|
Hôtel De Ville, Aix-en-Provence
The (, ''City Hall'') is a historic building in Aix-en-Provence, Bouches-du-Rhône, southern France, standing on Place d'Hôtel de Ville. It was designated a ''monument historique'' by the French government in 1995. History The first town hall in Aix-en-Provence was an ancient structure in the Place de l'Annonerie-Vieille. The city council relocated to the current site on the west side of the town square in 1326. During the Italian War of 1536–1538, the Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V invaded Provence and took Aix-en-Province in August 1536. After the French Army blocked his route, he retreated to Italy and his ally, Charles III, Duke of Savoy ordered the destruction of the town hall as well as the entire municipal archives. After the flames took hold, only a few minute books survived the fire. A clock tower surmounted by a metal frame supporting a bell was installed at the northeast corner of the town hall in 1510, and an astronomical clock was installed in the tower in 166 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture, sometimes referred to as Classical Revival architecture, is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassicism, Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy, France and Germany. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of Roman architecture, ancient Rome and ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer, more complete, and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediment
Pediments are a form of gable in classical architecture, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the cornice (an elaborated lintel), or entablature if supported by columns.Summerson, 130 In ancient architecture, a wide and low triangular pediment (the side angles 12.5° to 16°) typically formed the top element of the portico of a Greek temple, a style continued in Roman temples. But large pediments were rare on other types of building before Renaissance architecture. For symmetric designs, it provides a center point and is often used to add grandness to entrances. The cornice continues round the top of the pediment, as well as below it; the rising sides are often called the "raking cornice". The tympanum is the triangular area within the pediment, which is often decorated with a pedimental sculpture which may be freestanding or a relief sculpture. The tympanum may hold an inscription, or in modern times, a clock face. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marianne
Marianne () has been the national personification of the French Republic since the French Revolution, as a personification of liberty, equality, fraternity and reason, as well as a portrayal of the Goddess of Liberty. Marianne is displayed in many places in France and holds a place of honour in town halls and law courts. She is depicted in the ''Triumph of the Republic'', a bronze sculpture overlooking the Place de la Nation in Paris, as well as represented with another Parisian statue on the Place de la République. Her profile stands out on the official government logo of the country, and appears on French euro coins and on French postage stamps. She was also featured on the former franc currency and is officially used on most government documents. Marianne is a significant republican symbol; her French monarchist equivalent is often Joan of Arc. As a national icon Marianne represents opposition to monarchy and the championship of freedom and democracy against all fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis René Vialy
Louis-René Vialy (1680 - 17 February 1770), also spelled ''Vially'', ''Viali'' or ''Viallis'', was a French painter. Life The son of Jacques Vialy, a Sicilian painter born at Trapani but who moved to Provence, Louis-René Vialy was born at Aix-en-Provence. He began his career decorating sedan chairs, as attested by Mariette, who wrote that "it was a very popular taste in Provence to have ornamented sedan chairs". His father was naturalised as a French subject by letters registered at the cour des comptes of Aix-en-Provence in 1720 and died in Aix on 25 December 1745 aged 95. He was buried the following day in the old parish church of La Madeleine, beside Jean-Baptiste van Loo who had died on 29 September the same year. Louis-René at first studied under his father and very often attended the Vernets' studio - Antoine Vernet, decorative painter, was a family friend of Louis's father. Louis-René is normally named as the tutor of the young marine painter Joseph Vernet but this w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph André Cellony
Joseph André Cellony (1686, in Aix-en-Provence – 7 February 1746, in Aix-en-Provence) was a French painter. Life He was the only son of another painter renowned in Aix-en-Provence, Joseph Cellony (1663, Aix-en-Provence - 18 January 1731, Aix-en-Provence), who had been born to Pierre and Delphine Tassy. In 1692 Joseph senior was called "the most distinguished portraitist there is in this town. The resemblance that so great that one could not mistake the correction of his drawing and the bold touch of his brush in the manner of Fauchier, thus granting him his celebrity." After gaining the rudiments of painting in his father's studio, Joseph André was very soon sent to the studio of Hyacinthe Rigaud in Paris to perfect himself "in the art that his father strove at, who he excelled". "His touch was very soft and the fabrics and especially silks he painted imitated nature better by the transparency and glaze he used there."Roux Alphéran, op. cit. In 1716, the town undertook t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XI
Louis XI (3 July 1423 – 30 August 1483), called "Louis the Prudent" (), was King of France from 1461 to 1483. He succeeded his father, Charles VII. Louis entered into open rebellion against his father in a short-lived revolt known as the Praguerie in 1440. The king forgave his rebellious vassals, including Louis, to whom he entrusted the management of the Dauphiné, then a province in southeastern France. Louis's ceaseless intrigues, however, led his father to banish him from court. From the Dauphiné, Louis led his own political establishment and married Charlotte of Savoy, daughter of Louis, Duke of Savoy, against the will of his father. Charles VII sent an army to compel his son to his will, but Louis fled to Burgundy, where he was hosted by Philip the Good, the Duke of Burgundy, Charles's greatest enemy. When Charles VII died in 1461, Louis left the Burgundian court to take possession of his kingdom. His taste for intrigue and his intense diplomatic activity earned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles IV Of Anjou
Charles IV, Duke of Anjou, also Charles of Maine, Count of Le Maine and Guise (1446 – 10 December 1481), was the son of the House of Valois-Anjou, Angevin prince Charles IV, Count of Maine, Charles of Maine, Count of Maine and Isabelle of Luxembourg-Saint-Pol. He succeeded his father as Count of Maine, Guise, Mortain and Gien in 1472. He succeeded his uncle René I of Naples in 1480 as fourth Duke of Anjou and Count of Provence, according to the will of René, who had no surviving son. René's surviving daughter Yolande received County of Bar, Bar and was already Duchess of Lorraine. He also used the title of Duke of Calabria, in token of the claims to Naples he inherited from René. In 1474 he married Joan of Lorraine (1458 – 25 January 1480), daughter of Frederick II of Vaudémont, but they had no children. He died on 10 December 1481. He willed his inheritance to his cousin Louis XI of France, whose heirs thus obtained a claim to the affairs of Italy, pursued in the next ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative Moulding (decorative), moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, around the top edge of a pedestal, or along the top of an interior wall. A simple cornice may be formed with a crown, as in crown moulding atop an interior wall or above kitchen cabinets or a bookcase. A projecting cornice on a building has the function of throwing rainwater free of its walls. In residential building practice, this function is handled by projecting gable ends, roof eaves, and rain gutter, gutters. However, house eaves may also be called "cornices" if they are finished with decorative moulding. In this sense, while most cornices are also eaves (overhanging the sides of the building), not all eaves are usually considered cornices. Eaves are primarily functional and not necessarily decorative, while cornices have a decorative a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modillion
A modillion is an ornate bracket, more horizontal in shape and less imposing than a corbel. They are often seen underneath a Cornice (architecture), cornice which helps to support them. Modillions are more elaborate than dentils (literally translated as small teeth). All three are selectively used as adjectival historic past participles (''corbelled, modillioned, dentillated'') as to what co-supports or simply adorns any high structure of a building, such as a terrace of a roof (a flat area of a roof), parapet, pediment/entablature, balcony, cornice band or roof cornice. Modillions occur classically under a Corinthian order, Corinthian or a Composite order, Composite cornice but may support any type of eaves cornice. They may be carved or plain. See also * Glossary of architecture Gallery Abbaye Ste Foy à Conques (25) - Frises et corbeaux du chevet.jpg, Modillions carved with animal heads in the Abbaye Ste Foy in Conques (France). 20130809 dublin036.JPG, Trinity College, in Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nîmes
Nîmes ( , ; ; Latin: ''Nemausus'') is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Gard Departments of France, department in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region of Southern France. Located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Cévennes, the Communes of France, commune of Nîmes had an estimated population of 148,561 in 2019. Dubbed the most Roman city outside Italy, Nîmes has a rich history dating back to the Roman Empire when the city had a population of 50,000–60,000 and was the regional capital. Several famous monuments are in Nîmes, such as the Arena of Nîmes and the Maison Carrée. Because of this, Nîmes is often referred to as the "French Rome". Origins Nimes is situated where the alluvial plain of the Vistrenque River abuts the hills of Mont Duplan to the northeast, Montaury to the southwest, and to the west Mt. Cavalier and the knoll of Canteduc. Its name appears in inscriptions in Gaulish as ''dede matrebo Namausikabo'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maison Carrée
Maison (French for "house") may refer to: People * Edna Maison (1892–1946), American silent-film actress * Jérémy Maison (born 1993), French cyclist * Leonard Maison, New York state senator 1834–1837 * Nicolas Joseph Maison (1771–1840), Marshal of France and Minister of War * René Maison (1895–1962), Belgian operatic tenor * Rudolf Maison (1854–1904), German sculptor Places in France * Maison-des-Champs, a commune in the Aube department, Grand Est * Maison-Feyne, a commune in the Creuse department, Nouvelle-Aquitaine * Maison-Maugis Maison-Maugis () is a former commune in the Orne department in north-western France. On 1 January 2016, it was merged into the new commune of Cour-Maugis sur Huisne. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
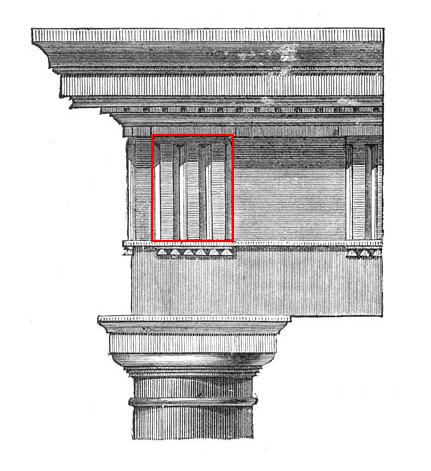
Triglyph
Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are called metopes. The raised spaces between the channels themselves (within a triglyph) are called ''femur'' in Latin or ''meros'' in Greek. In the strict tradition of classical architecture, a set of guttae, the six triangular "pegs" below, always go with a triglyph above (and vice versa), and the pair of features are only found in entablatures of buildings using the Doric order. The absence of the pair effectively converts a building from being in the Doric order to being in the Tuscan order. The triglyph is largely thought to be a tectonic and skeuomorphic representation in stone of the wooden beam ends of the typical primitive hut, as described by Vitruvius and Renaissance writers. The wooden beams were notched in three separate p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |