|
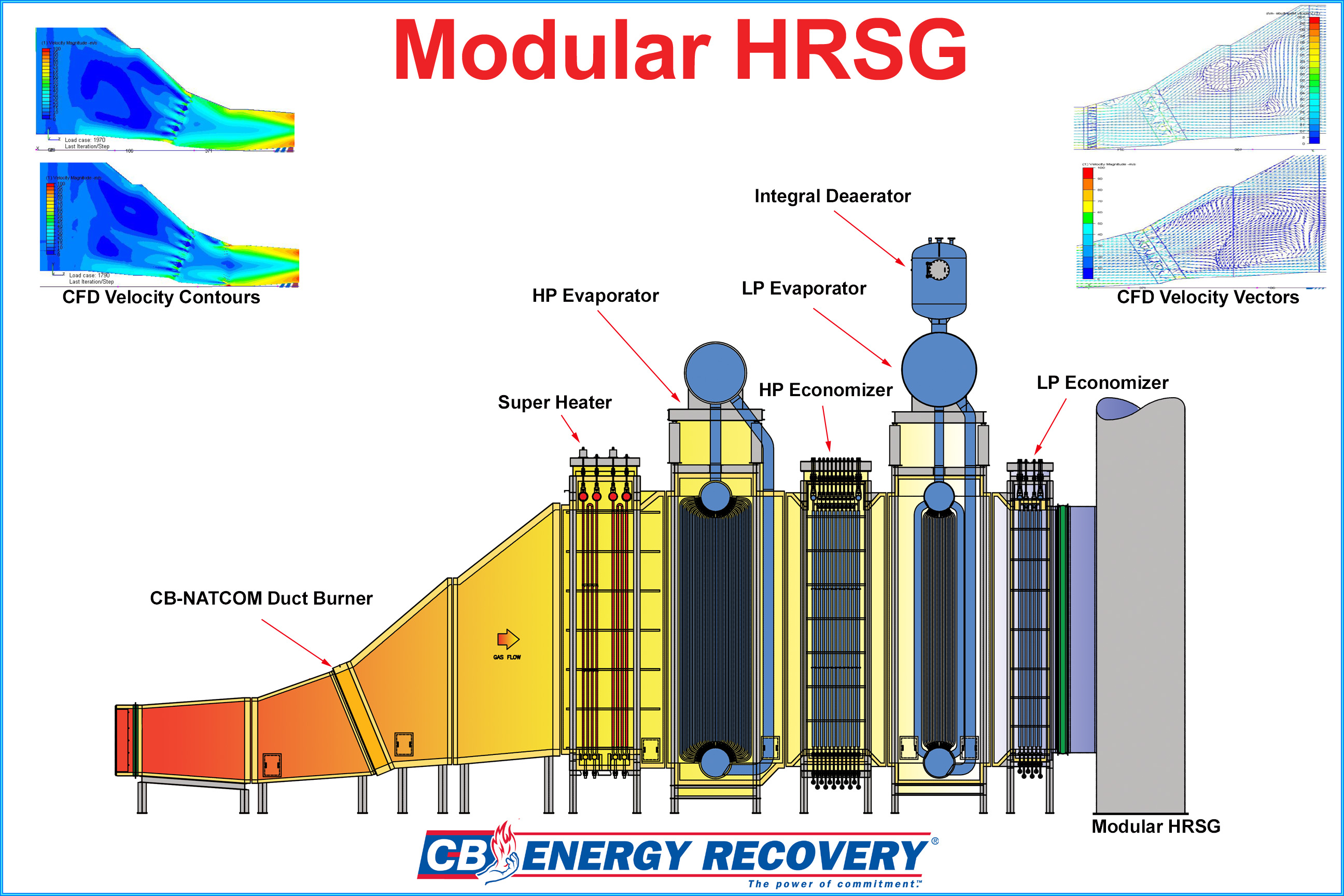
Heat Recovery Steam Generator
A heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) is a heat exchanger that recovers heat from a hot gas stream, such as a combustion turbine or other waste gas stream. It produces steam that can be used in a process (cogeneration) or used to drive a steam turbine (combined cycle). HRSGs HRSGs consist of four major components: the economizer, evaporator, superheater and water preheater. The different components are put together to meet the operating requirements of the unit. See the attached illustration of a Modular HRSG General Arrangement. Modular HRSGs can be categorized by a number of ways such as direction of exhaust gas flow or number of pressure levels. Based on the flow of exhaust gases, HRSGs are categorized into vertical and horizontal types. In horizontal type HRSGs, exhaust gas flows horizontally over vertical tubes whereas in vertical type HRSGs, exhaust gas flows vertically over horizontal tubes. Based on pressure levels, HRSGs can be categorized into single pressure and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engineering is the field dedicated to controlling and preventing corrosion. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metal in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen, hydrogen, or hydroxide. Rusting, the formation of red-orange iron oxides, is a well-known example of electrochemical corrosion. This type of corrosion typically produces oxides or salts of the original metal and results in a distinctive coloration. Corrosion can also occur in materials other than metals, such as ceramics or polymers, although in this context, the term "degradation" is more common. Corrosion degrades the useful properties of materials and structures including mechanical strength, appearance, and permeability to liquids and ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbosteamer
A turbosteamer is a BMW combined cycle engine using a waste heat recovery unit. Waste heat energy from the internal combustion engine is used to generate steam for a steam engine which creates supplemental power for the vehicle. The turbosteamer device is affixed to the exhaust and cooling system. It salvages the heat wasted in the exhaust and radiator (as much as 80% of heat energy) and uses a steam piston or turbine to relay that power to the crankshaft. The steam circuit produces and of torque at peak (for a 1.8 straight-4 engine), yielding an estimated 15% gain in fuel efficiency Fuel efficiency (or fuel economy) is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical energy, chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or Mechanical work, w .... Unlike gasoline-electric hybrids, these gains increase at higher, steadier speeds. Timescale BMW has been the pioneer of this concept as early as 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
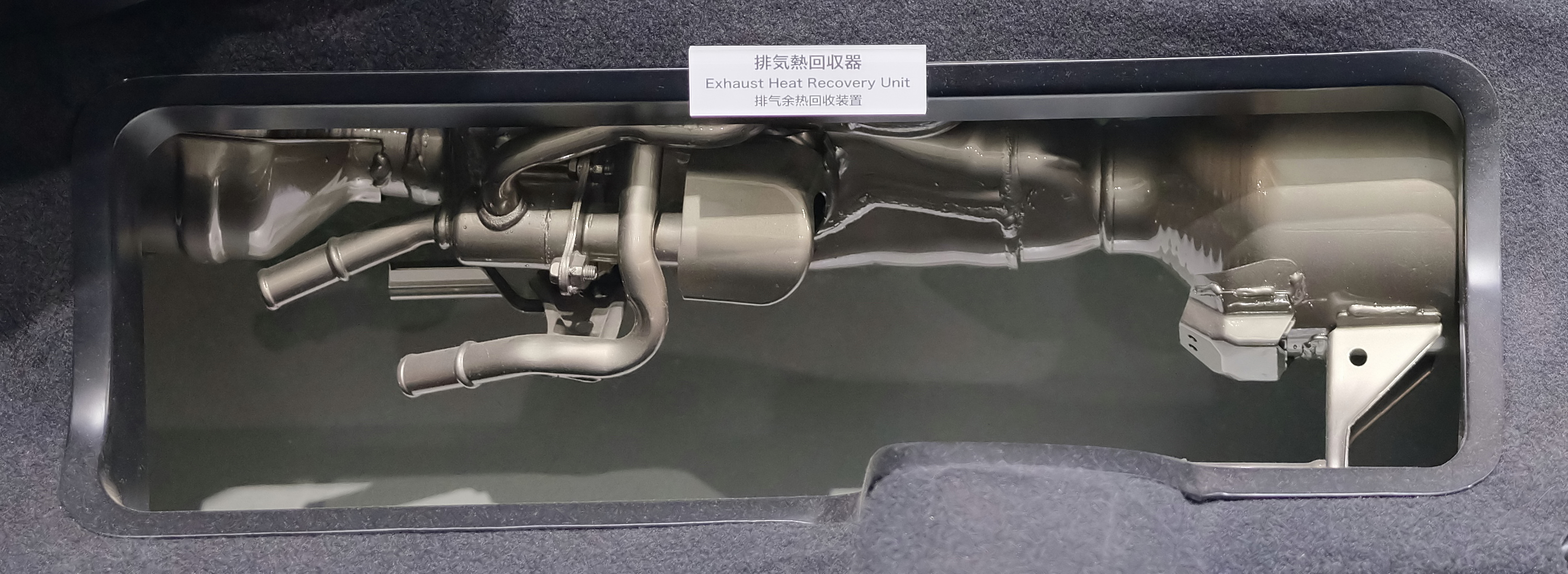
Exhaust Heat Recovery System
An exhaust heat recovery system turns waste heat energy in exhaust gases into electric energy for batteries or mechanical energy reintroduced on the crankshaft. The technology is of increasing interest as car and heavy-duty vehicle manufacturers continue to increase efficiency, saving fuel and reducing emissions. Thermal losses of an internal combustion engine While technological improvements have greatly reduced the fuel consumption of internal combustion engines, the peak thermal efficiency of a 4-stroke Otto cycle engine is around 35%, which means that 65% of the energy released from the fuel is lost as heat. High speed Diesel cycle engines fare better with around 45% peak efficiency, but are still far from the maximum theoretical efficiency, with 55% of the fuel energy content rejected as heat. Exhaust heat recovery technologies Rankine Rankine cycle systems vaporize pressurised water using a steam generator located in the exhaust pipe. As a result of the heating by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HRSG Cycle
A heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) is a heat exchanger that recovers heat from a hot gas stream, such as a combustion turbine or other waste gas stream. It produces steam that can be used in a process (cogeneration) or used to drive a steam turbine (combined cycle). HRSGs HRSGs consist of four major components: the economizer, evaporator, superheater and water preheater. The different components are put together to meet the operating requirements of the unit. See the attached illustration of a Modular HRSG General Arrangement. Modular HRSGs can be categorized by a number of ways such as direction of exhaust gas flow or number of pressure levels. Based on the flow of exhaust gases, HRSGs are categorized into vertical and horizontal types. In horizontal type HRSGs, exhaust gas flows horizontally over vertical tubes whereas in vertical type HRSGs, exhaust gas flows vertically over horizontal tubes. Based on pressure levels, HRSGs can be categorized into single pressure and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IGCC Diagram
IGCC may refer to: * Integrated gasification combined cycle integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) is a technology using a high pressure gasifier to turn coal and other carbon based fuels into pressurized synthesis gas. This enables removal of impurities from the fuel prior to generating electrici ..., a power generation technology * International Green Construction Code * UC Institute on Global Conflict and Cooperation {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District Heating
District heating (also known as heat networks) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heater, space heating and water heating. The heat is often obtained from a cogeneration plant burning fossil fuels or biomass, but heating plant, heat-only boiler stations, geothermal heating, heat pumps and central solar heating are also used, as well as heat waste from factories and nuclear power electricity generation. District heating plants can provide higher efficiencies and better pollution control than localized boilers. According to some research, district heating with combined heat and power (CHPDH) is the cheapest method of cutting carbon emissions, and has one of the lowest carbon footprints of all fossil generation plants. District heating is ranked number 27 in Drawdown (climate), Project Drawdown's 100 solutions to climate change, global warming. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desalination
Desalination is a process that removes mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination is the removal of salts and minerals from a substance. One example is Soil salinity control, soil desalination. This is important for agriculture. It is possible to desalinate saltwater, especially Seawater, sea water, to produce water for human consumption or irrigation. The by-product of the desalination process is brine. Many seagoing ships and submarines use desalination. Modern interest in desalination mostly focuses on cost-effective provision of fresh water for human use. Along with recycled wastewater, it is one of the few water resources independent of rainfall. Due to its energy consumption, desalinating sea water is generally more costly than fresh water from surface water or groundwater, Reclaimed water, water recycling and water conservation; however, these alternatives are not always available and depletion of reserves is a critical problem worldwide. Desalinati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical NameWorking Paper No. 61, 23rd Session, Vienna, 28 March – 4 April 2006. accessed 9 October 2010 It is connected to the Gulf of Oman in the east by the Strait of Hormuz. The river delta of the Shatt al-Arab forms the northwest shoreline. The Persian Gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive reefs (mostly rocky, but also Coral reef, coral), and abundant pearl oysters, however its ecology has been damaged by industrialization and oil spills. The Persian Gulf is in the Persian Gulf Basin, which is of Cenozoic origin and related to the subduction of the Arabian plate under the Zagros Mountains. The current flooding of the basin started 15,000 years ago due to sea level rise, rising sea levels of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Load
In mechanics and thermodynamics, thermal stress is mechanical stress created by any change in temperature of a material. These stresses can lead to fracturing or plastic deformation depending on the other variables of heating, which include material types and constraints. Temperature gradients, thermal expansion or contraction and thermal shocks are things that can lead to thermal stress. This type of stress is highly dependent on the thermal expansion coefficient which varies from material to material. In general, the greater the temperature change, the higher the level of stress that can occur. Thermal shock can result from a rapid change in temperature, resulting in cracking or shattering. Temperature gradients When a material is rapidly heated or cooled, the surface and internal temperature will have a difference in temperature. Quick heating or cooling causes thermal expansion or contraction respectively, this localized movement of material causes thermal stresses. Imagin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |