|
Maxivision
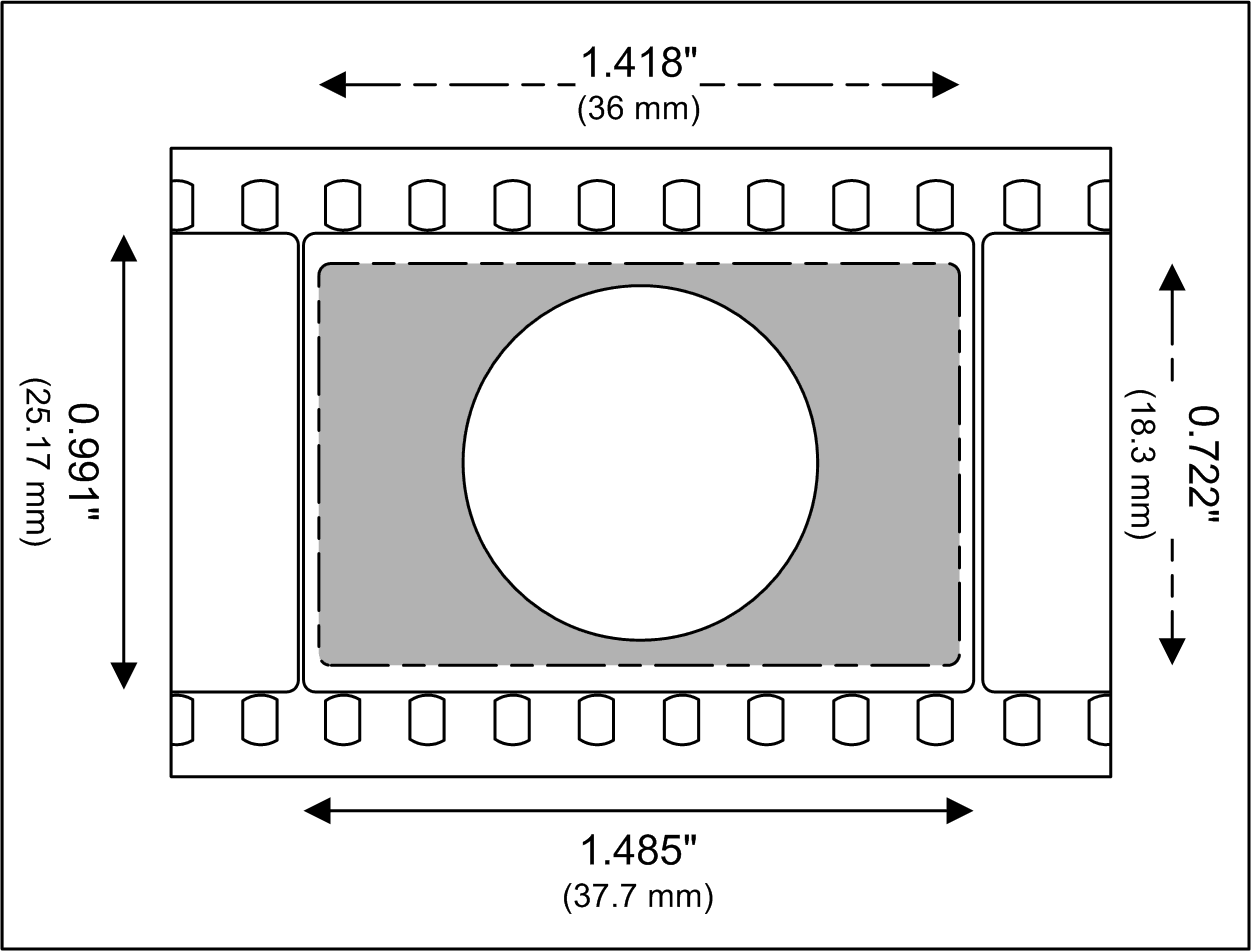
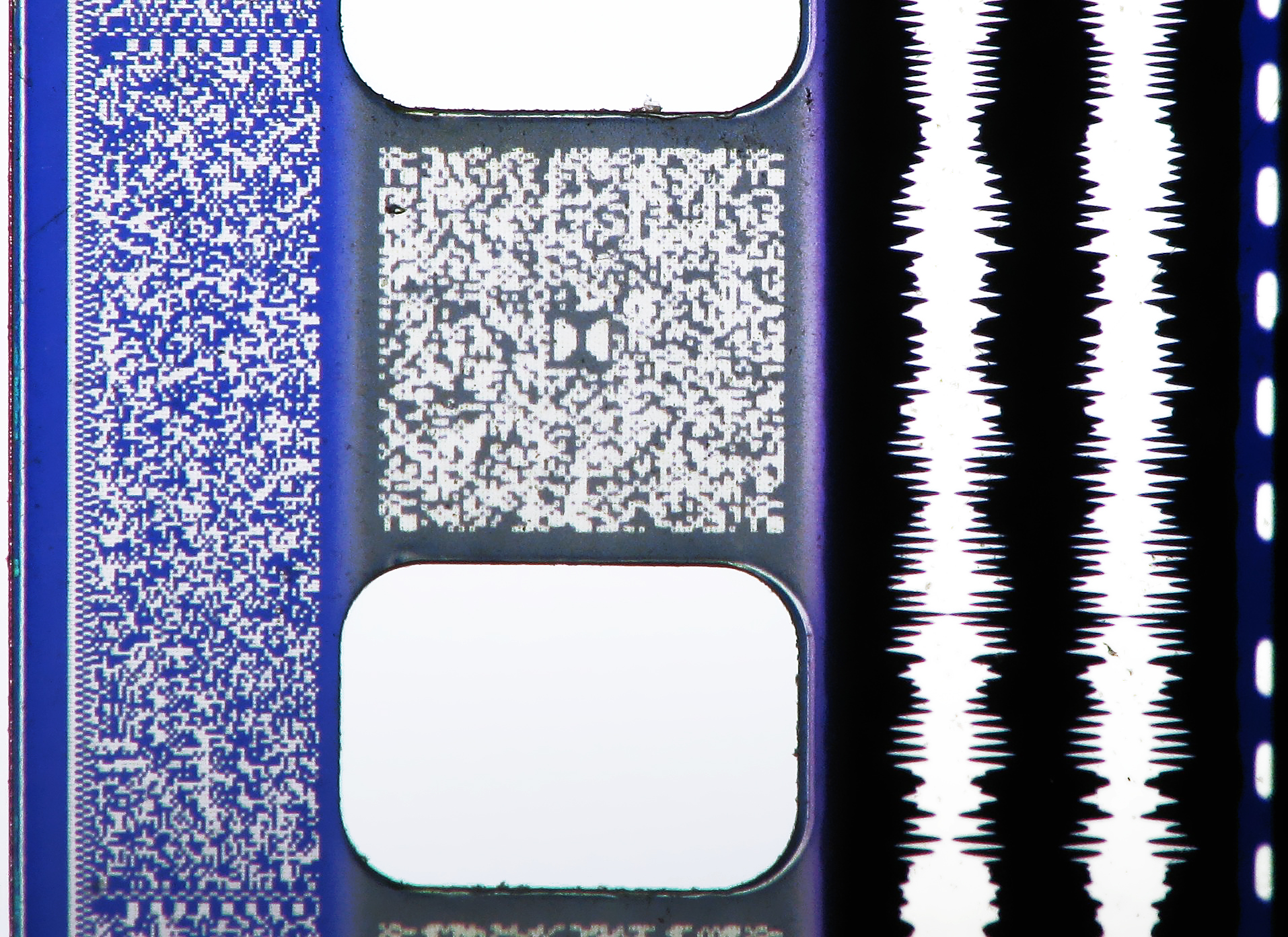
Maxivision 24 and Maxivision 48 are 35 mm film motion picture film formats. The system was designed by Dean Goodhill in 1999. The system uses normal thirty-five millimetre motion picture film, capturing images on three perforations of film per frame. The format can run either at the standard twenty-four frames per second, or at forty-eight frames per second, which reduces strobing effects and increases apparent resolution when combined with a system for reducing film movement in the gate and eliminating scratching. Because Maxivision uses only three film perforations per frame, the twenty-four-frame-per-second format uses 25% less film than standard four-perforation formats, and the 48 frame-per-second format only requires a 50% increase in the amount of film to yield twice the frame rate. The image is exposed into the region ordinarily reserved for the analog optical sound track which is rarely used now. This allows for a wider image on the same size film. This also redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Ebert
Roger Joseph Ebert ( ; June 18, 1942 – April 4, 2013) was an American Film criticism, film critic, film historian, journalist, essayist, screenwriter and author. He wrote for the ''Chicago Sun-Times'' from 1967 until his death in 2013. Ebert was known for his intimate, Midwestern writing style and critical views informed by values of populism and humanism. Writing in a prose style intended to be entertaining and direct, he made sophisticated cinematic and analytical ideas more accessible to non-specialist audiences. Ebert endorsed foreign and independent films he believed would be appreciated by mainstream viewers, championing filmmakers like Werner Herzog, Errol Morris and Spike Lee, as well as Martin Scorsese, whose first published review he wrote. In 1975, Ebert became the first film critic to win the Pulitzer Prize for Criticism. Neil Steinberg of the ''Chicago Sun-Times'' said Ebert "was without question the nation's most prominent and influential film critic," and Kenne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
35mm Movie Film
35 mm film is a film gauge used in filmmaking, and the film standard. In motion pictures that record on film, 35 mm is the most commonly used gauge. The name of the gauge is not a direct measurement, and refers to the nominal width of the 35 mm format photographic film, which consists of strips wide. The standard negative pulldown, image exposure length on 35 mm for movies ("single-frame" format) is four film perforations, perforations per Film frame, frame along both edges, which results in 16 frames per foot of film. A variety of largely proprietary gauges were devised for the numerous camera and projection systems being developed independently in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, along with various film feeding systems. This resulted in cameras, projectors, and other equipment having to be calibrated to each gauge. The 35 mm width, originally specified as inches, was introduced around 1890 by William Kennedy Dickson and Thomas Edison, using 120 film st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerkiness
Jerkiness (sometimes called strobing or choppy footage) describes the perception of individual still images while watching a motion picture. Description Motion pictures are made from still images shown in rapid sequence. Provided there is sufficient continuity between the images and provided the sequence is shown fast enough, the central nervous system interprets the sequence as continuous motion. However, some technologies cannot process or carry data fast enough for sufficiently high frame rates. For example, viewing motion pictures by Internet connection generally necessitates a greatly reduced frame rate, making jerkiness clearly apparent. In conventional cinematography, the images are filmed and displayed at 24 frames per second, at which speed jerkiness is not normally discernible. Television screens refresh at even higher frequencies. PAL and SÉCAM television (the standards in Europe) refresh at 25 or 50 (HDTV) frames per second. NTSC television displays (the standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Perforations
Film perforations, also known as perfs and sprocket holes, are the holes placed in the film stock during manufacturing and used for transporting (by sprockets and claws) and steadying (by pin registration) the film. Films may have different types of perforations depending on film gauge, film format, and intended usage. Perforations are also used as a standard measuring reference within certain camera systems to refer to the size of the frame. Some formats are referred to in terms of the ratio "perforations per frame/gauge size" to provide an easy way of denoting size. For instance, 35mm Academy is also known as 4 perf-35mm; VistaVision is 8 perf-35mm; the long-time standard Todd-AO 70 mm film is 5 perf-70mm; and IMAX is 15 perf-70mm. This description does not indicate whether the film transport is horizontal or vertical, but uncertainty is precluded because there are currently no horizontal systems using the same number of perforations on the same gauge as a vertical on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4 Perf
Negative pulldown is the manner in which an image is exposed on a film stock, described by the number of film perforations spanned by an individual frame. It can also describe whether the image captured on the negative is oriented horizontally or vertically. Changing the number of exposed perforations allows a cinematographer to change both the aspect ratio of the image and the size of the area on the film stock that the image occupies (which affects image clarity). The most common negative pulldowns for 35 mm film are 4-perf and 3-perf, the latter of which is usually used in conjunction with Super 35. 2-perf, used in Techniscope in the 1960s, is enjoying a slight resurgence due to the birth of digital intermediate techniques eliminating the need for optical lab work. Vertical pulldown is overwhelmingly the dominant axis of motion in cinematography, although horizontal pulldown is used in IMAX, VistaVision, and in 35 mm consumer and professional still cameras. Us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound-on-film
Sound-on-film is a class of sound film processes where the sound accompanying a picture is recorded on photographic film, usually, but not always, the same strip of film carrying the picture. Sound-on-film processes can either record an Analog signal, analog sound track or Digital data, digital sound track, and may record the signal either optical sound, optically or magnetism, magnetically. Earlier technologies were sound-on-disc, meaning the film's soundtrack would be on a separate phonograph record. History Sound on film can be dated back to the early 1880s, when Charles E. Fritts filed a patent claiming the idea. In 1923 a patent was filed by E. E. Ries, for a variable density soundtrack recording, which was submitted to the SMPE (now Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers, SMPTE), which used the mercury vapor lamp as a modulating device to create a variable-density soundtrack. Later, Theodore Case, Case Laboratories and Lee De Forest#Phonofilm sound-on-film pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. Overview In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by Doping (semiconductor), p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anamorphic
Anamorphic format is a cinematography technique that captures widescreen images using recording media with narrower native Aspect ratio (image), aspect ratios. Originally developed for 35 mm movie film, 35 mm film to create widescreen presentations without sacrificing image area, the technique has since been adapted to various film gauges, digital cinematography, digital sensors, and video formats. Rather than cropping or Matte (filmmaking)#Mattes and widescreen filming, matting the image and discarding visual information, anamorphic capture employs cylindrical lenses to horizontally compress or "squeeze" the image during recording. A complementary lens is then used during projection to expand the image back to its intended widescreen proportions. By utilizing the full height of the film frame or sensor, this method retains more image resolution than cropped non-anamorphic widescreen formats. Anamorphic lenses have more complex optics than standard spherical lenses, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Univisium
Univisium (Dog Latin, macaronic Latin for "unity of images") is a proposed universal film format created by cinematographer Vittorio Storaro, American Society of Cinematographers, ASC, AIC and his son, Fabrizio, to unify all future theatrical and television films into one respective aspect ratio (image), aspect ratio of 2:1. Predecessors The 2:1 aspect ratio was first used in the 1950s (April 1, 1953) for one of the two flat formats that Universal Pictures developed (alongside 1.85:1), the RKO Superscope format, and as an option in several other cinematographic formats. Another predecessor is Toho's Toho Pan Scope, used in the 1958 kaiju film ''Varan the Unbelievable'' and the 1957 Japanese re-release of ''Godzilla, King of the Monsters!'' (which in turn was the American localization of 1954's Godzilla (1954 film), ''Godzilla''), using an anamorphic process similar to Superscope with film shot in flat monochrome being cropped to 2:1 during editing. The main proposal In 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Showscan
Showscan is a cinematic process developed by Douglas Trumbull that uses 70mm film photographed and projected at 60 frames per second, 2.5 times the standard speed of movie film. History Trumbull first came to the public's attention for his work on the groundbreaking special effects in movies such as '' 2001: A Space Odyssey'' and ''The Andromeda Strain''. He also directed 1972's ''Silent Running''. Trumbull developed the Showscan film process in the late 1970s and early 1980s when he became interested in increasing the fidelity or definition of movies. Similar to the quality issues addressed later by high-definition television, the visual fidelity of movies was limited by the medium. When projected onto a large screen, the grain of 35 mm film stock is often quite visible, reducing the quality of the displayed image. The problem is further exacerbated by the larger grain in fast film stock often used to capture high-speed action. Trumbull chose 70 mm film for his new pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audiovisual Introductions In 1999
Audiovisual (AV) is electronic media possessing both a sound and a visual component, such as slide-tape presentations, films, television programs, corporate conferencing, church services, and live theater productions. Audiovisual service providers frequently offer web streaming, video conferencing, and live broadcast services. The professional audio visual industry has companies that provide hardware, software and services. These organizations are commonly referred to as ''systems integrators'' and perform both the installation and integration of different types of AV equipment from multiple manufacturers into spaces to create the AV experience for the user or audience. Computer-based audiovisual equipment is often used in education, with many schools and universities installing projection equipment and using interactive whiteboard technology. Components Aside from equipment installation, two significant elements of audiovisual are wiring and system control. If either of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |