|
Hexachlorophosphazene
Hexachlorophosphazene is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . The molecule has a cyclic, unsaturated backbone consisting of alternating phosphorus and nitrogen atoms, and can be viewed as a trimer of the hypothetical compound (phosphazyl dichloride). Its classification as a phosphazene highlights its relationship to benzene. There is large academic interest in the compound relating to the phosphorus-nitrogen bonding and phosphorus reactivity. Occasionally, commercial or suggested practical applications have been reported, too, utilising hexachlorophosphazene as a precursor chemical.Mark, J. E.; Allcock, H. R.; West, R. “Inorganic Polymers” Prentice Hall, Englewood, NJ: 1992. . Derivatives of noted interest include the hexalkoxyphosphazene lubricants obtained from nucleophilic substitution of hexachlorophosphazene with alkoxides, or chemically resistant inorganic polymers with desirable thermal and mechanical properties known as polyphosphazenes produced from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphosphazene
Polyphosphazenes include a wide range of hybrid inorganic chemistry, inorganic-organic chemistry, organic polymers with a number of different polymer architecture, skeletal architectures with the backbone phosphorus, P-nitrogen, N-P-N-P-N-. In nearly all of these materials two organic side groups are attached to each phosphorus center. Linear polymers have the formula (N=PR1R2)n, where R1 and R2 are organic (see graphic). Other architectures are cyclolinear and cyclomatrix polymers in which small phosphazene, phosphazene rings are connected together by organic chain units. Other architectures are available, such as block copolymer, polymer architecture, star, dendritic polymer, dendritic, or polymer architecture, comb-type structures. More than 700 different polyphosphazenes are known, with different side groups (R) and different molecular architectures. Many of these polymers were first synthesized and studied in the research group of Harry R. Allcock. __TOC__ Synthesis The method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexafluorophosphazene
Hexafluorophosphazene is an inorganic compound with the formula . It takes the form of a white powder or lumps. It is sensitive to moisture and heat. Structure The molecule has a cyclic, unsaturated backbone consisting of alternating phosphorus and nitrogen atoms, and can be viewed as a trimer of the hypothetical compound (phosphazyl difluoride). Its classification as a phosphazene highlights its relationship to benzene. Hexafluorophosphazene has a hexagonal ring with six equivalent P–N bonds. Each phosphorus atom is additionally bonded to two fluorine atoms. The molecule possesses D3h symmetry, and each phosphorus center is tetrahedral. The ring in hexachlorophosphazene Hexachlorophosphazene is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . The molecule has a cyclic, unsaturated backbone consisting of alternating phosphorus and nitrogen atoms, and can be viewed as a trimer of the hypothetical compound (p ... deviates from planarity and is slightly ruffled ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poly(dichlorophosphazene)
Poly(dichlorophosphazene), also called dichlorophosphazine polymer or phosphonitrilechloride polymer, is a chemical compound with formula (PNCl2)''n''. It is an inorganic (hence carbon-free) chloropolymer, whose backbone is a chain of alternating phosphorus and nitrogen atoms, connected by alternating single and double covalent bonds. The compound can be prepared by polymerization of hexachlorophosphazene ((PNCl2)3) by heating to ca. 250 °C.Hans Rytger Kricheldorf (1991), ''Handbook of Polymer Synthesis''Mario Gleria, Roger De Jaeger (2004) ''Phosphazenes: A Worldwide Insight''Nova Publishers, 2004. 1047 pages. , 9781590334232 It is an "inorganic rubber" and the starting material for many other polymers with the -P=N- backbone (polyphosphazenes), which have important commercial uses. History Poly(dichlorophosphazene) was discovered by H. N. Stokes in the 19th century, and at that time its superior properties over natural rubber were already noted.H. N. Stokes (1895)''On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphosphazene
Polyphosphazenes include a wide range of hybrid inorganic chemistry, inorganic-organic chemistry, organic polymers with a number of different polymer architecture, skeletal architectures with the backbone phosphorus, P-nitrogen, N-P-N-P-N-. In nearly all of these materials two organic side groups are attached to each phosphorus center. Linear polymers have the formula (N=PR1R2)n, where R1 and R2 are organic (see graphic). Other architectures are cyclolinear and cyclomatrix polymers in which small phosphazene, phosphazene rings are connected together by organic chain units. Other architectures are available, such as block copolymer, polymer architecture, star, dendritic polymer, dendritic, or polymer architecture, comb-type structures. More than 700 different polyphosphazenes are known, with different side groups (R) and different molecular architectures. Many of these polymers were first synthesized and studied in the research group of Harry R. Allcock. __TOC__ Synthesis The method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexafluorophosphazene
Hexafluorophosphazene is an inorganic compound with the formula . It takes the form of a white powder or lumps. It is sensitive to moisture and heat. Structure The molecule has a cyclic, unsaturated backbone consisting of alternating phosphorus and nitrogen atoms, and can be viewed as a trimer of the hypothetical compound (phosphazyl difluoride). Its classification as a phosphazene highlights its relationship to benzene. Hexafluorophosphazene has a hexagonal ring with six equivalent P–N bonds. Each phosphorus atom is additionally bonded to two fluorine atoms. The molecule possesses D3h symmetry, and each phosphorus center is tetrahedral. The ring in hexachlorophosphazene Hexachlorophosphazene is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . The molecule has a cyclic, unsaturated backbone consisting of alternating phosphorus and nitrogen atoms, and can be viewed as a trimer of the hypothetical compound (p ... deviates from planarity and is slightly ruffled ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared artificially, the two most common allotropes being white phosphorus and red phosphorus. With as its only stable isotope, phosphorus has an occurrence in Earth's crust of about 0.1%, generally as phosphate rock. A member of the pnictogen family, phosphorus readily forms a wide variety of organic compound, organic and inorganic compound, inorganic compounds, with as its main oxidation states +5, +3 and −3. The isolation of white phosphorus in 1669 by Hennig Brand marked the scientific community's first discovery since Antiquity of an element. The name phosphorus is a reference to the Phosphorus (morning star), god of the Morning star in Greek mythology, inspired by the faint glow of white phosphorus when exposed to oxygen. This property is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Compound
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where all the atoms are carbon (i.e., are carbocycles), none of the atoms are carbon (inorganic cyclic compounds), or where both carbon and non-carbon atoms are present ( heterocyclic compounds with rings containing both carbon and non-carbon). Depending on the ring size, the bond order of the individual links between ring atoms, and their arrangements within the rings, carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds may be aromatic or non-aromatic; in the latter case, they may vary from being fully saturated to having varying numbers of multiple bonds between the ring atoms. Because of the tremendous diversity allowed, in combination, by the valences of common atoms and their ability to form rings, the number of possible cyclic structures, even of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexane Conformation
Cyclohexane conformations are any of several three-dimensional shapes adopted by cyclohexane. Because many compounds feature structurally similar six-membered rings, the structure and dynamics of cyclohexane are important prototypes of a wide range of compounds. The internal angles of a regular, flat hexagon are 120°, while the preferred angle between successive bonds in a carbon chain is about 109.5°, the tetrahedral angle (the arc cosine of −). Therefore, the cyclohexane ring tends to assume non-planar (warped) conformations, which have all angles closer to 109.5° and therefore a lower strain energy than the flat hexagonal shape. Consider the carbon atoms numbered from 1 to 6 around the ring. If we hold carbon atoms 1, 2, and 3 stationary, with the correct bond lengths and the tetrahedral angle between the two bonds, and then continue by adding carbon atoms 4, 5, and 6 with the correct bond length and the tetrahedral angle, we can vary the three dihedral angles f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
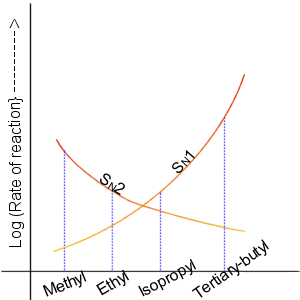
Nucleophilic Substitution
In chemistry, a nucleophilic substitution (SN) is a class of chemical reactions in which an electron-rich chemical species (known as a nucleophile) replaces a functional group within another electron-deficient molecule (known as the electrophile). The molecule that contains the electrophile and the leaving functional group is called the substrate. The most general form of the reaction may be given as the following: :\text\mathbf + \ce + \text\mathbf The electron pair (:) from the nucleophile (Nuc) attacks the substrate () and bonds with it. Simultaneously, the leaving group (LG) departs with an electron pair. The principal product in this case is . The nucleophile may be electrically neutral or negatively charged, whereas the substrate is typically neutral or positively charged. An example of nucleophilic substitution is the hydrolysis of an alkyl bromide, R-Br under basic conditions, where the attacking nucleophile is hydroxyl () and the leaving group is bromide (). :O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organyl substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands. Alkoxides, although generally not stable in protic solvents such as water, occur widely as intermediates in various reactions, including the Williamson ether synthesis.excerpt Transition metal alkoxides are widely used for coatings and as catalysts. Enolates are unsaturated alkoxides derived by deprotonation of a bond adjacent to a ketone or aldehyde. The nucleophilic center for simple alkoxides is located on the oxygen, whereas the nucleophilic site on enolates is delocalized onto both carbon and oxygen sites. Ynolates are also unsaturated alkoxides derived from acetylenic alcohols. Phenoxides are close relatives of the alkoxides, in which the alkyl group is replaced by a phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picometre
The picometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: pm) or picometer (American spelling) is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to , or one trillionth of a metre, which is the SI base unit of length. The picometre is one thousand femtometres, one thousandth of a nanometre ( nm), one millionth of a micrometre (also known as a micron), one billionth of a millimetre, and one trillionth of a metre. The symbol μμ was once used for it. It is also one hundredth of an ångström, an internationally known (but non-SI) unit of length. Use The picometre's length is of an order so small that its application is almost entirely confined to particle physics, quantum physics, chemistry, and acoustics. Atoms are between 62 and 520 pm in diameter, and the typical length of a carbon–carbon single bond is 154 pm. Smaller units still may be used to describe smaller particles (some of which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many forms of polymerization and different systems exist to categorize them. In chemical compounds, polymerization can occur via a variety of reaction mechanisms that vary in complexity due to the functional groups present in the reactants and their inherent steric effects. In more straightforward polymerizations, alkenes form polymers through relatively simple radical reactions; in contrast, reactions involving substitution at a carbonyl group require more complex synthesis due to the way in which reactants polymerize. As alkenes can polymerize in somewhat straightforward radical reactions, they form useful compounds such as polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which are produced in high tonnages each year due to their usefulnes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |