|
Harran Stela
The Harran Stela (not to be confused with the Harran inscription) was discovered in 1956 in the ruins of Harran, in what is now southeast Turkey. It consists of two parts, both of which show, at the top, Nabonidus worshipping symbols of the Sun, Ishtar, and the moon-god Sin. The Stela was likely composed between 542–540 BC. The stela is significant as a text that demonstrates the adoration of Nabonidus to the Sun, Ishtar, and especially Sin, departing from traditional Babylonian exaltation of the chief god Marduk. Text The following translation is that of C. J. Gadd. (This is) the great miracle of Sin that none of the (other) gods and goddesses knew (how to achieve), that has not happened in the country from the days of old, that the people of the country have (not) observed nor written down on clay tables to be preserved for eternity, that (you), Sin, the lord of all the gods and goddesses residing in heaven, have come down from heaven to (me) Nabonidus, king of Babylon! For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
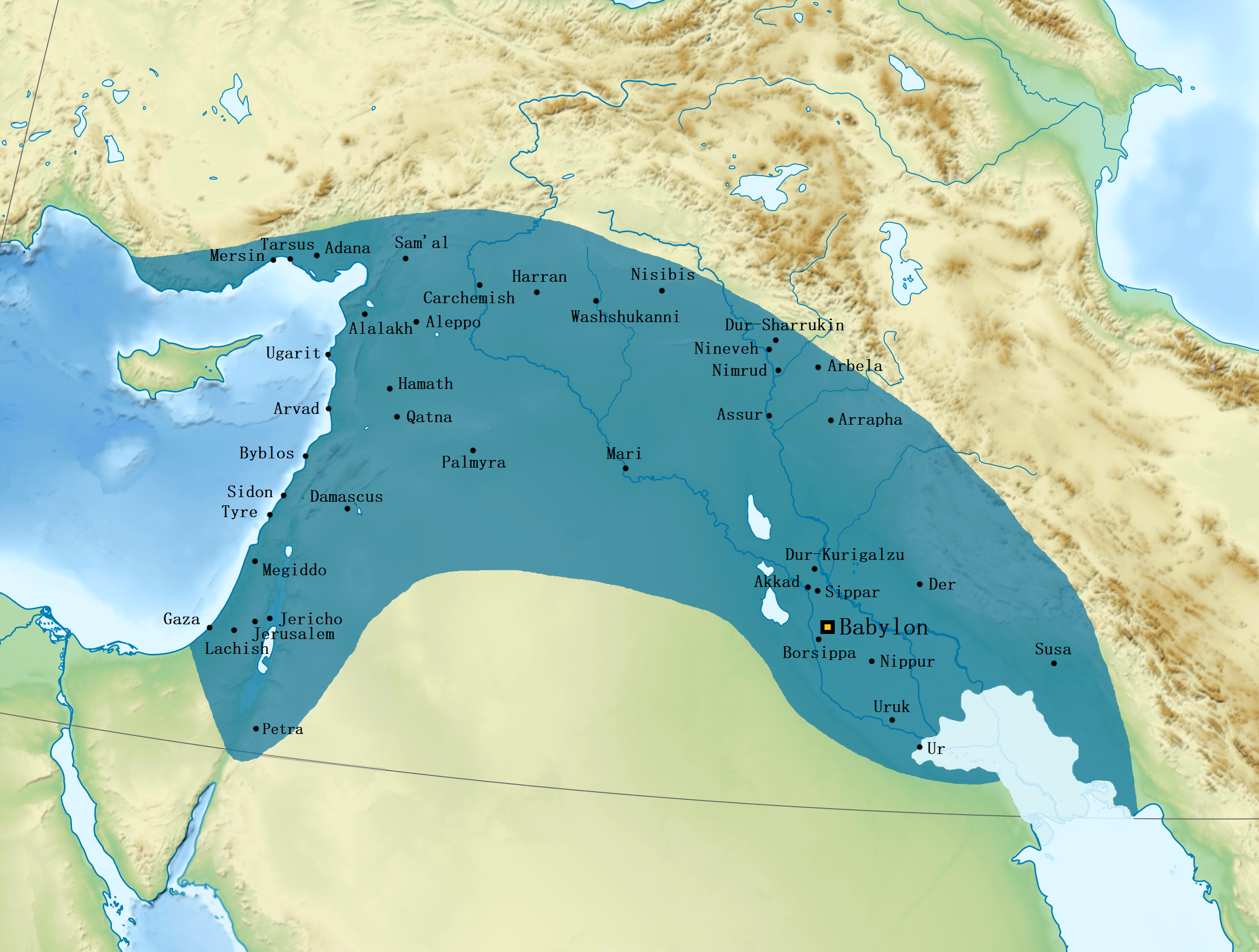
Harran
Harran is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Şanlıurfa Province, Turkey. Its area is 904 km2, and its population is 96,072 (2022). It is approximately southeast of Urfa and from the Syrian border crossing at Akçakale. Harran was founded at some point between the 25th and 20th centuries BC, possibly as a merchant colony by Sumerian traders from Ur. Over the course of its early history, Harran rapidly grew into a major Mesopotamian cultural, commercial and religious center. It was made a religiously and politically influential city through its association with the moon-god Sin (mythology), Sin; many prominent Mesopotamian rulers consulted with and renovated the moon-temple of Ekhulkhul in Harran. Harran came under Assyrian rule under Adad-nirari I ( BC) and became a provincial capital often second in importance only to the Assyrian capital of Assur itself. During the collapse of the Assyrian Empire, Harran briefly served as the final capital of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sanliurfa Province
Urfa, officially called Şanlıurfa (), is a city in southeastern Turkey and the capital of Şanlıurfa Province. The city was known as Edessa from Hellenistic period, Hellenistic times and into Christian times. Urfa is situated on a plain about east of the Euphrates. Its climate features extremely hot, dry summers and cool, moist winters. About northeast of the city is the famous Neolithic site of Göbekli Tepe, the world's oldest known temple, which was founded in the 10th millennium BC. The area was part of a network of the first human settlements where the Neolithic Revolution, agricultural revolution took place. Because of its association with Jewish history, Jewish, History of Christianity, Christian, and History of Islam, Islamic history, and a legend according to which it was the hometown of Abraham, Urfa is nicknamed the "City of Prophets." Religion is important in Urfa. The city "has become a center of fundamentalist Islamic beliefs" and "is considered one of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq, Syria, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; and the Aegean Sea, Greece, and Bulgaria to the west. Turkey is home to over 85 million people; most are ethnic Turkish people, Turks, while ethnic Kurds in Turkey, Kurds are the Minorities in Turkey, largest ethnic minority. Officially Secularism in Turkey, a secular state, Turkey has Islam in Turkey, a Muslim-majority population. Ankara is Turkey's capital and second-largest city. Istanbul is its largest city and economic center. Other major cities include İzmir, Bursa, and Antalya. First inhabited by modern humans during the Late Paleolithic, present-day Turkey was home to List of ancient peoples of Anatolia, various ancient peoples. The Hattians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Harran Inscription
The Harrān inscription (not to be confused with the Babylonian Harran Stela) is an Arabic-Greek bilingual Christian dedicatory at a martyrium in the Harran village, which is in the city of as-Suwayda (south of Damascus) in Syria. It dates to 567–568. The inscription has one section in Greek and another in Paleo-Arabic and, while the content between the two overlaps, there are also substantial differences. The use of Arabic in the composition of inscription was probably important to the cultural identity of the authors, as otherwise Greek was the imperial language of the Byzantine Empire which controlled the region at the time. Text The text that follows is from the translation of George Bevan. Greek Asaraël, son of Talemos, the phylarch founded this martyrion of St John in the first year of the indiction in year 463.112 May the writer be remembered Arabic 1. Sharahil son of Zalim built this martyrion 2. nthe year 463, after the rebellion 3. of Khaybar 4. by one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nabonidus
Nabonidus (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-naʾid'', meaning "May Nabu be exalted" or "Nabu is praised") was the last king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from 556 BC to the fall of Babylon to the Achaemenian Empire under Cyrus the Great in 539 BC. Nabonidus was the last native ruler of ancient Mesopotamia, the end of his reign marking the end of thousands of years of Sumero-Akkadian language, Akkadian states, Monarchy, kingdoms and empires. He was also the last independent king of Babylon. Regarded as one of the most vibrant and individualistic rulers of his time, Nabonidus is characterised by some scholars as an unorthodox religious reformer and as the first archaeologist. The origins of Nabonidus, his connection to previous royalty, and subsequently what claim he had to the throne remain unclear, given that Nabonidus made no genealogical claims of kinship to previous kings. This suggests that he was neither related nor connected to the Chaldean dynasty of Babylonian rulers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ishtar
Inanna is the List of Mesopotamian deities, ancient Mesopotamian goddess of war, love, and fertility. She is also associated with political power, divine law, sensuality, and procreation. Originally worshipped in Sumer, she was known by the Akkadian Empire, Akkadians, Babylonian religion, Babylonians, and Assyrians as Ishtar. Her primary title is Queen of Heaven (antiquity), "the Queen of Heaven". She was the patron goddess of the Eanna temple at the city of Uruk, her early main religious center. In archaic Uruk, she was worshipped in three forms: morning Inanna (Inana-UD/hud), evening Inanna (Inanna sig), and princely Inanna (Inanna NUN), the former two reflecting the phases of her associated planet Venus. Her most prominent symbols include the Lion of Babylon, lion and the Star of Ishtar, eight-pointed star. Her husband is the god Dumuzid (later known as Tammuz), and her (attendant) is the goddess Ninshubur, later conflated with the male deities Ilabrat and Papsukkal. Inanna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Labashi-Marduk
Labashi-Marduk ( or , meaning "O Marduk, may I not come to shame") was the fifth and penultimate king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling in 556 BC. He was the son and successor of Neriglissar. Though classical authors such as Berossus wrote that Labashi-Marduk was just a child when he became king, Babylonian documents indicate that he had been in charge of his own affairs before his rise to the throne, suggesting he was an adult, though possibly still relatively young. Labashi-Marduk's reign was very short, lasting only one to three months, with the last evidence of Neriglissar's life dating in April 556 BC and documents dated to Labashi-Marduk's successor, Nabonidus, appearing in May that same year and becoming widespread in Babylonia by the end of June. Nabonidus's son Belshazzar led a coup against the king, deposing and killing Labashi-Marduk and proclaiming Nabonidus as king. The reason for Labashi-Marduk's deposition is unknown, Berossus simply describes the justificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Belshazzar
Belshazzar ( Babylonian cuneiform: ''Bēl-šar-uṣur'', meaning " Bel, protect the king"; ''Bēlšaʾṣṣar'') was the son and crown prince of Nabonidus (), the last king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire. Through his mother, he might have been a grandson of Nebuchadnezzar II (), though this is not certain and the claims to kinship with Nebuchadnezzar may have originated from royal propaganda. Belshazzar played a pivotal role in the ''coup d'état'' that overthrew the king Labashi-Marduk () and brought Nabonidus to power in 556 BC. Since Belshazzar was the main beneficiary of the coup, through confiscating and inheriting Labashi-Marduk's estates and wealth, it is likely that he was the chief orchestrator. Through proclaiming his father as the new king, Belshazzar also made himself the first-in-line to the throne. As Nabonidus was relatively old at the time, Belshazzar could expect to become king within a few years. Nabonidus was absent from Babylon from 553 BC to 543 or 542 BC, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tayma
Tayma (; Taymanitic: 𐪉𐪃𐪒, , vocalized as: ) or Tema is a large oasis with a long history of settlement, located in northwestern Saudi Arabia at the point where the trade route between Medina and Dumah (Sakakah) begins to cross the Nafud desert. Tayma is located southeast of the city of Tabuk, and about north of Medina. It is located in the western part of the Nafud desert. History The historical significance of Tayma is based on the existence there of an oasis, which helped it become a stopping point on commercial desert routes. An important event was the presence there of Nabonidus, the last Neo-Babylonian emperor, who took residence there in the mid- 6th century BC. Bronze Age: Egyptian inscription Recent archaeological discoveries show that Tayma has been inhabited since at least the Bronze Age. In 2010, the Ministry of Tourism of Saudi Arabia announced the discovery of the Pharaonic Tayma inscription by Ramesses III about 60 kilometers northwest of Tayma. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
6th-century BC Inscriptions
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. Owing in part to the collapse of the Roman Empire along with its literature and civilization, the sixth century is generally considered to be the least known about in the Dark Ages. In its second golden age, the Sassanid Empire reached the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Akkadian Inscriptions
Akkadian or Accadian may refer to: * Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire * Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language * Akkadian literature, literature in this language * Akkadian cuneiform, early writing system * Akkadian mythology, early Mesopotamian religion See also * Acadian (other) * Akadia (other) * Akkad (other) Akkad may refer to: * Akkad (city), the capital of the Akkadian Empire *Akkadian Empire, the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia * Akkad SC, Iraqi football club People with the name * Abbas el-Akkad, Egyptian writer * Abdulrahman Akkad, Syrian LGB ... {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Archaeology Of The Achaemenid Empire
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |