|
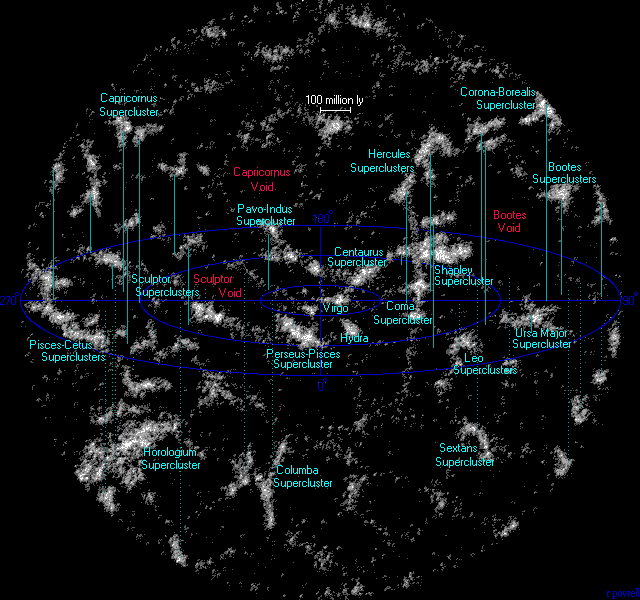
Hercules Superclusters
The Hercules Superclusters (SCl 160) refers to a set of two nearby superclusters of galaxies. Relative to other local superclusters, Hercules is considered particularly large, being approximately 330 Mly in diameter. The Northern Local Supervoid lies in front of the superclusters, and is as big as the superclusters themselves. The redshifts of the member galaxies lie between 0.0304 and 0.0414. The region includes Abell 2147, Hercules Cluster, Abell 2151 (Hercules Cluster), and Abell 2152 galaxy clusters. An extremely long Galaxy filament, filament of galaxies has been found, that connects this group of clusters to the Abell 2197 and Abell 2199 pair. Abell 2162 in the nearby constellation Corona Borealis is also a member. The Hercules Superclusters are near the Coma Supercluster, helping make up part of the CfA2 Great Wall. In the 1930s, Harlow Shapley studied the structure of the distribution of galaxies in the Hercules (constellation), constellation of Hercules, and was probabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superclusters
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn is part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is part of the Laniakea Supercluster, which is part of the Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex. The large size and low density of superclusters means that they, unlike clusters, expand with the Hubble expansion. The number of superclusters in the observable universe is estimated to be 10 million. Existence The existence of superclusters indicates that the galaxies in the Universe are not uniformly distributed; most of them are drawn together in groups and clusters, with groups containing up to some dozens of galaxies and clusters up to several thousand galaxies. Those groups and clusters and additional isolated galaxies in turn form even larger structures called superclusters. Their existenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abell 2199
Abell 2199 is a galaxy cluster in the Abell catalogue featuring the brightest cluster galaxy NGC 6166, a cD galaxy. Abell 2199 is the definition of a Bautz-Morgan type I cluster due to NGC 6166. See also * Hercules (Chinese astronomy) * List of Abell clusters * List of largest galaxies * List of nearest galaxies * List of NGC objects (6001–7000) * X-ray astronomy X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to ... References 2199 Galaxy clusters Hercules (constellation) Abell richness class 2 Hercules Superclusters {{galaxy-cluster-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Abell Clusters
The Abell catalogue is a catalogue of approximately 4,000 galaxy clusters with at least 30 members, almost complete to a redshift of ''z'' = 0.2. It was originally compiled by the American astronomer George O. Abell in 1958 using plates from National Geographic Society – Palomar Observatory Sky Survey, POSS, and extended to the southern hemisphere by Abell, Harold Corwin, Corwin and Ronald Olowin, Olowin in 1987. The name "Abell" is also commonly used as a designation for objects he compiled in a catalogue of 86 planetary nebulae in 1966. The proper designation for the galaxy clusters is ACO, as in "ACO 13", while the planetary-nebula designation is the single letter A, as in "A 39". 1–1999 2000–4076 Southern catalogue S1–S1174 See also * Lists of astronomical objects * List of galaxy groups and clusters References External linksAbell's 1958 paper and catalog [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observable Universe
The observable universe is a Ball (mathematics), spherical region of the universe consisting of all matter that can be observation, observed from Earth; the electromagnetic radiation from these astronomical object, objects has had time to reach the Solar System and Earth since the beginning of the metric expansion of space, cosmological expansion. Assuming the universe is isotropy, isotropic, the distance to the edge of the observable universe is equidistant, the same in every direction. That is, the observable universe is a sphere, spherical region centered on the observer. Every location in the universe has its own observable universe, which may or may not overlap with the one centered on Earth. The word ''observable'' in this sense does not refer to the capability of modern technology to detect light or other information from an object, or whether there is anything to be detected. It refers to the physical limit created by the speed of light itself. No signal can travel faster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abell Catalogue
The Abell catalog of rich clusters of galaxies is an all-sky catalog of 4,073 rich galaxy clusters of nominal redshift ''z'' ≤ 0.2. This catalog supplements a revision of George O. Abell's original "Northern Survey" of 1958, which had only 2,712 clusters, with a further 1,361 clustersthe "Southern Survey" of 1989, published after Abell's death by co-authors Harold G. Corwin and Ronald P. Olowin from those parts of the south celestial hemisphere that had been omitted from the earlier survey. The Abell catalog, and especially its clusters, are of interest to amateur astronomers as challenge objects to be viewed in dark locations on large aperture amateur telescopes. The Northern Survey The original catalog of 2,712 rich clusters of galaxies was published in 1958 by George O. Abell (1927–1983), who was then studying at the California Institute of Technology. The catalog, which formed part of Abell's PhD thesis, was prepared by means of a visual inspection of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Russia. The territory of Estonia consists of the mainland, the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,300 other islands and islets on the east coast of the Baltic Sea. Its capital Tallinn and Tartu are the two largest List of cities and towns in Estonia, urban areas. The Estonian language is the official language and the first language of the Estonians, majority of its population of nearly 1.4 million. Estonia is one of the least populous members of the European Union and NATO. Present-day Estonia has been inhabited since at least 9,000 BC. The Ancient Estonia#Early Middle Ages, medieval indigenous population of Estonia was one of the last pagan civilisations in Europe to adopt Christianity following the Northern Crusades in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harlow Shapley
Harlow Shapley (November 2, 1885 – October 20, 1972) was an American astronomer, who served as head of the Harvard College Observatory from 1921–1952, and political activist during the latter New Deal and Fair Deal. Shapley used Cepheid variable stars to estimate the size of the Milky Way Galaxy and the Sun's position within it.Bart J. Bok. ''Harlow Shapely 1885–1972 A Biographical Memoir''. National Academy of Sciences In 1953 he proposed his "liquid water belt" theory, a concept now known as a habitable zone.Richard J. Hugget, ''Geoecology: An Evolutionary Approach''. p. 10 Background Shapley was born on a farm five miles outside Nashville, Missouri, to Willis and Sarah (née Stowell) Shapley. He went to school in Jasper, Missouri, but not beyond elementary school. He worked as a journalist after studying at home and covering crime stories as a newspaper reporter for the ''Daily Sun'' in Chanute, Kansas, and intermittently for the ''Times'' of Joplin, Missouri. In Chanu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CfA2 Great Wall
The Great Wall (also called Coma Wall), sometimes specifically referred to as the CfA2 Great Wall, is an immense galaxy filament. It is one of the largest known superstructures in the observable universe. This structure was discovered c. 1989 by a team of American astronomers led by Margaret J. Geller and John Huchra while analyzing data gathered by the second CfA Redshift Survey of the Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA). Characteristics According to Chown, "The filament is about 300 million lightyears wide, 15 million lightyears thick and it snakes for at least 500 million lightyears across the Universe." Components It was discovered in 1989 by Margaret Geller and John Huchra based on redshift survey data from the CfA Redshift Survey. It is not known how much further the wall extends due to the light absorption in the plane of the Milky Way The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coma Supercluster
The Coma Supercluster (SCl 117) is a nearby supercluster of galaxies that includes the Coma Cluster (Abell 1656) and the Leo Cluster (Abell 1367). Located 300 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Coma Berenices, it is in the center of the Great Wall and a part of the Coma Filament. It is roughly spherical, about 98 mega light-years in diameter, and contains more than 3,000 galaxies. Although the extent of the Coma Cluster has been understood since around 1900, it took several decades for the existence of the supercluster to be discovered; this was due to the very large physical separation (around 21 Mpc) and angular separation (around 20°) between the Coma and Leo Clusters. In 1977, further analysis of the redshifts of hundreds of galaxies within the supercluster confirmed that these were all part of a larger group of clusters. Despite this, it was still one of the first superclusters to be discovered, and helped astronomers understand the large scale structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Astronomical Journal
''The Astronomical Journal'' (often abbreviated ''AJ'' in scientific papers and references) is a peer-reviewed monthly scientific journal owned by the American Astronomical Society (AAS) and currently published by IOP Publishing. It is one of the premier journals for astronomy in the world. Until 2008, the journal was published by the University of Chicago Press on behalf of the AAS. The reasons for the change to the IOP were given by the society as the desire of the University of Chicago Press to revise its financial arrangement and their plans to change from the particular software that had been developed in-house. The other two publications of the society, the ''Astrophysical Journal'' and its supplement series, followed in January 2009. The journal was established in 1849 by Benjamin A. Gould. It ceased publication in 1861 due to the American Civil War, but resumed in 1885. Between 1909 and 1941 the journal was edited in Albany, New York. In 1941, editor Benjamin Boss arranged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corona Borealis
Corona Borealis is a small constellation in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its brightest stars form a semicircular arc. Its Latin name, inspired by its shape, means "northern crown". In classical mythology Corona Borealis generally represented the crown given by the god Dionysus to the Cretan princess Ariadne and set by her in the heavens. Other cultures likened the pattern to a circle of elders, an eagle's nest, a bear's den or a smokehole. Ptolemy also listed a southern counterpart, Corona Australis, with a similar pattern. The brightest star is the magnitude 2.2 Alpha Coronae Borealis. The yellow supergiant R Coronae Borealis is the prototype of a rare class of giant stars—the R Coronae Borealis variables—that are extremely hydrogen deficient, and thought to result from the merger of two white dwarfs. T Coronae Borealis, als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abell 2162
Abell 2162 is a galaxy cluster in the Abell catalogue located in the constellation Corona Borealis. It is a member of the Hercules Superclusters, the redshifts of the member galaxies of which lie between 0.0304 and 0.0414. The cluster hosts a massive Type-cD galaxy called NGC 6086. See also * Abell catalogue * List of Abell clusters * X-ray astronomy X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to ... References Further reading * 2162 Galaxy clusters Corona Borealis Hercules Superclusters {{galaxy-cluster-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |