|
High Frame Rate
In motion picture technology—either film or video—high frame rate (HFR) refers to higher frame rates than typical prior practice. The frame rate for motion picture film cameras was typically 24 frames per second (fps) with multiple flashes on each frame during projection to prevent flicker. Analog television and video employed interlacing where only half of the image (known as a video field) was recorded and played back/refreshed at once but at twice the rate of what would be allowed for progressive video of the same bandwidth, resulting in smoother playback, as opposed to progressive video which is more similar to how celluloid works. The field rate of analog television and video systems was typically 50 or 60 fields per second. Usage of frame rates higher than 24 fps for feature motion pictures and higher than 30 fps for other applications are emerging trends. Filmmakers may capture their projects in a high frame rate so that it can be evenly converted to multipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film
A film, also known as a movie or motion picture, is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, emotions, or atmosphere through the use of moving images that are generally, since the 1930s, synchronized with sound and (less commonly) other sensory stimulations. Etymology and alternative terms The name "film" originally referred to the thin layer of photochemical emulsion on the celluloid strip that used to be the actual medium for recording and displaying motion pictures. Many other terms exist for an individual motion-picture, including "picture", "picture show", "moving picture", "photoplay", and "flick". The most common term in the United States is "movie", while in Europe, "film" is preferred. Archaic terms include "animated pictures" and "animated photography". "Flick" is, in general a slang term, first recorded in 1926. It originates in the verb flicker, owing to the flickering appearance of early films ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Momentum (IMAX Film)
''Momentum'' was the first film shot and released in the IMAX#IMAX HD, IMAX HD film format, which ran at High Frame Rate, 48 frames per second, and was also one of the first films to use Ambisonic surround sound. The film was produced for the Canada pavilion at Seville Expo '92 by National Film Board of Canada, by the same creative team that made the 1986 3-D film, 3D IMAX film ''Transitions (film), Transitions'' for Expo 86. The film takes viewers across Canada, demonstrating the ability of the 48 frame/s process to portray motion on the giant IMAX screen with reduced strobing. References External links * * 1992 short documentary films Films without speech National Film Board of Canada documentaries IMAX short films IMAX documentary films Films directed by Colin Low (filmmaker) Films directed by Tony Ianzelo World's fair films 1992 films Seville Expo '92 Canadian short documentary films Films scored by Eldon Rathburn National Film Board of Canada short films 1990s Cana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wide Release
In the motion picture industry, a wide release (short for nationwide release) is a film playing at the same time at cinemas in most markets across a country. This is in contrast to the formerly common practice of a roadshow theatrical release in which a film opens at a few cinemas in key cities before circulating among cinemas around a country, or a limited release in which a film is booked at fewer cinemas (such as " art house" venues) in larger cities in anticipation of lesser commercial appeal. In some cases, a film that sells well in limited release will then "go wide". Since 1994, a wide release in the United States and Canada has been defined by Nielsen EDI as a film released in more than 600 theaters. The practice emerged as a successful marketing strategy in the 1970s, and became increasingly common in subsequent decades, in parallel with the expansion of the number of screens available at multiplex cinemas. With the switch to digital formats – lowering the added cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
An Unexpected Journey
An Unexpected Journey may refer to: * ''An Unexpected Journey'' (album), a 2013 album by Joker Xue *'' The Hobbit: An Unexpected Journey'', a 2012 film, part one of the film adaptation of ''The Hobbit'' {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hobbit (film Series)
''The Hobbit'' is a trilogy of fantasy adventure films directed by Peter Jackson. The films are subtitled ''The Hobbit: An Unexpected Journey , An Unexpected Journey'' (2012), ''The Hobbit: The Desolation of Smaug , The Desolation of Smaug'' (2013), and ''The Hobbit: The Battle of the Five Armies , The Battle of the Five Armies'' (2014). The films are based on J. R. R. Tolkien's 1937 novel ''The Hobbit'', but much of the trilogy was inspired by the appendices to his 1954–55 ''The Lord of the Rings'', which expand on the story told in ''The Hobbit''. Additional material and new characters were created specially for the films. The series is a prequel to Jackson's The Lord of the Rings (film series), ''The Lord of the Rings'' film trilogy. The screenplays were written by Fran Walsh, Philippa Boyens, Jackson, and Guillermo del Toro, who had been chosen to direct before his departure from the project. The films take place in the fictional world of Middle-earth, sixty years before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Jackson
Sir Peter Robert Jackson (born 31 October 1961) is a New Zealand filmmaker. He is best known as the director, writer, and producer of the ''Lord of the Rings'' trilogy (2001–2003) and the ''Hobbit'' trilogy (2012–2014), both of which are adapted from the novels of the same name by J. R. R. Tolkien. Other notable films include the critically lauded drama '' Heavenly Creatures'' (1994), the horror comedy '' The Frighteners'' (1996), the epic monster remake film '' King Kong'' (2005), the World War I documentary film '' They Shall Not Grow Old'' (2018) and the documentary '' The Beatles: Get Back'' (2021). He is the fifth-highest-grossing film director of all-time, with his films having made over $6.5 billion worldwide. Jackson began his career with the " splatstick" horror comedy '' Bad Taste'' (1987) and the black comedy '' Meet the Feebles'' (1989) before filming the zombie comedy '' Braindead'' (1992). He shared a nomination for Academy Award for Best Original Screenpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oversampling
In signal processing, oversampling is the process of sampling (signal processing), sampling a signal at a sampling frequency significantly higher than the Nyquist rate. Theoretically, a bandwidth-limited signal can be perfectly reconstructed if sampled at the Nyquist rate or above it. The Nyquist rate is defined as twice the Bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth of the signal. Oversampling is capable of improving Resolution (audio), resolution and signal-to-noise ratio, and can be helpful in avoiding aliasing and phase distortion by relaxing anti-aliasing filter performance requirements. A signal is said to be oversampled by a factor of ''N'' if it is sampled at ''N'' times the Nyquist rate. Motivation There are three main reasons for performing oversampling: to improve anti-aliasing performance, to increase resolution and to reduce noise. Anti-aliasing Oversampling can make it easier to realize analog anti-aliasing filters. Without oversampling, it is very difficult to impl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
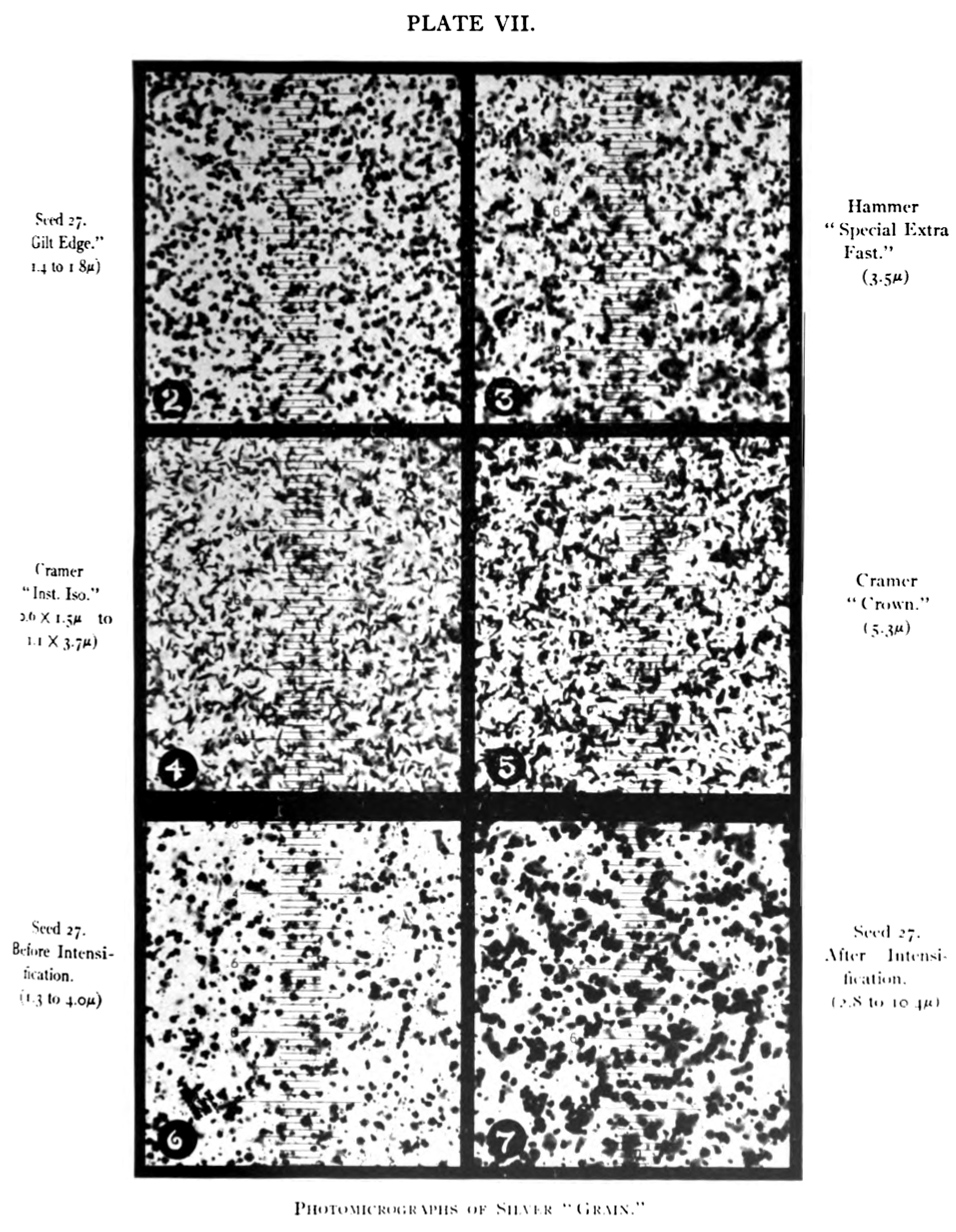
Film Grain
Film grain or film granularity is the random optical texture of processed photographic film. Film grain develops due to the presence of small particles of a metallic silver, or dye clouds, developed from silver halide that have received enough photons. While film grain is a function of such particles (or dye clouds) it is not a particle but an optical effect. The magnitude of the effect (also known as amount of grain) depends on both the film stock and the definition at which it is observed. It can be objectionably noticeable in an over-enlarged film photograph. Chemical background The size and morphology of the silver halide grains play crucial role in the image characteristics and exposure behavior. There is a tradeoff between the crystal size and light sensitivity (film speed); larger crystals have better chance to receive enough energy to flip them into developable state, as they have higher probability of receiving several photons needed for forming the Ag4 clusters that st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Speed
Film speed is the measure of a photographic film's sensitivity to light, determined by sensitometry and measured on various numerical scales, the most recent being the ISO system introduced in 1974. A closely related system, also known as ISO, is used to describe the relationship between exposure and output image lightness in digital cameras. Prior to ISO, the most common systems were ASA in the United States and DIN in Europe. The term ''speed'' comes from the early days of photography. Photographic emulsions that were more sensitive to light needed less time to generate an acceptable image and thus a complete exposure could be finished faster, with the subjects having to hold still for a shorter length of time. Emulsions that were less sensitive were deemed "slower" as the time to complete an exposure was much longer and often usable only for still life photography. Exposure times for photographic emulsions shortened from hours to fractions of a second by the late 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Cinema Initiatives
Digital Cinema Initiatives, LLC (DCI) is a consortium of major motion picture studios, formed to establish specifications for a common systems architecture for digital cinema systems. The organization was formed in March 2002 by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer, Paramount Pictures, Sony Pictures, 20th Century Studios, Universal Studios, Walt Disney Studios and Warner Bros. The primary purpose of DCI is to establish and document specifications for an open architecture for digital cinema that ensures a uniform and high level of technical performance, reliability and quality. By establishing a common set of content requirements, distributors, studios, exhibitors, d-cinema manufacturers and vendors can be assured of interoperability and compatibility. Because of the relationship of DCI to many of Hollywood's key studios, conformance to DCI's specifications is considered a requirement by software developers or equipment manufacturers targeting the digital cinema market. Specification O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
35 Mm Movie Film
35 mm film is a film gauge used in filmmaking, and the film standard. In motion pictures that record on film, 35 mm is the most commonly used gauge. The name of the gauge is not a direct measurement, and refers to the nominal width of the 35 mm format photographic film, which consists of strips wide. The standard negative pulldown, image exposure length on 35 mm for movies ("single-frame" format) is four film perforations, perforations per Film frame, frame along both edges, which results in 16 frames per foot of film. A variety of largely proprietary gauges were devised for the numerous camera and projection systems being developed independently in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, along with various film feeding systems. This resulted in cameras, projectors, and other equipment having to be calibrated to each gauge. The 35 mm width, originally specified as inches, was introduced around 1890 by William Kennedy Dickson and Thomas Edison, using 120 film st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxivision
Maxivision 24 and Maxivision 48 are 35 mm film motion picture film formats. The system was designed by Dean Goodhill in 1999. The system uses normal thirty-five millimetre motion picture film, capturing images on three perforations of film per frame. The format can run either at the standard twenty-four frames per second, or at forty-eight frames per second, which reduces strobing effects and increases apparent resolution when combined with a system for reducing film movement in the gate and eliminating scratching. Because Maxivision uses only three film perforations per frame, the twenty-four-frame-per-second format uses 25% less film than standard four-perforation formats, and the 48 frame-per-second format only requires a 50% increase in the amount of film to yield twice the frame rate. The image is exposed into the region ordinarily reserved for the analog optical sound track which is rarely used now. This allows for a wider image on the same size film. This also redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |