|
Hexanitrostilbene
Hexanitrostilbene (HNS), also called JD-X, is an organic compound with the formula O2N)3C6H2CHsub>2. It is a yellow-orange solid.Jacques Boileau, Claude Fauquignon, Bernard Hueber and Hans H. Meyer "Explosives" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2009, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. It is used as a heat-resistant high explosive. It is slightly soluble (0.1 - 5 g/100 mL) in butyrolactone, DMF, DMSO, and ''N''-methylpyrrolidone. Production and use It is produced by oxidizing trinitrotoluene (TNT) with a solution of sodium hypochlorite. HNS boasts a higher insensitivity to heat than TNT, and like TNT it is insensitive to impact. When casting TNT, HNS is added at 0.5% to form erratic micro-crystals within the TNT, which prevent cracking. Because of its insensitivity but high explosive properties, HNS is used in space missions. It was the main explosive fill in the seismic source generating mortar ammunition canisters used as part of the Apollo Lunar Active Seismic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of UN Numbers 0301 To 0400
UN numbers from UN0301 to UN0400 as assigned by the United Nations Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods are as follows: __NOTOC__ UN 0301 to UN 0400 See also * Explosives shipping classification system The Explosive Shipping Classification System exists as part of the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Good: Model Regulations. The system describes the classification of explosives, divisions within that class that descri ... External links ADR Dangerous Goods cited on 3 July 2015.UN Dangerous Goods List from 2015 cited on 3 July 2015.UN Dangerous Goods List from 2013 cited on 3 July 2015. {{UN number list navbox Lists of UN numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathryn Grove Shipp
Kathryn Grove Shipp (1904 – October 14, 1977) was an American organic chemist, a specialist in explosives, affiliated with the Naval Ordnance Laboratory from 1957 to 1970. In 1967, she was one of the six recipients of the Federal Woman's Award. Early life Kathryn Elmira Grove was born in Annandale, Pennsylvania. She and her sister Ruth were raised in the household of an uncle and aunt, William Smith Conner and Carolyn W. Conner, in Madera, California, after their parents died. She graduated from Madera High School in 1921 and from Mills College in 1925, where she studied under Aurelia Henry Reinhardt. She completed her doctorate in organic chemistry at Yale University in 1930, with a postdoctoral year of further studies at Oxford on a National Research Council fellowship. While at Yale, she was the first woman graduate student to hold the Dupont Fellowship in Chemistry. Career Shipp was an assistant instructor in chemistry at Vassar College in 1925. She left paid employme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibroseis
A seismic source is a device that generates controlled seismic energy used to perform both reflection and refraction seismic surveys. A seismic source can be simple, such as dynamite, or it can use more sophisticated technology, such as a specialized air gun. Seismic sources can provide single pulses or continuous sweeps of energy, generating seismic waves, which travel through a medium such as water or layers of rocks. Some of the waves then reflect and refract and are recorded by receivers, such as geophones or hydrophones. Seismic sources may be used to investigate shallow subsoil structure, for engineering site characterization, or to study deeper structures, either in the search for petroleum and mineral deposits, or to map subsurface faults or for other scientific investigations. The returning signals from the sources are detected by seismic sensors (geophones or hydrophones) in known locations relative to the position of the source. The recorded signals are then subjecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive Chemicals
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances. The potential energy stored in an explosive material may, for example, be: * chemical energy, such as nitroglycerin or Dust explosion, grain dust * pressure, pressurized gas compressor, gas, such as a gas cylinder, aerosol can, or boiling liquid expanding vapor explosion * nuclear weapon, nuclear energy, such as in the fissile isotopes uranium-235 and plutonium-239 Explosive materials may be categorized by the speed at which they expand. Materials that detonate (the front of the chemical reaction moves faster through the material than the speed of sound) are said to be "high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RE Factor
TNT equivalent is a convention for expressing energy, typically used to describe the energy released in an explosion. A ton of TNT equivalent is a unit of energy defined by convention to be (). It is the approximate energy released in the detonation of a metric ton (1,000 kilograms) of trinitrotoluene (TNT). In other words, for each gram of TNT exploded, (or 4184 joules) of energy are released. This convention intends to compare the destructiveness of an event with that of conventional explosive materials, of which TNT is a typical example, although other conventional explosives such as dynamite contain more energy. A related concept is the physical quantity TNT-equivalent mass (or mass of TNT equivalent), expressed in the ordinary units of mass and its multiples: kilogram (kg), megagram (Mg) or tonne (t), etc. Kiloton and megaton The "kiloton (of TNT equivalent)" is a unit of energy equal to 4.184 terajoules (). A kiloton of TNT can be visualized as a cube of TNT on a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNT Equivalent
TNT equivalent is a convention for expressing energy, typically used to describe the energy released in an explosion. A ton of TNT equivalent is a unit of energy defined by convention to be (). It is the approximate energy released in the detonation of a metric ton (1,000 kilograms) of trinitrotoluene (TNT). In other words, for each gram of TNT exploded, (or 4184 joules) of energy are released. This convention intends to compare the destructiveness of an event with that of conventional explosive materials, of which TNT is a typical example, although other conventional explosives such as dynamite contain more energy. A related concept is the physical quantity TNT-equivalent mass (or mass of TNT equivalent), expressed in the ordinary units of mass Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Ordnance Laboratory
The Naval Ordnance Laboratory (NOL) was a facility in the White Oak, Maryland, White Oak area of Montgomery County, Maryland. The location is now used as the headquarters of the Food and Drug Administration, U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Origins The U.S. Navy Mine Unit, later the Mine Laboratory at the Washington, D.C., Navy Yard, was established in 1918, and the first Officer in Charge (OIC) arrived in February 1919, marking the beginning of the Laboratory. In 1929 the Mine Laboratory was merged with the Experimental Ammunition Station in Indian Head, Maryland, Indian Head to form the Naval Ordnance Laboratory. NOL began slowly, and it was not until the beginnings of World War II, when Germany's aircraft-laid magnetic mine began to cause serious problems for the Allies of World War II, Allies. As the importance of NOL's work became apparent, it also became apparent that there wasn't enough space at the Navy Yard to accommodate the necessary research facilities. In 1944, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
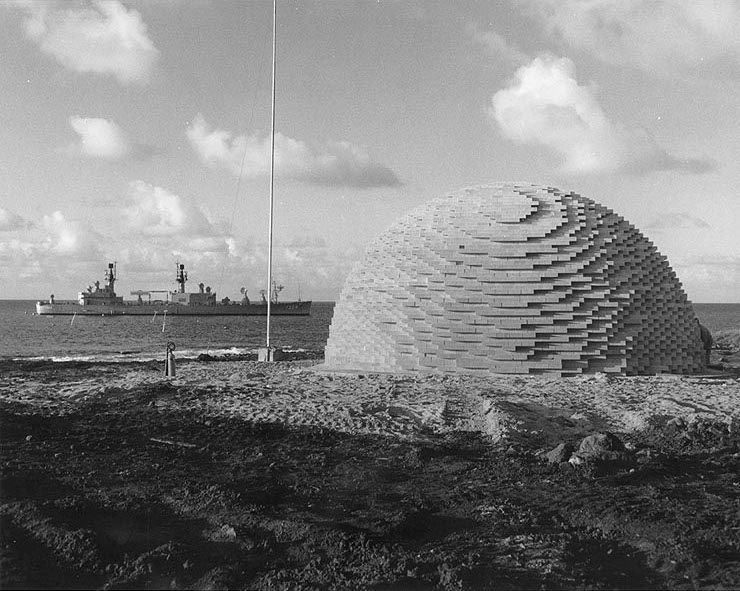
Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package
The Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) comprised a set of scientific instruments placed by the astronauts at the landing site of each of the five Apollo program, Apollo missions to land on the Moon following Apollo 11 (Apollos Apollo 12, 12, Apollo 14, 14, Apollo 15, 15, Apollo 16, 16, and Apollo 17, 17). Apollo 11 left a smaller package called the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package, or EASEP. Background The instrumentation and experiments that would comprise ALSEP were decided in February 1966. Specifically, the experiments, institutions responsible, and principal investigators and coinvestigators were: * Passive Lunar Seismic Experiment: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Frank Press; Columbia University, George Sutton; Georgia Tech, Robert Hostetler * Lunar Surface Magnetometer: Ames Research Center, C. P. Sonett; Marshall Space Flight Center, Jerry Modisette. * Medium-Energy Solar Wind Spectrometer, Solar Wind: Jet Propulsion Laboratory, C. W. Snyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortar (weapon)
A mortar today is usually a simple, lightweight, man-portable, Muzzleloader, muzzle-loaded cannon, consisting of a Smoothbore, smooth-bore (although some models use a Rifling, rifled barrel) metal tube fixed to a base plate (to spread out the recoil) with a lightweight bipod mount and a Sight (device), sight. Mortars are typically used as indirect fire weapons for close fire support with a variety of ammunition. Historically mortars were heavy Siege, siege artillery. Mortars launch explosive shell (projectile), shells (technically called Bomb, bombs) in high arching Projectile motion, ballistic trajectories. History Mortars have been used for hundreds of years. The earliest reported use of mortars was in Korea in a 1413 naval battle when Korean gunsmiths developed the ''wan'gu'' (gourd-shaped mortar) (완구, 碗口). The earliest version of the ''wan'gu'' dates back to 1407. Ch'oe Hae-san (1380–1443), the son of Ch'oe Mu-sŏn (1325–1395), is generally credited with inventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinitrotoluene
Troponin T (shortened TnT or TropT) is a part of the troponin complex, which are proteins integral to the contraction of skeletal and heart muscles. They are expressed in skeletal and cardiac myocytes. Troponin T binds to tropomyosin and helps position it on actin, and together with the rest of the troponin complex, modulates contraction of striated muscle. The cardiac subtype of troponin T is especially useful in the laboratory diagnosis of heart attack because it is released into the blood-stream when damage to heart muscle occurs. It was discovered by the German physician Hugo A. Katus at the University of Heidelberg, who also developed the troponin T assay. Subtypes * Slow skeletal troponin T1, TNNT1 (19q13.4, ) * Cardiac troponin T2, TNNT2 (1q32, ) * Fast skeletal troponin T3, TNNT3 (11p15.5, ) Reference values The 99th percentile cutoff for cardiac troponin T (cTnT) is 0.01 ng/mL. The reference range for the high sensitivity troponin T is a normal 52 ng/L. Backgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Hypochlorite
Sodium hypochlorite is an alkaline inorganic chemical compound with the formula (also written as NaClO). It is commonly known in a dilute aqueous solution as bleach or chlorine bleach. It is the sodium salt of hypochlorous acid, consisting of sodium cations () and hypochlorite anions (, also written as and ). The anhydrous compound is unstable and may decompose explosively. It can be crystallized as a pentahydrate , a pale greenish-yellow solid which is not explosive and is stable if kept refrigerated. Sodium hypochlorite is most often encountered as a pale greenish-yellow dilute solution referred to as chlorine bleach, which is a household chemical widely used (since the 18th century) as a disinfectant and bleaching agent. In solution, the compound is unstable and easily decomposes, liberating chlorine, which is the active principle of such products. Sodium hypochlorite is still the most important chlorine-based bleach. Its corrosive properties, common availability, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |