service for both URLs and XRIs proved so useful that in November 2007 the XRI Resolution 2.0 specification formally added the URL-based method of XRDS discovery (Section 6). This format and discovery protocol subsequently became part of OpenID Authentication 2.0. XRDS Simple In early 2008, work on OAut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine-readable Data
In communications and computing, a machine-readable medium (or computer-readable medium) is a medium capable of storing data in a format easily readable by a digital computer or a sensor. It contrasts with ''human-readable'' medium and data. The result is called machine-readable data or computer-readable data, and the data itself can be described as having machine-readability. Data Machine-readable data must be structured data. Attempts to create machine-readable data occurred as early as the 1960s. At the same time that seminal developments in machine-reading and natural-language processing were releasing (like Weizenbaum's ELIZA), people were anticipating the success of machine-readable functionality and attempting to create machine-readable documents. One such example was musicologist Nancy B. Reich's creation of a machine-readable catalog of composer William Jay Sydeman's works in 1966. In the United States, the OPEN Government Data Act of 14 January 2019 defines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Web
The social web is a set of social relations that link people through the World Wide Web. The social web encompasses how websites and software are designed and developed in order to support and foster social interaction. These online social interactions form the basis of much online activity including online shopping, education, gaming and social networking services. The social aspect of Web 2.0 communication has been to facilitate interaction between people with similar tastes. These tastes vary depending on who the target audience is, and what they are looking for. For individuals working in the public relation department, the job is consistently changing and the impact is coming from the social web. The influence held by the social network is large and ever changing. As people's activities on the Web and communication increase, information about their social relationships become more available. Social networking services such as Facebook enable people and organizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spam (e-mail)
Email spam, also referred to as junk email, spam mail, or simply spam, refers to unsolicited messages sent in bulk via email. The term originates from a Monty Python sketch, where the name of a canned meat product, "Spam," is used repetitively, mirroring the intrusive nature of unwanted emails. Since the early 1990s, spam has grown significantly, with estimates suggesting that by 2014, it comprised around 90% of all global email traffic. Spam is primarily a financial burden for the recipient, who may be required to manage, filter, or delete these unwanted messages. Since the expense of spam is mostly borne by the recipient, it is effectively a form of "postage due" advertising, where the recipient bears the cost of unsolicited messages. This cost imposed on recipients, without compensation from the sender, makes spam an example of a "negative externality" (a side effect of an activity that affects others who are not involved in the decision). The legal definition and status of sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
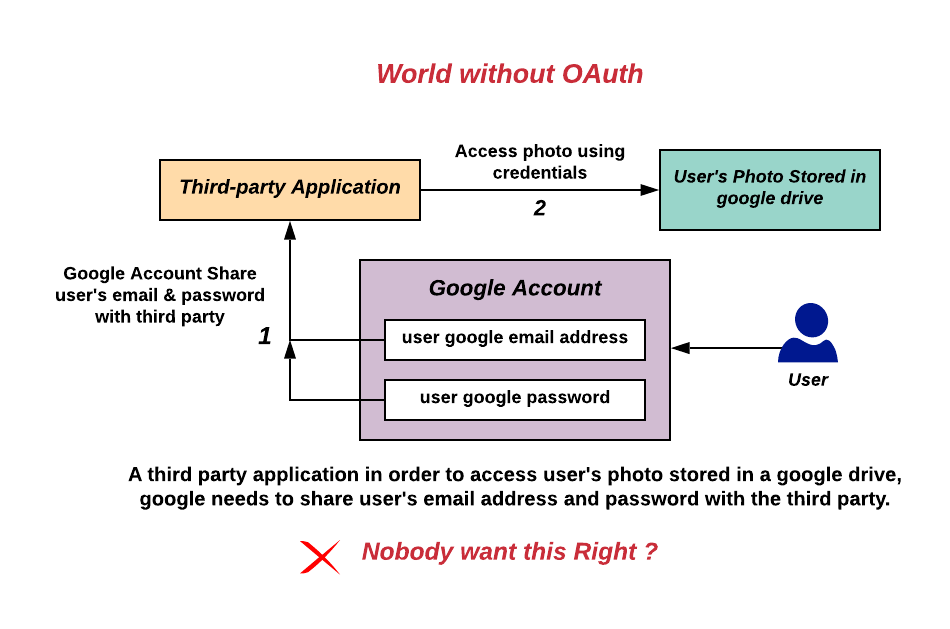
OAuth
OAuth (short for open authorization) is an open standard for access delegation, commonly used as a way for internet users to grant websites or applications access to their information on other websites but without giving them the passwords. This mechanism is used by companies such as Amazon, Google, Meta Platforms, Microsoft, and Twitter to permit users to share information about their accounts with third-party applications or websites. Generally, the OAuth protocol provides a way for resource owners to provide a client application with secure delegated access to server resources. It specifies a process for resource owners to authorize third-party access to their server resources without providing credentials. Designed specifically to work with Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), OAuth essentially allows access tokens to be issued to third-party clients by an authorization server, with the approval of the resource owner. The third party then uses the access token to access th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include hyperlinks to other resources that the user can easily access, for example by a mouse click or by tapping the screen in a web browser. Development of HTTP was initiated by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN in 1989 and summarized in a simple document describing the behavior of a client and a server using the first HTTP version, named 0.9. That version was subsequently developed, eventually becoming the public 1.0. Development of early HTTP Requests for Comments (RFCs) started a few years later in a coordinated effort by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), with work later moving to the IETF. HTTP/1 was finalized and fully documented (as version 1.0) in 1996. It evolved ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means precisely or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all synonyms of one another: they are ''synonymous''. The standard test for synonymy is substitution: one form can be replaced by another in a sentence without changing its meaning. Words may often be synonymous in only one particular sense: for example, ''long'' and ''extended'' in the context ''long time'' or ''extended time'' are synonymous, but ''long'' cannot be used in the phrase ''extended family''. Synonyms with exactly the same meaning share a seme or denotational sememe, whereas those with inexactly similar meanings share a broader denotational or connotational sememe and thus overlap within a semantic field. The former are sometimes called cognitive synonyms and the latter, near-synonyms, plesionyms or poecilonyms. Lexic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Router
A router is a computer and networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks, including internetworks such as the global Internet. Routers perform the "traffic directing" functions on the Internet. A router is connected to two or more data lines from different IP networks. When a data packet comes in on a line, the router reads the network address information in the packet header to determine the ultimate destination. Then, using information in its routing table or routing policy, it directs the packet to the next network on its journey. Data packets are forwarded from one router to another through an internetwork until it reaches its destination node. The most familiar type of IP routers are home and small office routers that forward IP packets between the home computers and the Internet. More sophisticated routers, such as enterprise routers, connect large business or ISP networks to powerful core routers that forward data at high speed along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IP Address
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label such as that is assigned to a device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. IP addresses serve two main functions: network interface identification, and location addressing. Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) was the first standalone specification for the IP address, and has been in use since 1983. IPv4 addresses are defined as a 32-bit number, which became too small to provide enough addresses as the internet grew, leading to IPv4 address exhaustion over the 2010s. Its designated successor, IPv6, uses 128 bits for the IP address, giving it a larger address space. Although IPv6 deployment has been ongoing since the mid-2000s, both IPv4 and IPv6 are still used side-by-side . IP addresses are usually displayed in a human-readable notation, but systems may use them in various different computer number formats. CIDR notation can also be used to designate how much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |